5.5.1 Outline the binomial system of nomenclature
The binomial system of nomenclature was devised by Carolus Linnaeus as a way of classifying organisms that was globally recognised and could demonstrate evolutionary relationships between organisms (and thus allow for the prediction of features closely related organisms may share)
According to the binomial system of nomenclature, every organism is designated a scientific name with two parts:
- Genus is written first and is capitalised (e.g. Homo)
- Species follows and is written in lower case (e.g. Homo sapiens)
- Some species may also have a sub-species designation (e.g. Homo sapiens sapiens)
- Conventions: When typing, the name should be in italics; whereas when hand writing, it should be underlined
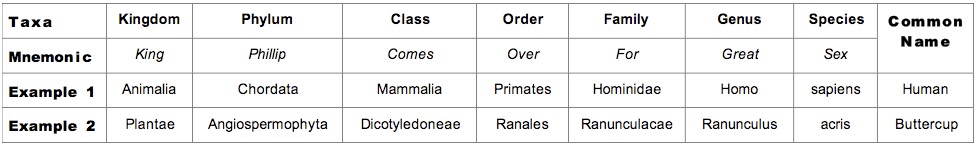
5.5.2 List the seven levels in the hierarchy of taxa - kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species - using an example from two different kingdoms for each level
When classifying living things, organisms are grouped according to a series of hierarchical taxa - the more similar their characteristics, the closer the grouping
Classification of Animals and Plants
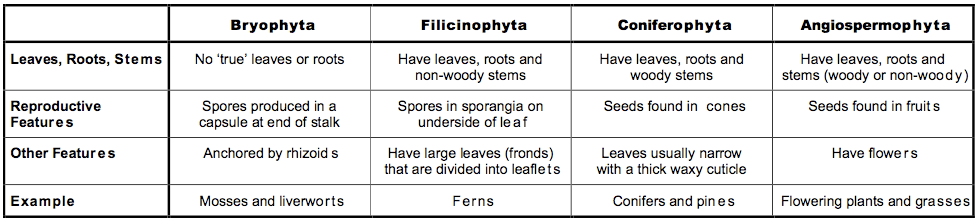
5.5.3 Distinguish between the following phyla of plants, using simple external recognition features: bryophyta, filicinophyta, coniferophyta and angiospermophyta

5.5.4 Distinguish between the following phyla of animals, using simple external recognition features: porifera, cnidaria, platyhemlnthes, annelida, mollusca and arthropoda


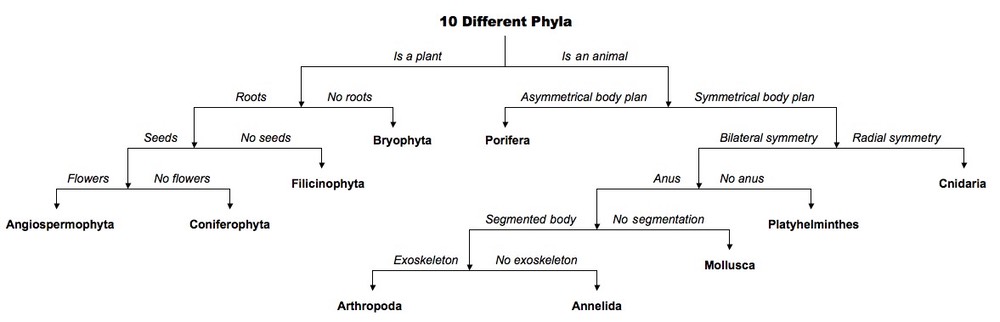
5.5.5 Apply and design a key for up to eight organisms
A dichotomous key is a method of identification whereby a group of organisms are sequentially divided into two categories until all are identified
Example of a Dichotomous Key:
1. Organism is a plant ...................................................................................... Go to Q2
Organism is not a plant (animal) ................................................................ Go to Q5
2. Has no 'true' leaves or roots ....................................................................... Bryophyta
Has leaves and roots ................................................................................... Go to Q3
3. Has no seeds (sporangia) .......................................................................... Filicinophyta
Has seeds ..................................................................................................... Go to Q4
4. Has no flowers ............................................................................................. Coniferophyta
Has flowers ................................................................................................... Angiospermophyta
5. Asymmetrical body plan ............................................................................. Porifera
Symmetrical body plan ............................................................................... Go to Q6
6. Has radial symmetry ................................................................................... Cnidaria
Has bilateral symmetry ............................................................................... Go to Q7
7. Has no anus ................................................................................................. Platyhelminthes
Has an anus ................................................................................................. Go to Q8
8. Has a segmented body .............................................................................. Go to Q9
Has no visible body segmentation ........................................................... Mollusca
9. Have an exoskeleton ................................................................................. Arthropoda
Have no exoskeleton ................................................................................. Annelida
Dichotomous Key as a Flowchart