F.5.1 Define the terms photoautotroph, photoheterotroph, chemoautotroph and chemoheterotroph
Photoautotroph: An organism that uses light energy to generate ATP and produce organic compounds from inorganic substances
Photoheterotroph: An organism that uses light energy to generate ATP and obtains organic compounds from other organisms
Chemoautotroph: An organism that uses energy from chemical reactions to generate ATP and produce organic compounds from inorganic substances
Chemoheterotroph: An organism that uses energy from chemical reactions to generate ATP and obtains organic compounds from other organisms
F.5.2 State one example of a photoautrotroph, photoheterotroph, chemoautotroph and chemoheterotroph
Photoautotroph: Cyanobacteria
Photoheterotroph: Rhodospirillum
Chemoautotroph: Nitrobacter
Chemoheterotroph: Lactobacillus
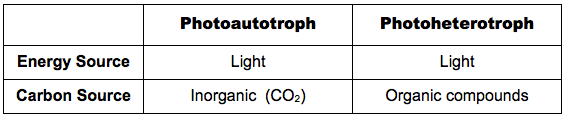
F.5.3 Compare photoautotrophs with photoheterotrophs in terms of energy sources and carbon sources
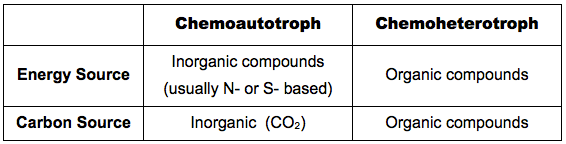
F.5.4 Compare chemoautotrophs with chemoheterotrophs in terms of energy source and carbon source
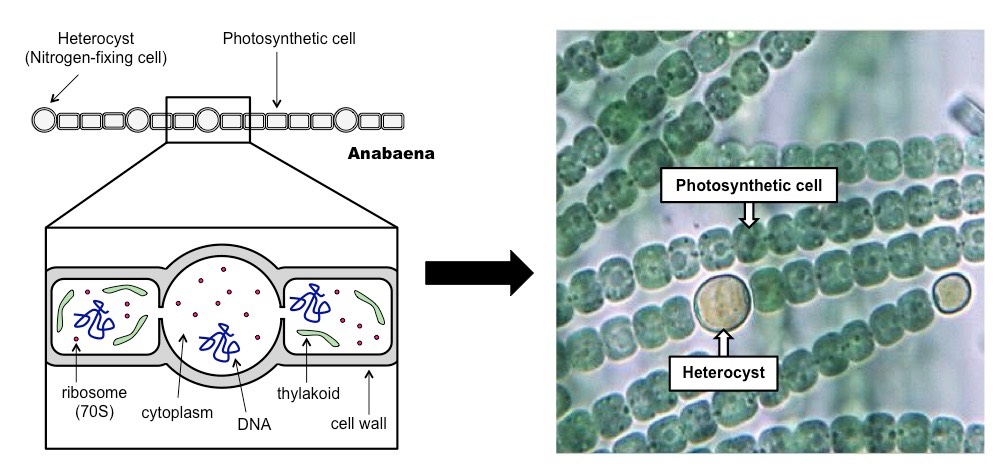
F.5.5 Draw and label a diagram of a filamentous cyanobacterium
F.5.5 Explain the use of bacteria in the bioremediation of soil and water
Bioremediation is the process by which microorganisms are used to return an environment altered by contaminants to its natural state
- The enzymes produced by specific bacteria may be able to breakdown contaminating material, so that it can be filtered out of the environment
- Examples of bioremediation include:

Bioremediation of an Oil Spill with Pseudomonas aeruginosa