2.3.1 Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell
2D Representation 3D Representation
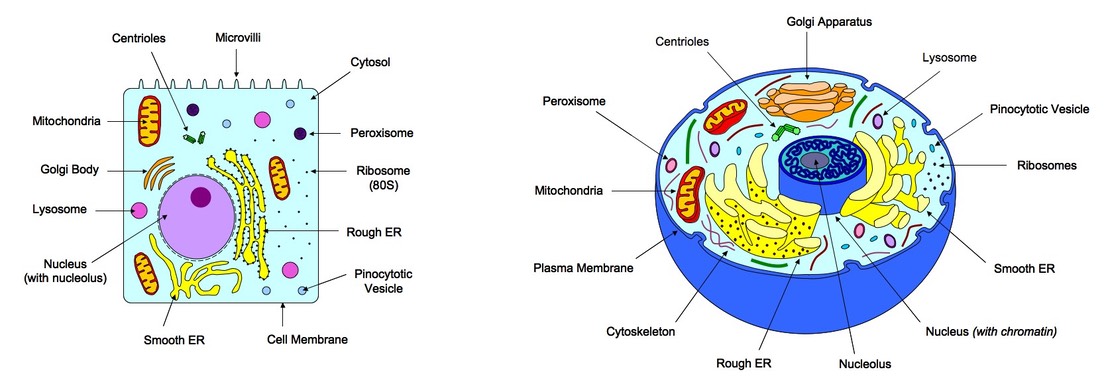
2.3.2 Annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with the functions of each named structure
Cell Membrane: Semi-permeable barrier that controls the entry and exit of substances
Cytosol: The fluid portion of the cytoplasm (does not include the organelles or other insoluble materials)
Nucleus: Contains hereditary material (DNA) and thus controls cell activities (via transcription) and mitosis (via DNA replication)
Nucleolus: Site of the production and assembly of ribosome components
Ribosome: Complexes of RNA and protein that are responsible for polypeptide synthesis (eukaryotic ribosomes are larger than prokaryotes - 80S)
Mitochondria: Site of aerobic respiration, which produces large quantities of chemical energy (ATP) from organic compounds
Golgi Apparatus: An assembly of vesicles and folded membranes involved in the sorting, storing and modification of secretory products
Lysosome: Site of hydrolysis / digestion / breakdown of macromolecules
Peroxisome: Catalyses breakdwon of toxic substances like hydrogen peroxide and other metabolites
Centrioles: Microtubule-organising centres involved in cell division (mitosis / meiosis and cytokinesis)
Endoplasmic Reticulum: A system of membranes involved in the transport of materials between organelles
- Rough ER: Studded with ribosomes and involved in the synthesis and transport of proteins destined for secretion
- Smooth ER: Involved in the synthesis and transport of lipids and steroids, as well as metabolism of carbohydrates
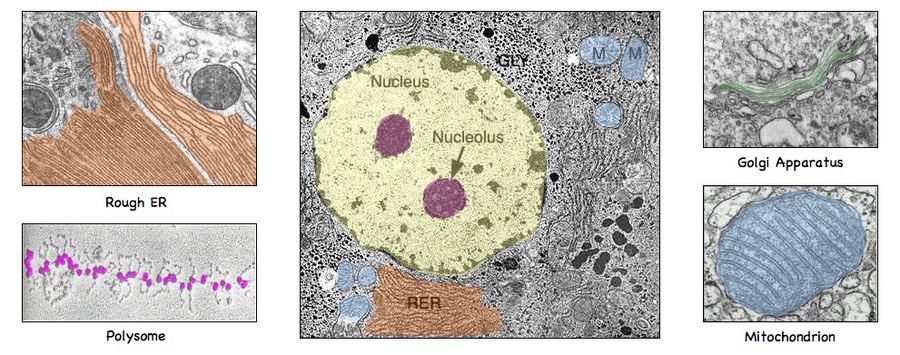
2.3.3 Identify the structures in 2.2.1 in electron micrographs of a liver cell
Electron Micrograph of a Liver Cell
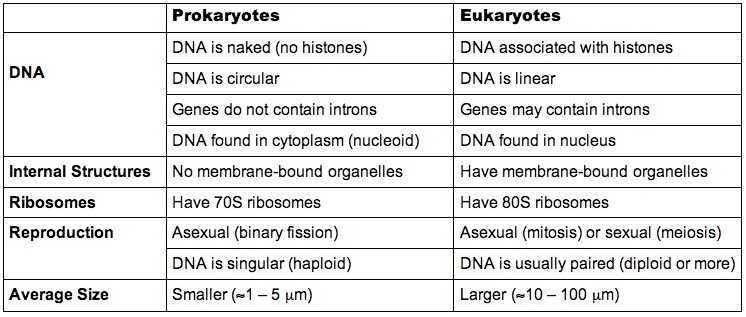
2.3.4 Compare prokaryote and eukaryote cells
Similarities:
- Both have a cell membrane
- Both contain ribosomes
- Both have DNA and cytoplasm
Differences:
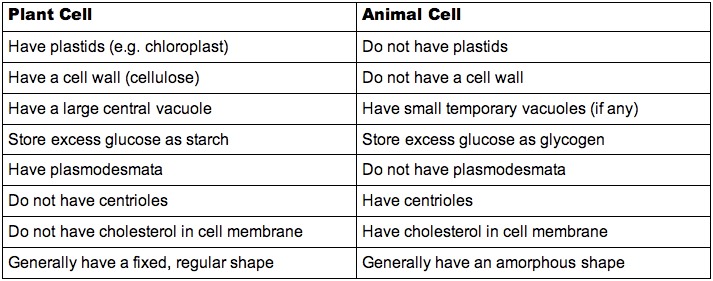
2.3.5 State three differences between plant and animal cells
Labelled Diagram of a Generalised Plant Cell

2.3.6 Outline two roles of extracellular components
Plants
The cell wall in plants is made from cellulose secreted from the cell, which serves the following functions:
- Provides support and mechanical strength for the cell (maintains cell shape)
- Prevents excessive water uptake by maintaining a stable, turgid state
- Serves as a barrier against infection by pathogens
Animals
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is made from glycoproteins secreted from the cell, which serve the following functions:
- Provides support and anchorage for cells
- Segregates tissues from one another
- Regulates intercellular communication by sequestering growth factors