F.3.1 State that reverse transcriptase catalyses the production of DNA from RNA
Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme isolated from retroviruses which catalyses the production of DNA from an RNA template
F.3.2 Explain how reverse transcriptase is used in molecular biology
- Reverse transcriptase is used as part of recombinant DNA technology to produce genes for gene transfer
- The enzyme catalyses the production of a complementary (single) strand of copy DNA (cDNA) from an mRNA template
- As RNA undergoes post-transcriptional modification (i.e. splicing) prior to forming mRNA, cDNA does not contain introns
- As bacteria lack the machinery for intron removal, genes spliced into bacterial hosts need introns removed in order to generate functional proteins
- Examples of how reverse transcriptase has been used in molecular biology include:
- The mass production of human insulin by E. coli cells
- The generation of cDNA libraries for use in DNA microarrays (DNA fingerprinting)
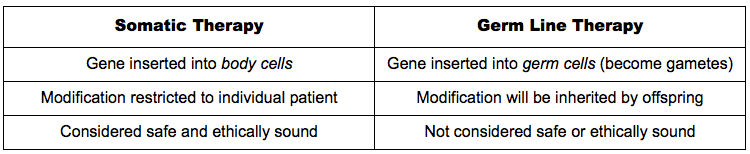
F.3.3 Distinguish between somatic and germ line therapy
Gene therapy is the insertion of genes into an individual's cells and tissues in order to treat genetic diseases
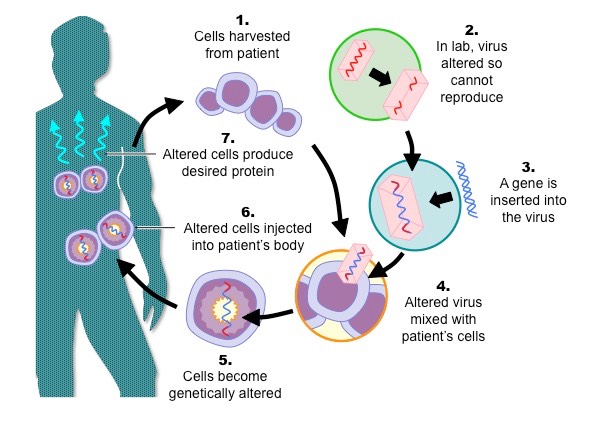
F.3.4 Outline the use of viral vectors in gene therapy
- Viral vectors have been used to facilitate the replacement of defective genes with healthy, functional copies
- Individuals with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) may have be unable to synthesise the enzyme adenosine deaminase (ADA)
- White blood cells or bone marrow cells are removed and, using a viral vector, a copy of the normal gene is integrated into the cell's genome
- When the cells are replaced in the body of the patient the normal gene is expressed, resulting in the production of ADA and the treatment of SCID
- There are still technical problems to be solved before this becomes viable technology – e.g. ensuring correct amount at right time and place
Overview of the Use of Viral Vectors in Gene Therapy
F.3.5 Discuss the risks of gene therapy
The risks associated with gene therapy include:
- Undesirable health effects (e.g. cancers / death)
- If gene insertion occurs in the wrong location it may affect the functioning of pre-existing genes that are vital within the genome
- Viral vectors may infect healthy cells or tissues
- Virus may revert to original form (mutate) and become pathogenic
- Virus entry may trigger an immune response leading to inflammation, toxicity and organ failure
- Treatment must be repeated at regular intervals, increasing likelihood of adverse treatment response with time