B.5.1 Define fitness
Fitness is the physical condition of a body that allows it to perform exercise of a particular type
- Fitness is specific to the type of activity being performed (e.g. a strong swimmer may not be a strong runner)
B.5.2 Discuss speed and stamina as measures of fitness
- Speed is the rate at which movement is performed and relies predominantly on fast-twitch muscle fibres
- Stamina is the capacity for sustained exercise or performance and relies more on slow-twitch muscle fibres
- Measures of fitness can be used to show improvement in performance (e.g. timing duration of activity: longer = ñ stamina; shorter = ñ speed)
- As performance improves, there should also be a shortening of the time taken for the heart to return to resting rate
B.5.3 Distinguish between fast and slow muscle fibres
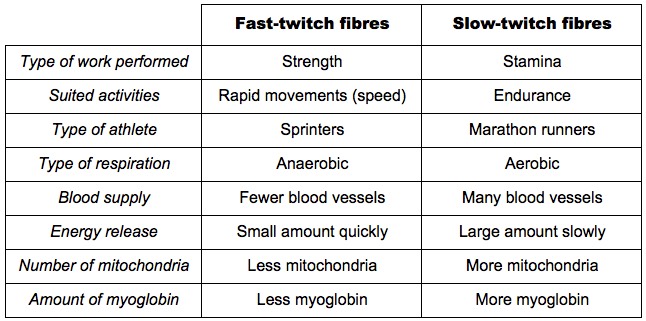
- Fast and slow muscle fibres are differentiated by the time needed between contractions of the muscle fibres
- Fast muscle fibres have greater oxygen needs, lower myoglobin levels and provide a maximum work rate over a shorter period of time (strength)
- Slow muscle fibres have a very good blood supply, plenty of myoglobin and are capable of sustained activity and high rates of aerobic respiration
Comparison of Fast and Slow Muscle Fibres
B.5.4 Distinguish between the effects of moderate-intensity and high-intensity exercise on fast and slow muscle fibres
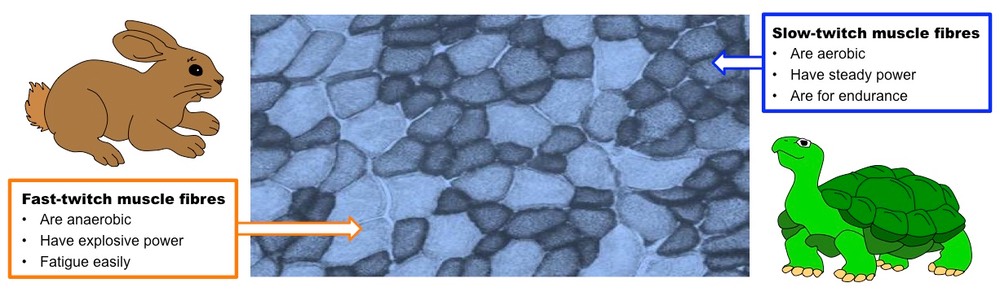
- Fast muscle fibres can release large amounts of energy in a short period of time via anaerobic respiration – they contain large amounts of glycogen
- Slow muscle fibres release energy more slowly by aerobic respiration but continue for longer – they rely more on respiratory substrates in the blood
- Moderate-intensity exercise (e.g. long-distance running or swimming) stimulate the development (in size) of slow muscle fibres
- High-intensity exercises (e.g. sprinting or weight-lifting) stimulate the development (in size) of fast muscle fibres
Fast and Slow Muscle Fibres
B.5.5 Discuss the ethics of using performance-enhancing substances, including anabolic steroids
Arguments For:
- Some naturally occurring substances can vary according to individual genetics, so it would level out all athletes
- Should be able to advance sporting performance to the maximum possible level (greater spectacle)
- Allows injured athletes to recover faster
- Would provide employment and economic benefit by opening up a new market
Arguments Against:
- Many performance-enhancing substances have negative side effects (e.g. high doses of anabolic steroids can cause liver disease)
- Would function to give some athletes an unfair advantage over others (wealthy would benefit at expense of the poor)
- Some may be artificially synthesised and so not represent normal processes (i.e. are unnatural)
- As currently illegal, using the substances provides profits for criminal organisations