H.3.1 Draw and label a diagram showing a transverse section of the ileum as seen under a light microscope
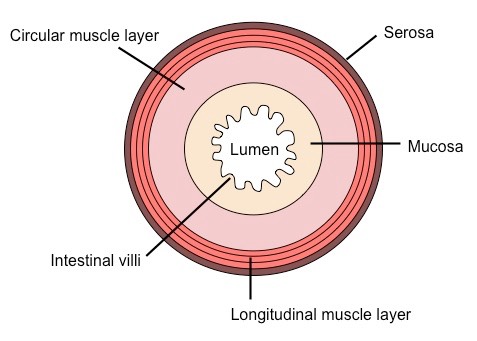
![]() Longitudinal Section of the Ileum
Longitudinal Section of the Ileum
H.3.2 Explain the structural features of an epithelial cell of a villus as seen in electron micrographs, including microvilli, mitochondria, pinocytotic vesicles and tight junctions
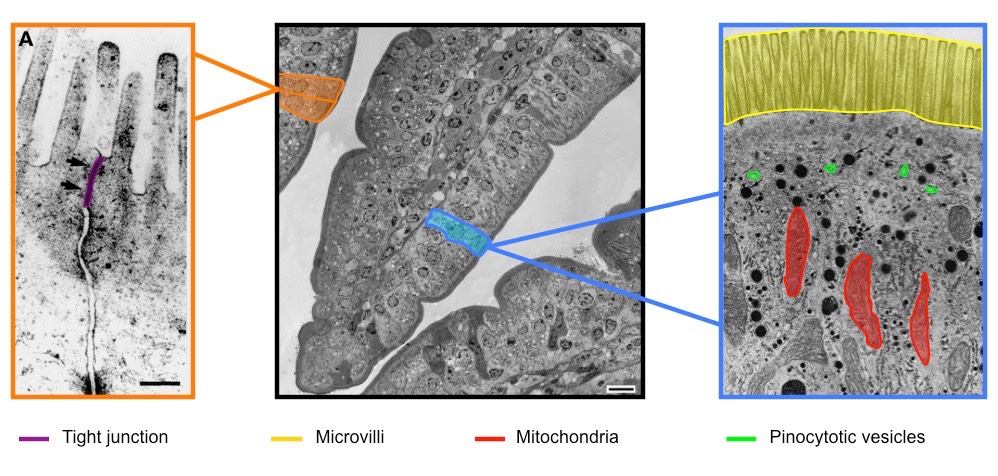

Microvilli
- The microvilli border significantly increases surface area of plasma membrane (>100x), allowing for more absorption of digested food materials
- The membrane is embedded with digestive enzymes (e.g. peptidases, disaccharase) and channel proteins to assist in material uptake
Mitochondria
- Large numbers of mitochondria provide energy (ATP) for active transport processes (uptake against concentration gradient)
Pinocytotic vesicles
- Pinocytosis (cell "drinking") is the non-specific ingestion of fluid and dissolved solutes (a quick way to translocate digested food products in bulk)
- Pinocytotic vesicles (near the microvilli) contain fluid and dissolved food materials from the lumen of the ileum
Tight junctions
- Tight junctions are occluding associations between the plasma membrane of two adjacent cells, creating an impermeable barrier
- They keep digestive fluids separate from tissue fluids and ensure the one way flow of food materials by maintaining a concentration gradient
H.3.3 Explain the mechanisms used by the ileum to absorb and transport food, including facilitated diffusion, active transport and endocytosis

Diffusion
- Lipids are absorbed by simple diffusion (can pass freely through hydrophobic core of the plasma membrane)
Facilitated Diffusion
- Channel proteins help hydrophilic food molecules pass through the hydrophobic portion of the phospholipid bilayer
- Water-soluble molecules (e.g. fructose), minerals and vitamins are absorbed by facilitated diffusion
Active Transport
- Protein pumps in the plasma membrane hydrolyse ATP to translocate molecules against the concentration gradient
- Epithelial cells will often use active transport to traffic high concentrations of food material into the cell so it can freely diffuse into the bloodstream
- Glucose, amino acids and mineral ions are all absorbed by active transport
Endocytosis
- Endocytosis involves the invagination of the plasma membrane to create an internal vesicle containing extracellular materials
- Each pinocytotic vesicle contains a small droplet of fluid from the lumen of the ileum
- The vesicles contain channels and pumps from the plasma membrane and so digested food can be absorbed from the vesicle into the cytoplasm
H.3.4 List the materials that are not absorbed and are egested
- Bile pigments
- Epithelial cells of the intestinal lining
- Lignin
- Cellulose
- Human flora / bacteria