Variation
Natural selection requires genetic variation to exist within a population in order to allow for the differential targeting of heritable characteristics
-
Genetic variation can be generated via mutations, meiotic divisions, sexual reproduction and gene flow
Mutation
-
A gene mutation is a change to the nucleotide sequence of a section of DNA that encodes a particular trait
-
Mutations can give rise to new versions of a gene (called alleles) and hence change the characteristics of an organism
-
Only germ line mutations (in gametes) produce heritable variation – somatic mutations (in body cells) are not passed on to offspring
Meiosis
-
Meiosis is a reduction division that reassorts parental chromosomes to create new gene combinations in gametes
-
The assortment of homologous chromosomes is random, meaning different combinations of chromosomes are generated upon each meiotic division
-
Additionally, genetic information can be exchanged between homologous chromosomes (crossing over) to create novel gene combinations
Sexual Reproduction
-
The fusion of gametes from two different parental sources will result in the production of offspring that are genetically distinctive
-
Because every gamete is unique (due to random assortment), the fertilisation of an egg and sperm should always generate different zygotes
Gene Flow
-
Gene flow describes the movement of alleles between interbreeding populations as a consequence of migration (or pollen transfer)
-
Gene flow creates variation within a given population by introducing new alleles from an alternate population source
-
Gene flow maintains the genetic compatibility between the two separate populations and hence functions to prevent speciation
Sources of Variation
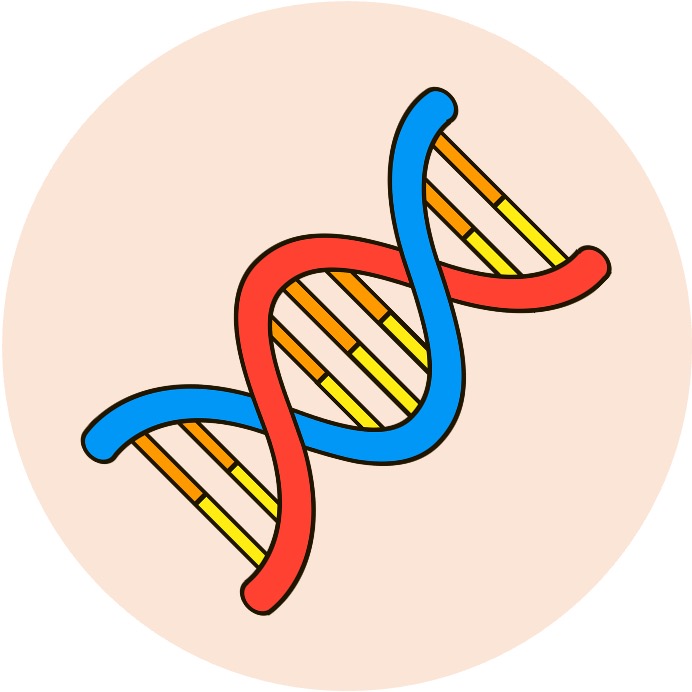
Mutation
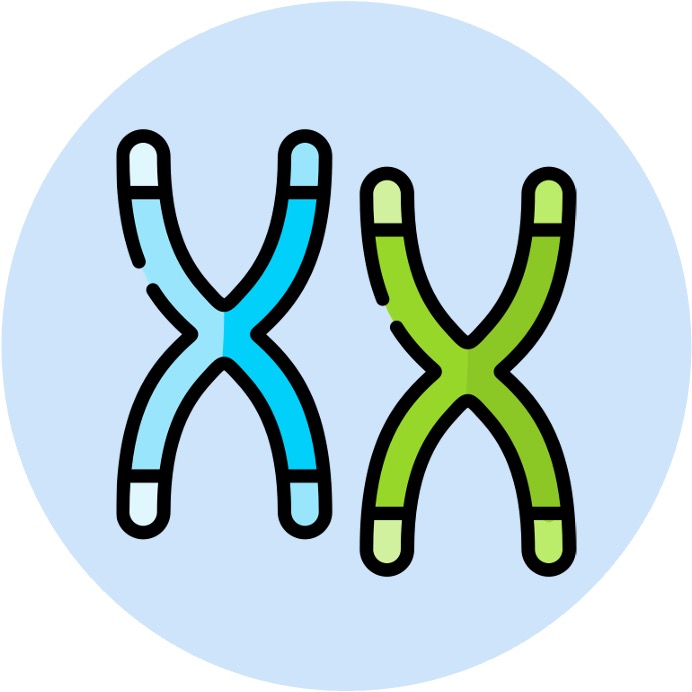
Meiosis
Fertilisation