Types of Mutations
Point mutations are changes to a single base in the DNA code and may involve either base substitutions, insertions or deletions
Base Substitutions
A base substitution mutation may create either a silent, missense or nonsense mutation depending on how the change impacts the polypeptide sequence
-
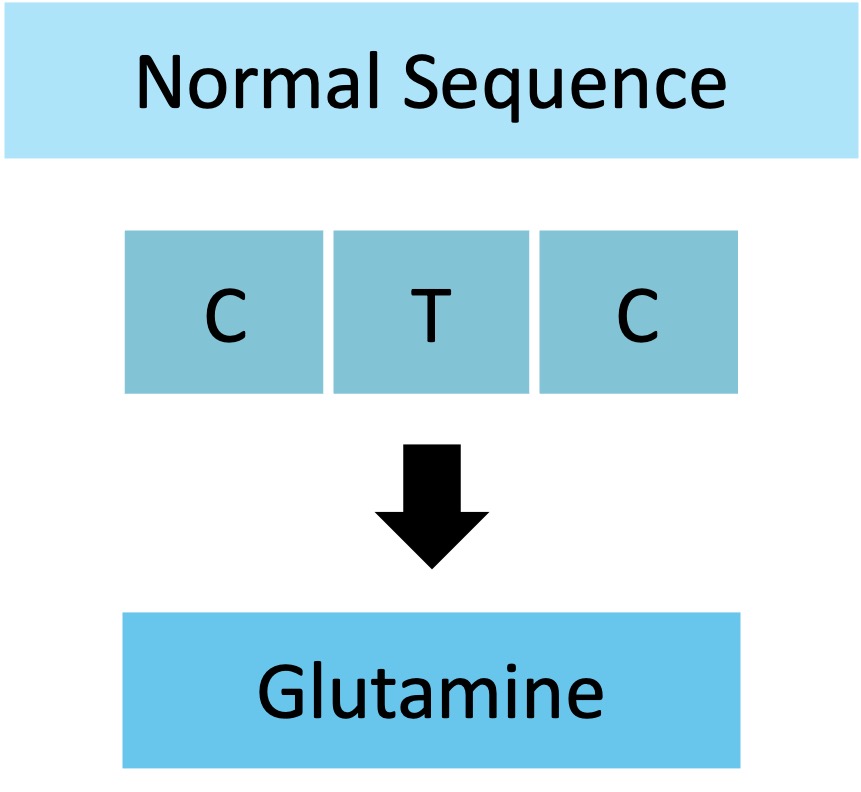
Silent mutations occur when the DNA change does not alter the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide
-
This is possible because the genetic code is degenerate and certain codons may code for the same amino acid
-
-
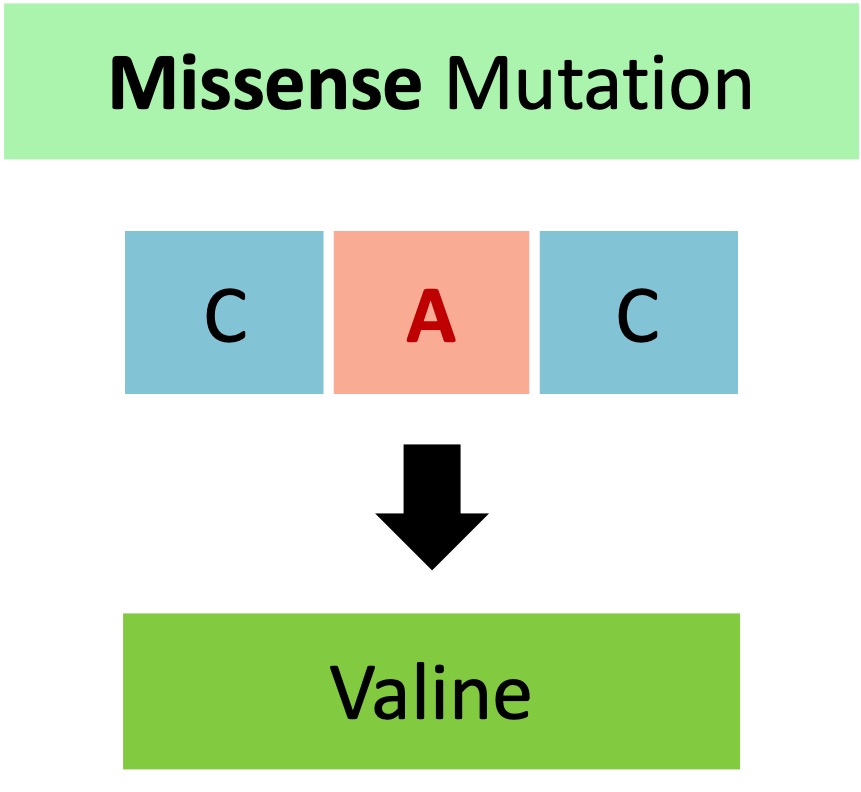
Missense mutations occur when the DNA change alters a single amino acid in the polypeptide chain
-
Sickle cell anaemia is a disease caused by a single base substitution mutation (GAG → GTG ; Glu → Val)
-
-
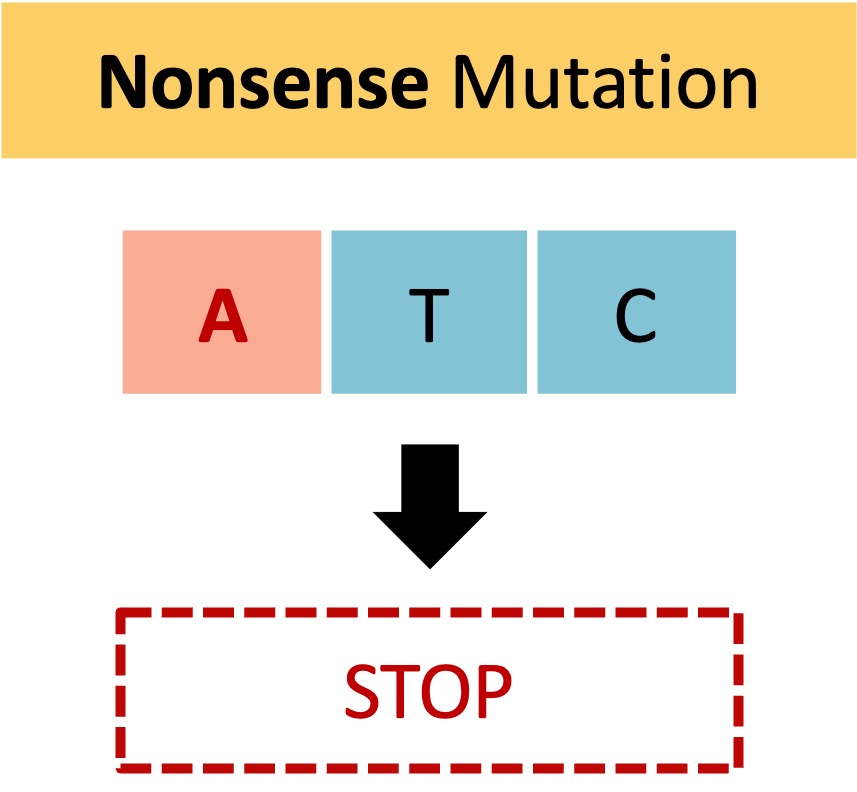
Nonsense mutations occur when the DNA change creates a premature STOP codon which truncates the polypeptide
-
Cystic fibrosis is a disease which may result from a nonsense mutation (this may not be the only cause though)
-

Frameshift Mutations
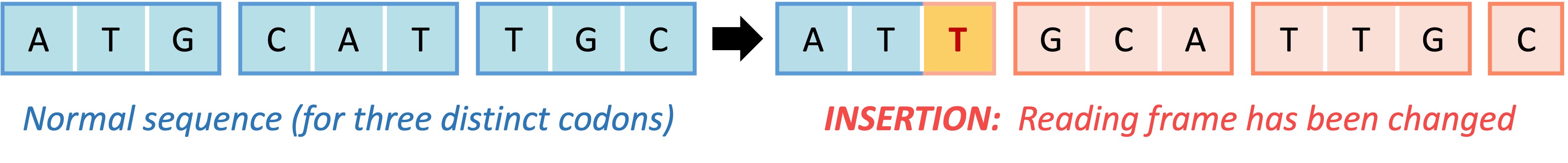
Frameshift mutations involve either the addition (insertion) or removal (deletion) of a single base of DNA, changing the reading frame
-
This change will affect every codon beyond the point of mutation and thus may dramatically change the amino acid sequence
-
Hence, frameshift mutations typically have a significant impact on cellular activity, as there is a high likelihood the polypeptide will cease to function

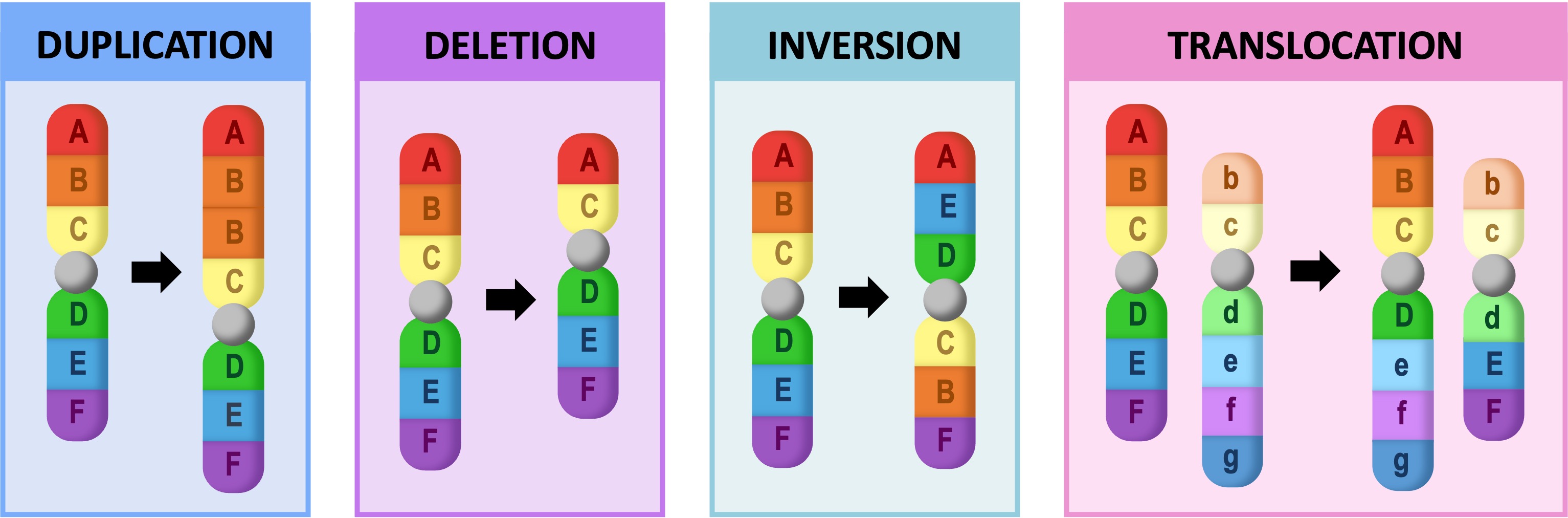
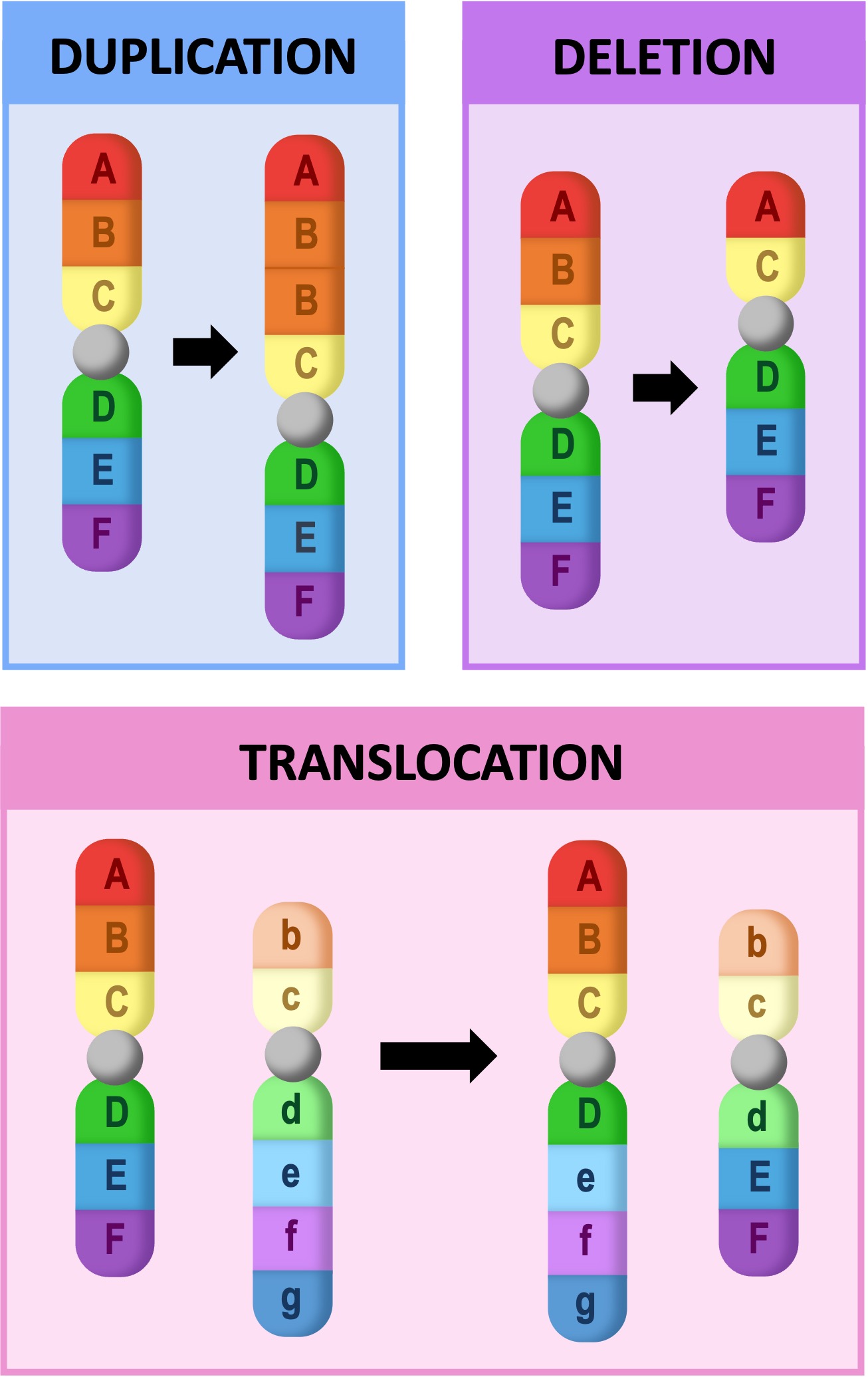
Block Mutations
Block mutations are changes to segments of a chromosome, resulting in large scale changes in the DNA of an organism
-
Block mutations are commonly caused by transposons (mobile genetic elements that can change positions within the genome)
-
There are many different types of block mutations that can exist, including large scale insertions (duplications), deletions or translocations