Types of Diversity
Biological diversity (biodiversity) describes the variation seen in living organisms at all levels of biological organisation
-
Biodiversity is vital for the integrity of ecosystems – the greater the biodiversity the more stable and resistant to change an ecosystem will be
There are three forms of biodiversity that work together to create the complexity of life that is seen on Earth:
-
Genetic Diversity – The variety of genes and characteristics that are present within a population of a species
-
Genetic diversity is increased by mutations or sexual reproduction and is decreased by natural selection and genetic drift
-
-
Species Diversity – The range of different species that are found within a particular habitat or ecosystem
-
Species diversity is measured in terms of species richness (number of different species) and species evenness (number of individuals in a species)
-
-
Ecosystem Diversity – The variety of habitat types or ecological niches within a given area of land or water
-
Ecosystems can be categorised according to the specific climate, vegetation and animal life within the region (biome)
-
Types of Biodiversity






Simpson’s Reciprocal Index
The Simpson’s reciprocal index can be used to measure the relative biodiversity of a given community
-
It takes into account both the number of species present (richness) and the number of individuals per species (evenness)
-
A higher index value is indicative of a greater degree of biodiversity within the community
The Simpson’s reciprocal index (D) requires the collection of two pieces of data to complete the formula below:
-
The number of individuals for each particular species (n)
-
The total number of individuals within the sample (N)
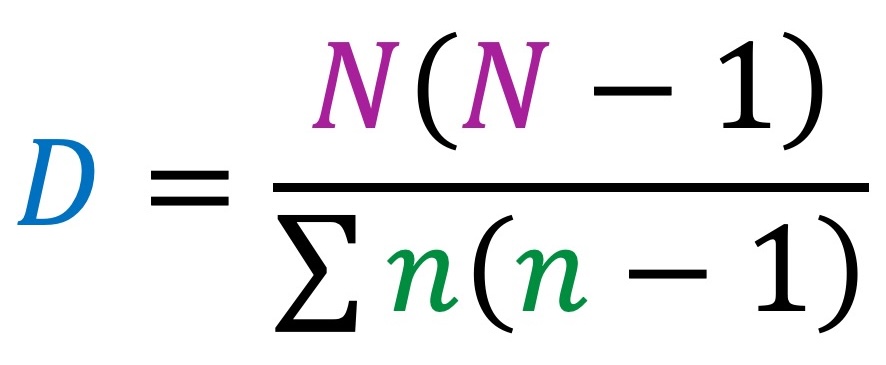
Simpson’s reciprocal index can be used to compare communities to identify intrinsic qualities:
-
A high index value suggests a stable site with many different niches and low competition (high richness and evenness)
-
A low index value suggests a site with few potential niches where only a few species dominate (low richness and evenness)
-
The index value may change in response to an ecological disturbance (such as human intervention or natural disasters)
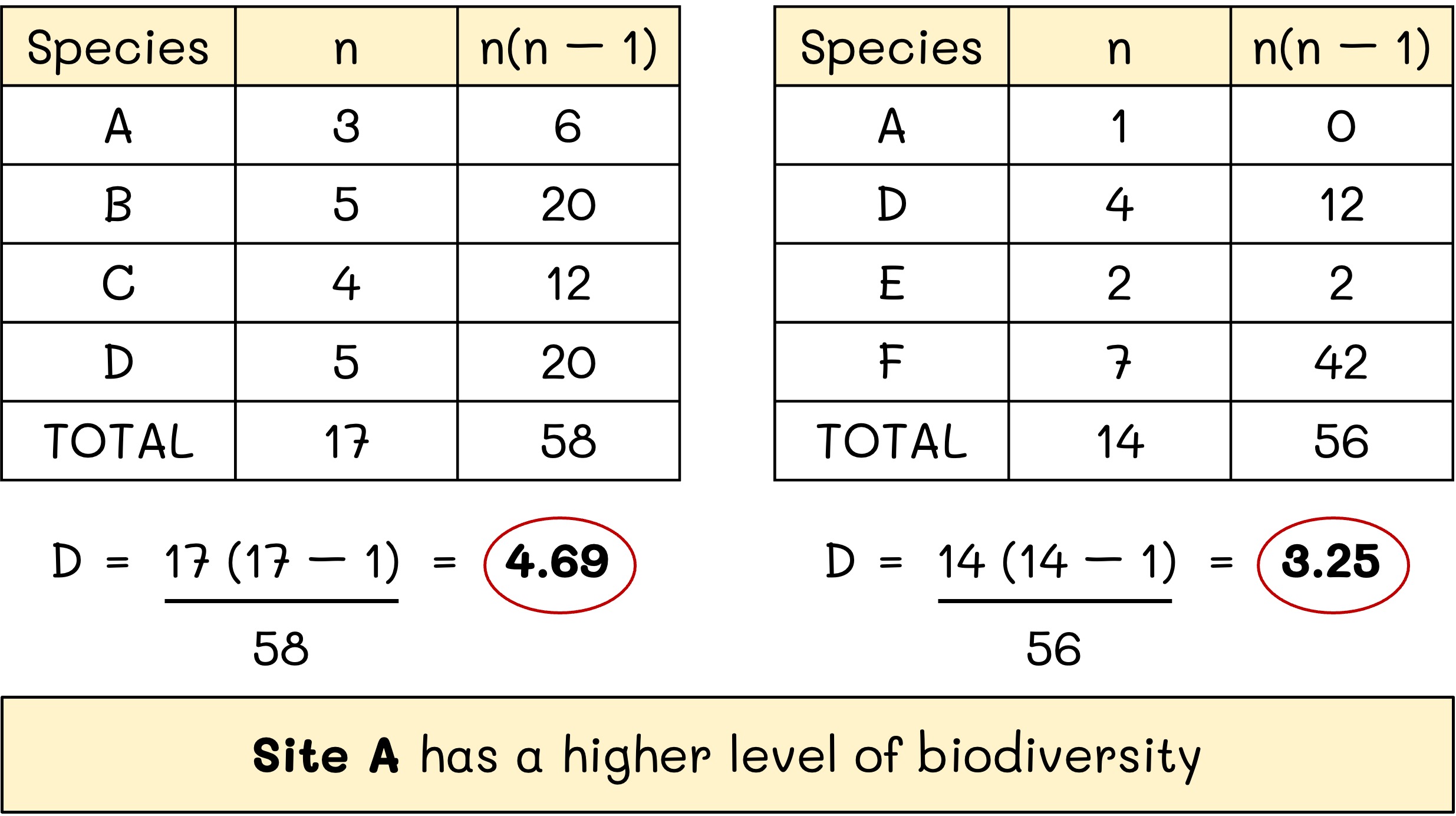
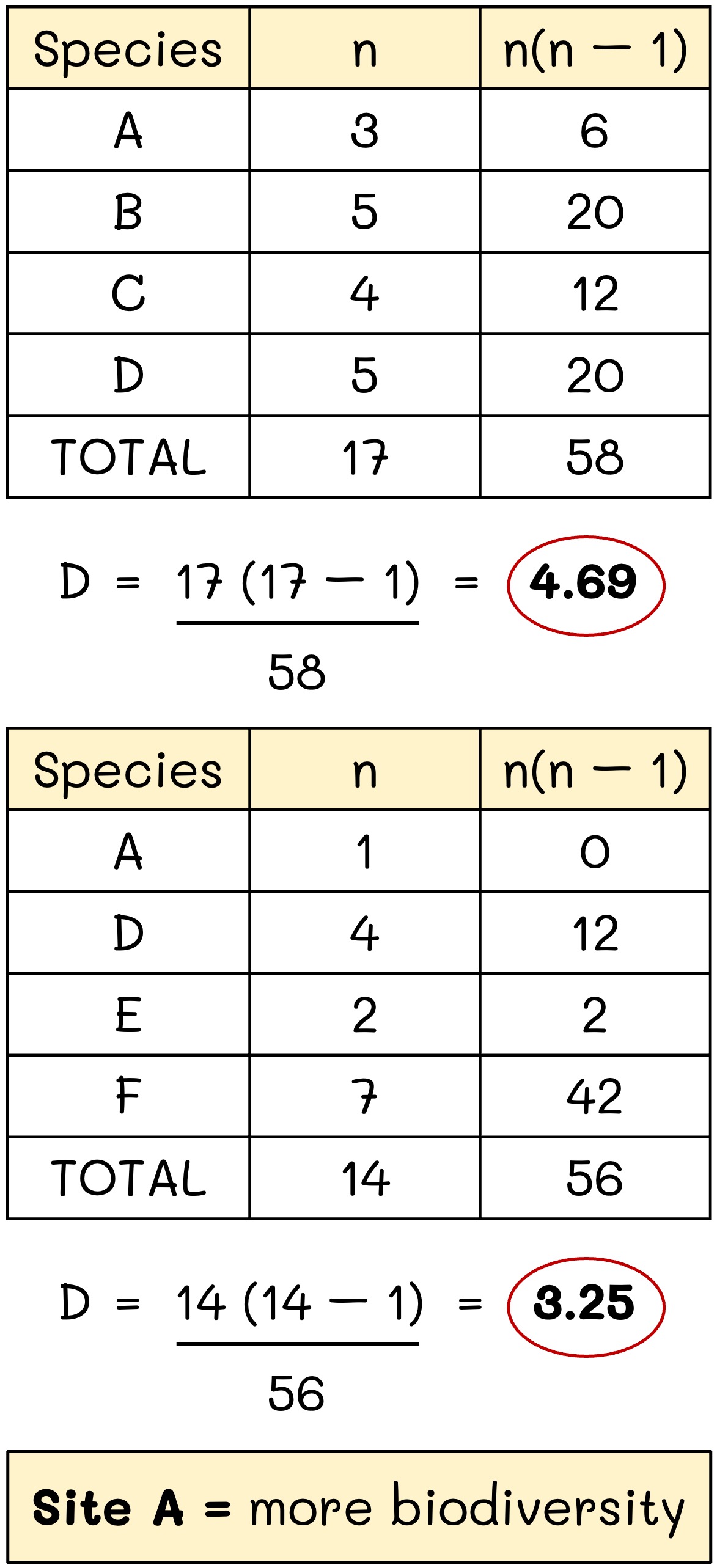
Worked Example:
The Simpson’s reciprocal index was used to assess the biodiversity at two different locations (letters represent species):
-
Site A: A = 3, B = 5, C = 4, D = 5
-
Site B: A = 1, D = 4, E = 2, F = 7