Trophic Levels
The position an organism occupies within a feeding sequence is known as a trophic level
-
Producers always occupy the first trophic level in a feeding sequence
-
Consumers feed on producers and are labelled according to their order (primary, secondary, etc.)
The trophic levels in a community are:
-
Level
Classification
-
1
Producer
-
2
Primary Consumer
-
3
Secondary Consumer
-
4
Tertiary Consumer
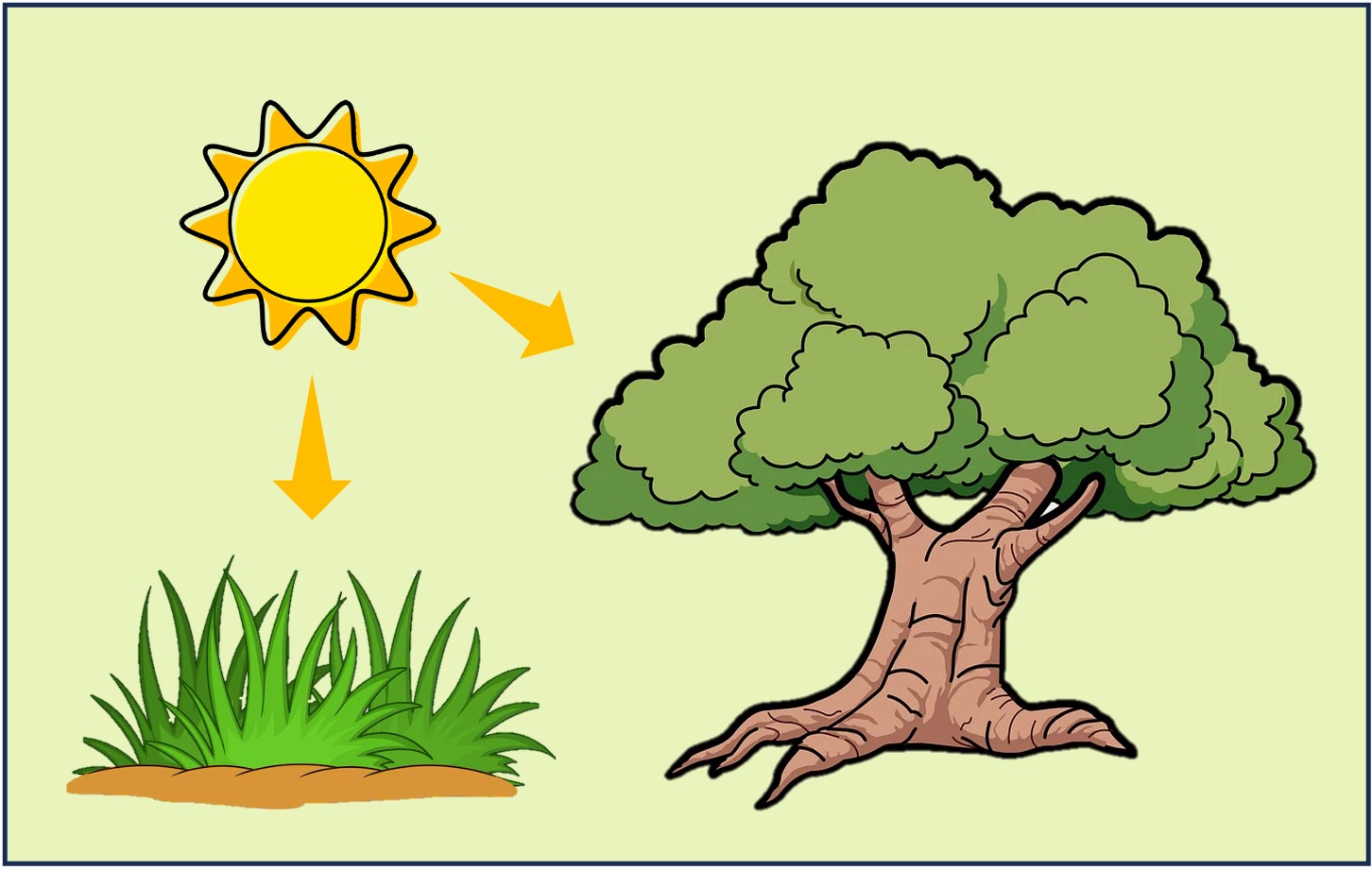
Producers
Autotrophs are organisms that synthesise organic compounds (i.e. food) from simple inorganic substances
-
Most autotrophs derive the energy for this process from sunlight (via photosynthesis)
-
Some autotrophs may use energy from the oxidation of inorganic molecules (via chemosynthesis)
Because autotrophs make their own organic compounds without relying on other organisms, they are said to be producers
-
Producers must always occupy the first trophic level of any feeding sequence
Autotrophs (Producers)
Consumers
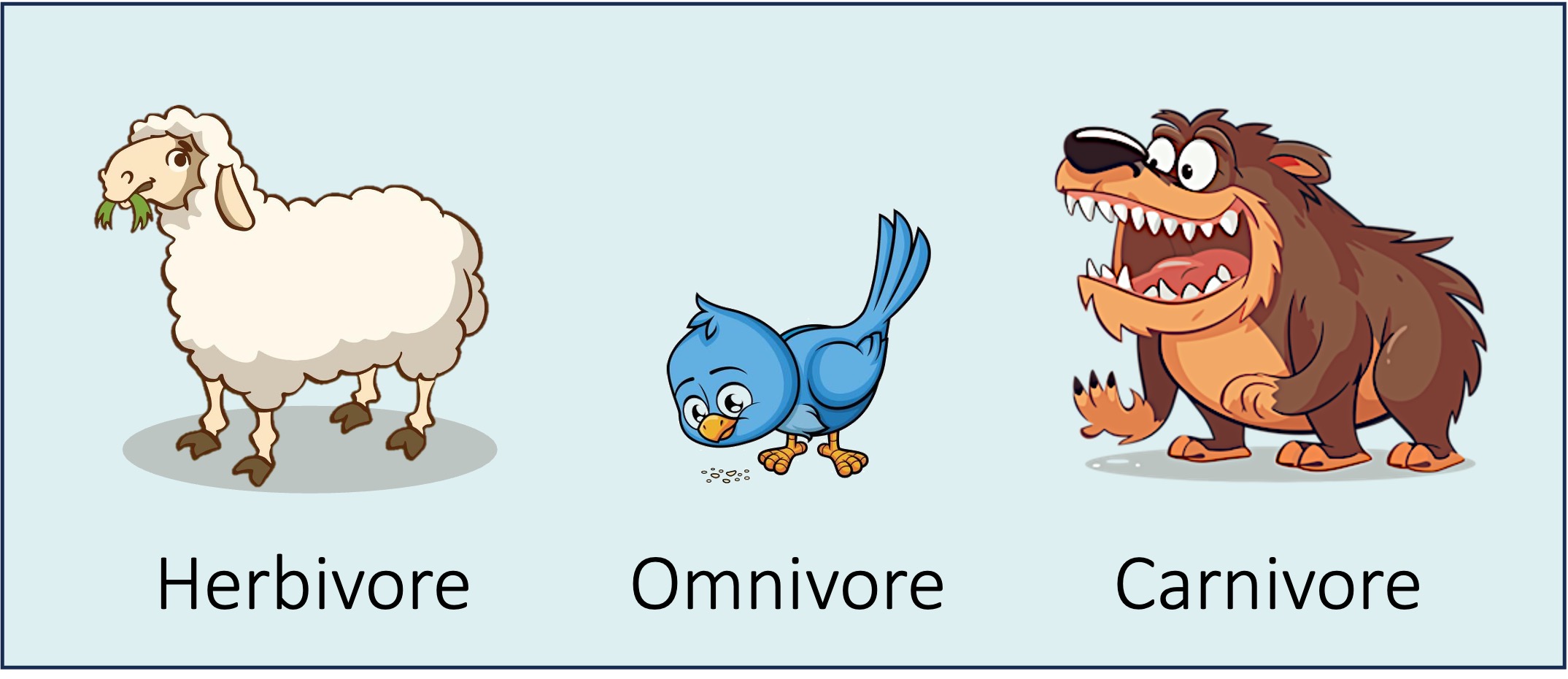
Heterotrophs obtain organic molecules from other organisms via different feeding mechanisms and different food sources
-
Herbivores are heterotrophs that feed principally on plant matter (e.g. cows, sheep, rabbits)
-
Carnivores are heterotrophs that feed principally on animal matter (e.g. crocodiles, wolves, tigers)
-
Omnivores are heterotrophs that have a diet composed of both plant and animal matter (e.g. pandas, humans)
Heterotrophs that feed via internal digestion (i.e. holozoic nutrition) are said to be consumers
-
Consumers occupy all subsequent trophic levels after an initial producer
Heterotrophs (Consumers)
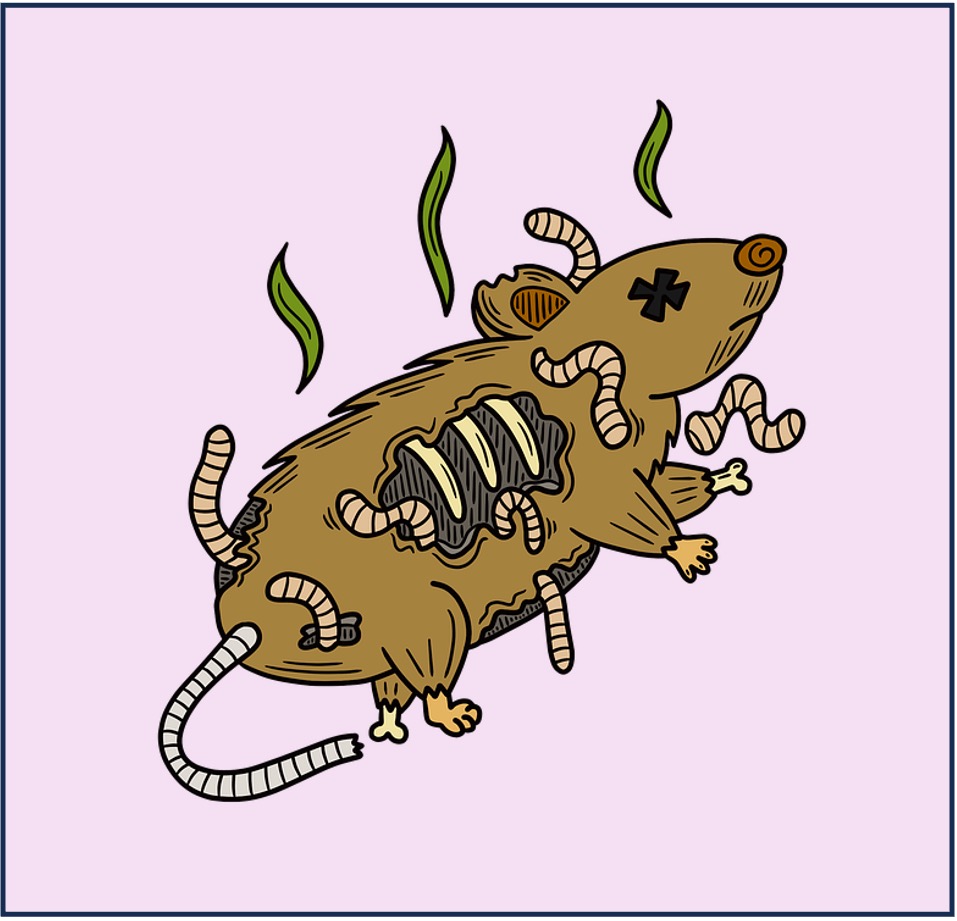
Decomposers
Saprotrophs are heterotrophs that gain organic nutrients from dead organisms via external digestion
-
Saprotrophs live on (or in) non-living organic matter, secrete digestive enzymes into it and absorbing the products of digestion
-
Common examples of saprotrophs include bacteria and fungi (e.g. mushrooms, molds)
Because saprotrophs use enzymatic secretion to facilitate external digestion, they are said to be decomposers
-
Decomposers will feed at every trophic level after the producers and so are not typically represented in feeding sequences
Saprotrophs (Decomposers)