Translation
Translation involves the synthesis of an amino acid sequence (polypeptide) by the ribosome
-
Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic code that determines the order of amino acids in a polypeptide sequence
-
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is responsible for transporting amino acids to the ribosome according to the mRNA sequence
Ribosomes
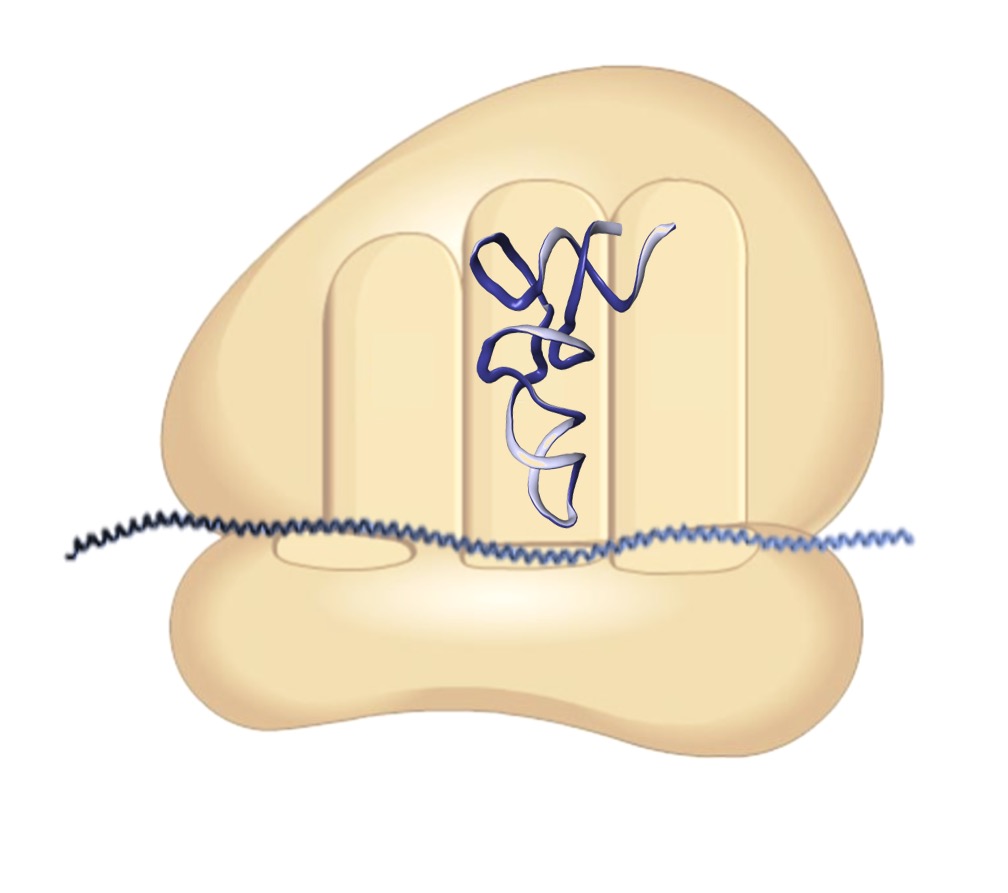
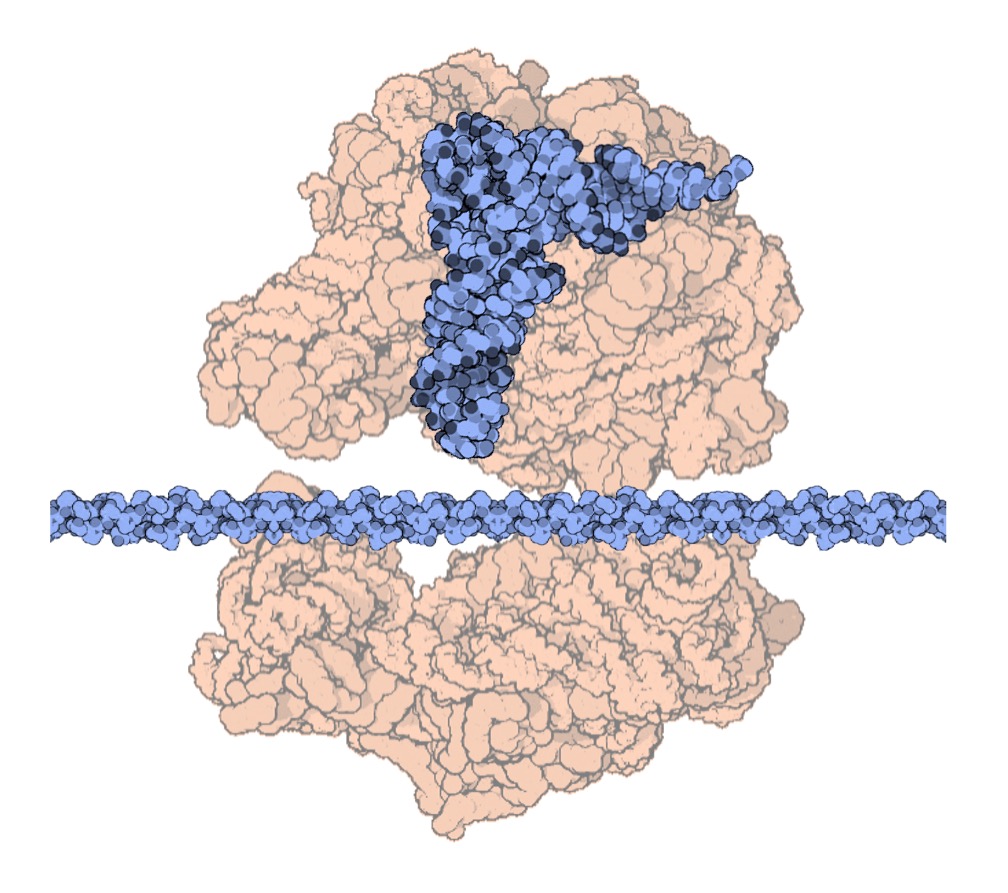
Ribosomes consist of two distinct subunits in order to interact with the different types of RNA:
-
The small subunit of the ribosome binds to the messenger RNA and decodes the genetic message
-
The large subunit can simultaneously bind to two tRNA molecules and mediates peptide bond formation
Ribosomes are composed of both ribosomal RNA (which contributes to the catalytic activity) and protein (which provides structural stability)
Ribosome Structure
Simple Model
Spacefill Model
Codons
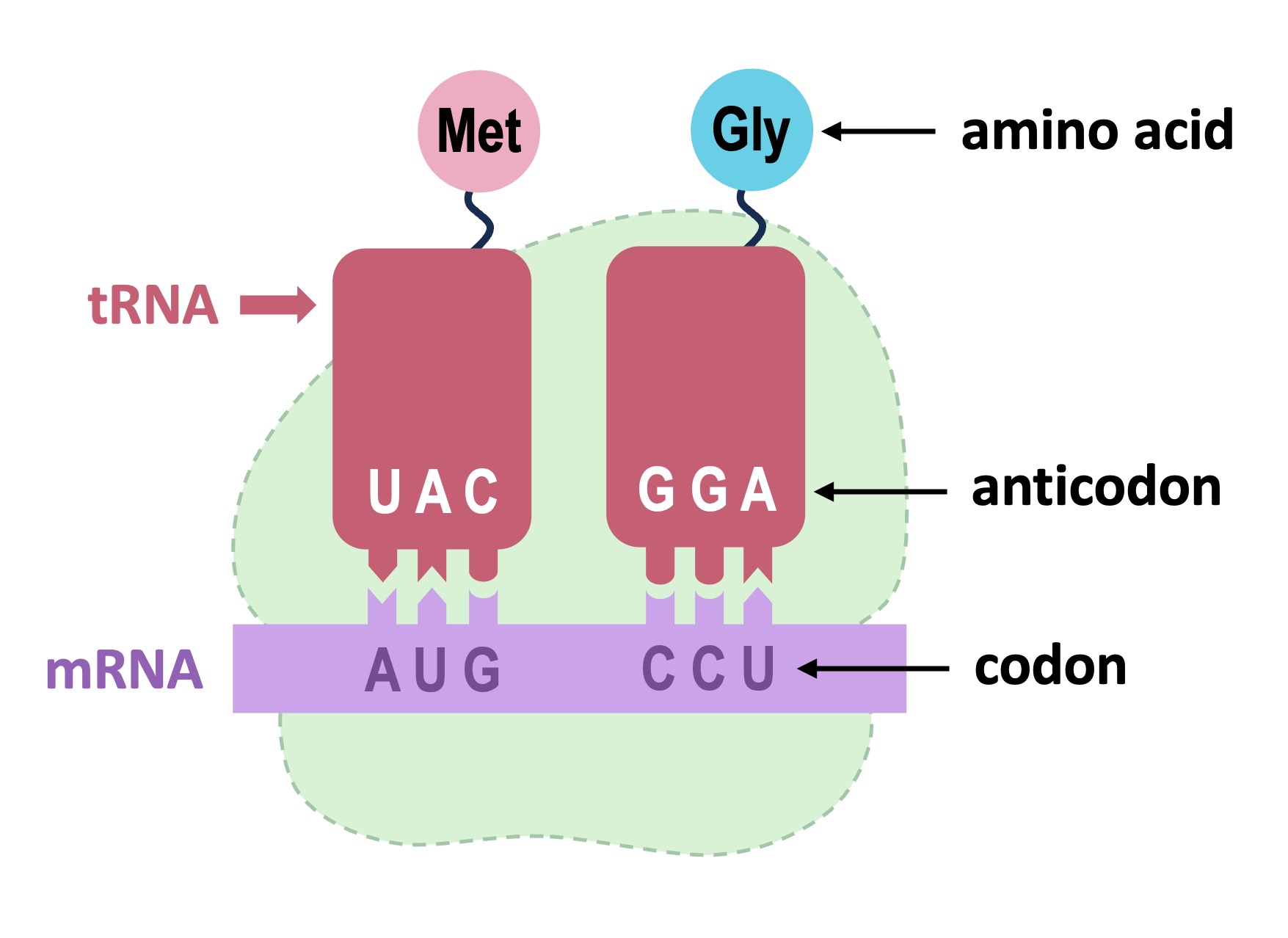
The base sequence of an mRNA molecule is read by the ribosome in triplets of bases called codons
-
Each codon encodes a specific amino acid and the order of codons within an mRNA transcript determines the polypeptide sequence
Amino acids are brought to the ribosome by a tRNA molecule possessing a complementary sequence to the codon
-
This complementary sequence of bases (called the anticodon) ensures the correct amino acid is paired to the correct codon
Codons vs Anticodons
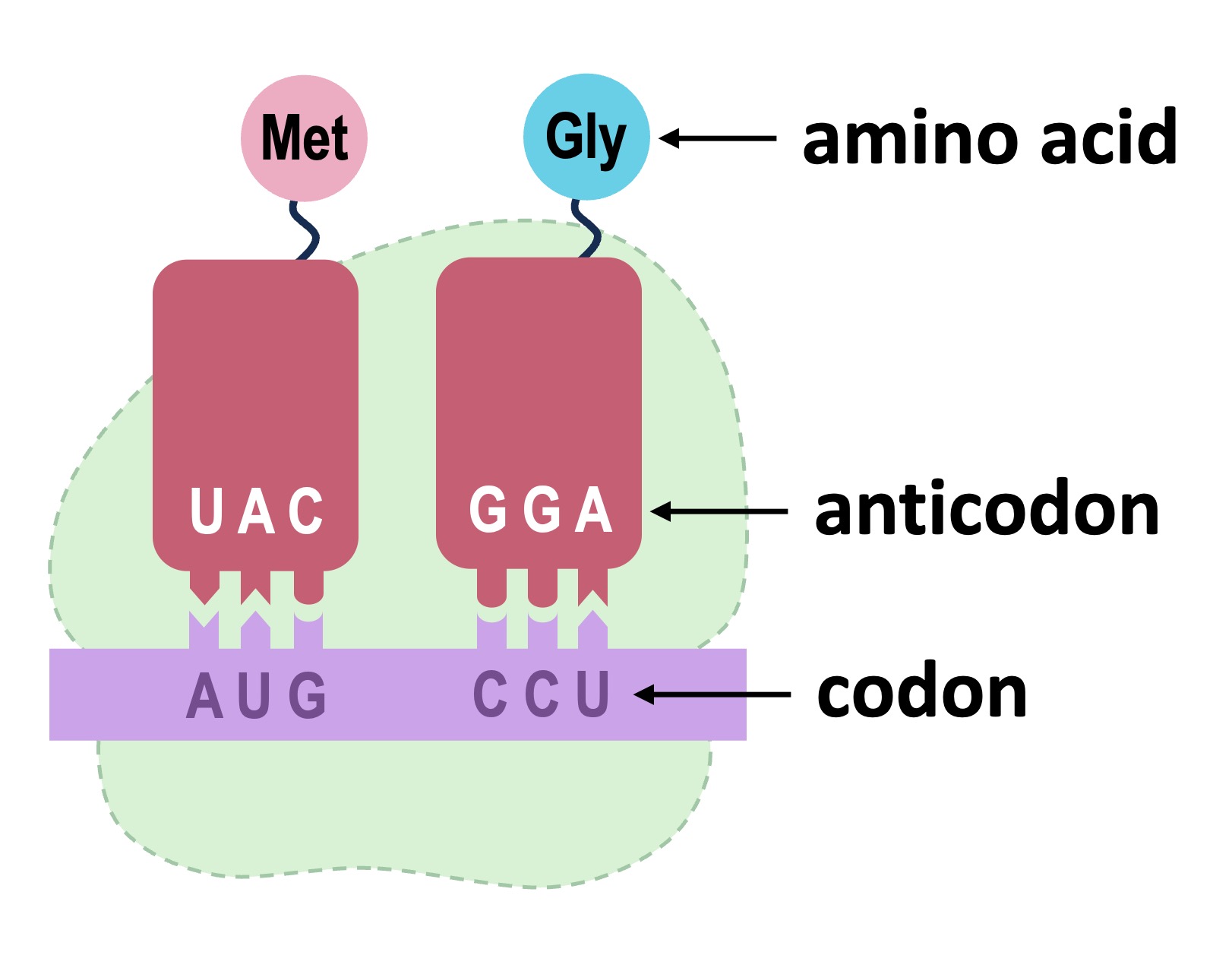
Polypeptide Synthesis
Polypeptides are synthesised as the ribosome moves along the mRNA transcript and joins together the amino acids carried by tRNA
-
Translation always begins at a specific START codon (AUG) and terminates at a STOP codon
-
As the ribosome moves along the mRNA transcript, tRNA molecules bring amino acids according to the codon sequence
-
The ribosome links the amino acids together via a condensation reaction to form a peptide bond
-
As new tRNA molecules bring more amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain, deacylated tRNA molecules are released by the ribosome
Translation Overview
Translation Mnemonic
An easy way to remember the different components involved in translation is with the mnemonic device: Mr Cat App
-
MR: Messenger RNA binds to the Ribosome (via the small subunit)
-
CAT: Codons (on mRNA) are recognised by complementary Anticodons on Transfer RNA
-
APP: Amino acids are joined by the ribosome via Peptide bonds to form Polypeptides

Translation: Mister Cat App