Transcription
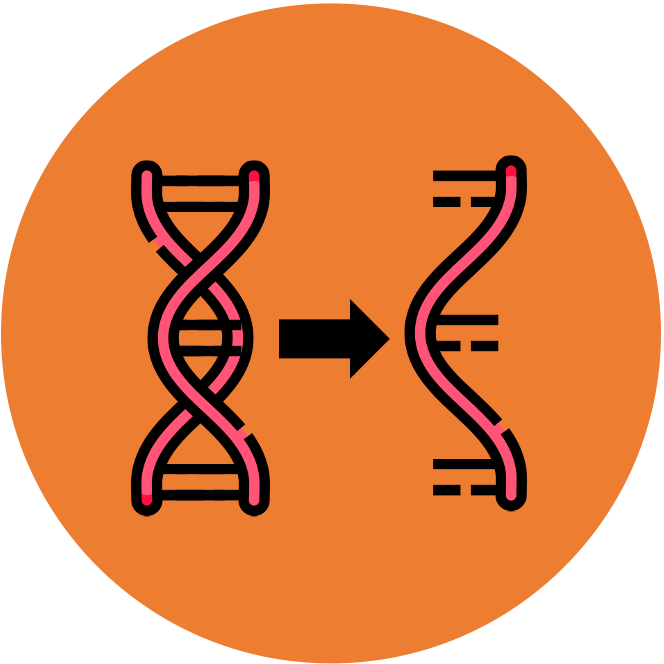
Transcription is the process by which an RNA sequence is produced from a DNA template
-
Transcription is mediated by the enzyme RNA polymerase, which separates the DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs
-
While the DNA strands are separated, free nucleotides align opposite their exposed complementary base partner
-
RNA polymerase then covalently joins the free nucleotides together (5’ → 3’) to generate an RNA transcript of the DNA sequence
-
Once the RNA sequence has been synthesised, RNA polymerase detaches from the DNA molecule and the double helix reforms
Transcription Animation
Sense versus Antisense
The segment of double-stranded DNA that codes for an RNA sequence is called a gene – but only one strand is actually transcribed
-
The strand that is transcribed is called the template strand and is complementary in sequence to the RNA transcript (it is ‘antisense')
-
The strand that is not transcribed is called the coding strand and is identical in sequence to the RNA transcript (it is ‘sense')
-
The only difference between the transcript and the coding strand is that RNA uses uracil instead of thymine
-
Transcription Summary