Summation
Nerve impulses arise from the differential distribution of ions across a membrane and hence cannot occur when no membrane is present
-
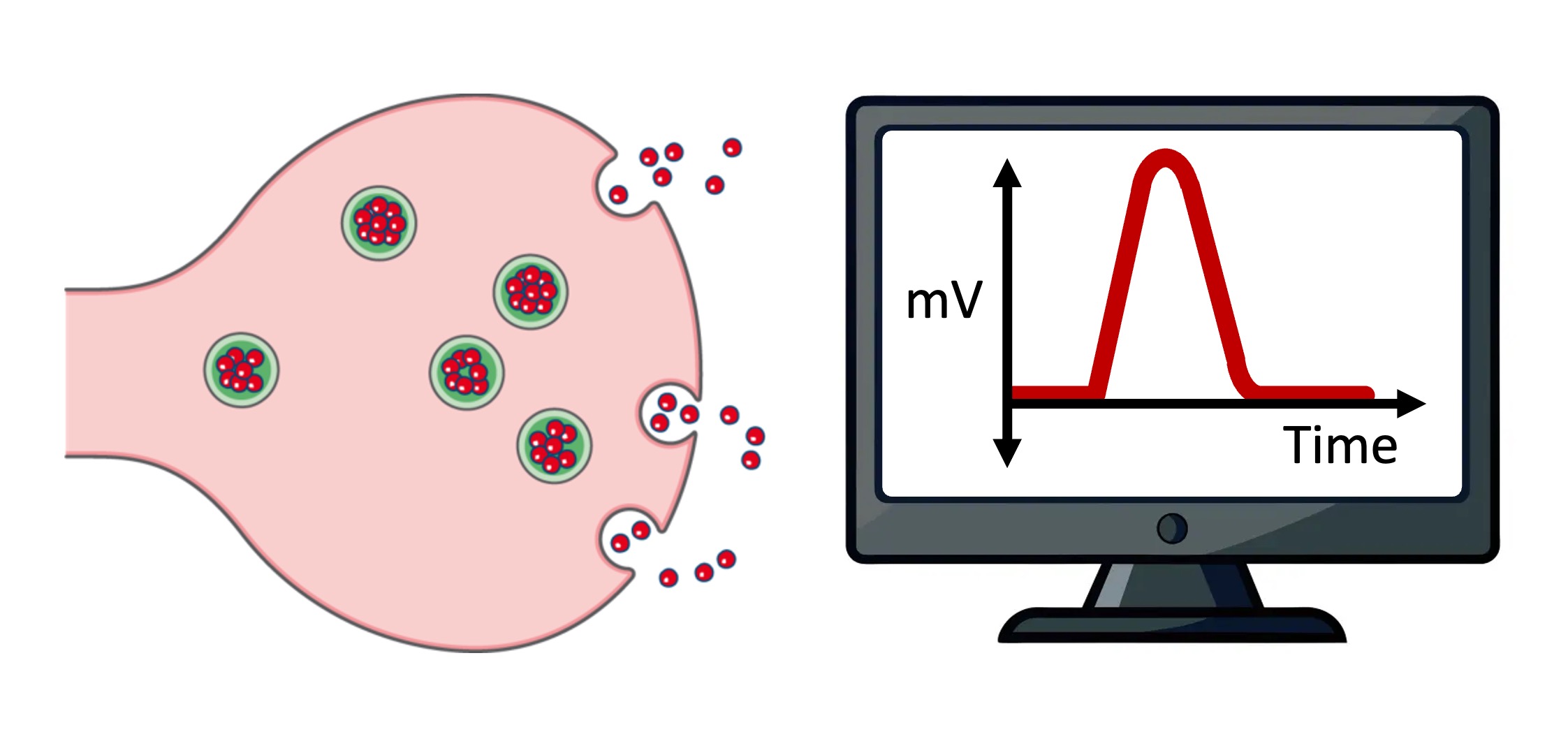
Electrical signals must be converted into chemical signals for communication to continue across a synaptic cleft
Neurotransmitters are the chemicals that are released into the synapse to bind to receptors on the post-synaptic membrane of target cells
-
Neurotransmitters open ligand-gated ion channels and cause small changes in membrane potential known as graded potentials
An action potential is only initiated if a threshold potential is reached, so as to open the voltage-gated ion channels within the axon
-
Excitatory neurotransmitters (e.g. noradrenaline) cause depolarisation by opening ligand-gated sodium or calcium channels
-
Inhibitory neurotransmitters (e.g. GABA) cause hyperpolarisation by opening ligand-gated potassium or chlorine channels
The combined action of all neurotransmitters acting on a target neuron determines whether a threshold potential is reached
-
If overall there is more depolarisation than hyperpolarisation and a threshold potential is reached, the neuron will fire
-
If overall there is more hyperpolarisation than depolarisation and a threshold potential is not reached, the neuron will not fire
For a typical neuron, the threshold potential (required to open voltage-gated ion channels) is approximately –55 mV
Graded Potentials
Depolarisation
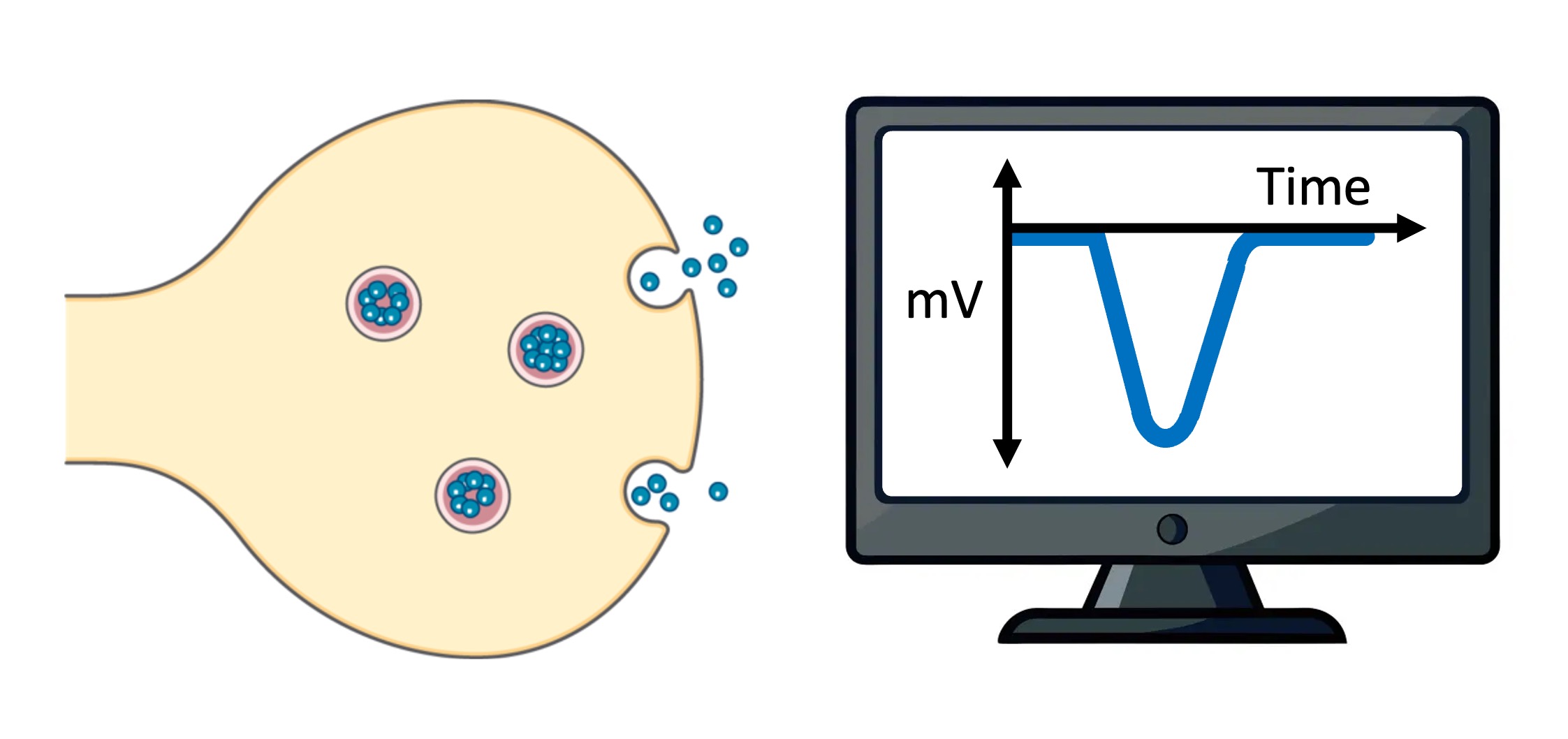
Hyperpolarisation
Summation
Neurotransmitters can trigger either excitatory post-synaptic potentials (EPSPs) or inhibitory post-synaptic potentials (IPSPs)
-
EPSPs trigger depolarisation in the post-synaptic membrane, IPSPs trigger hyperpolarisation in the post-synaptic membrane
-
If the combination of signals reaches a threshold level, an action potential will be triggered in the post-synaptic neuron
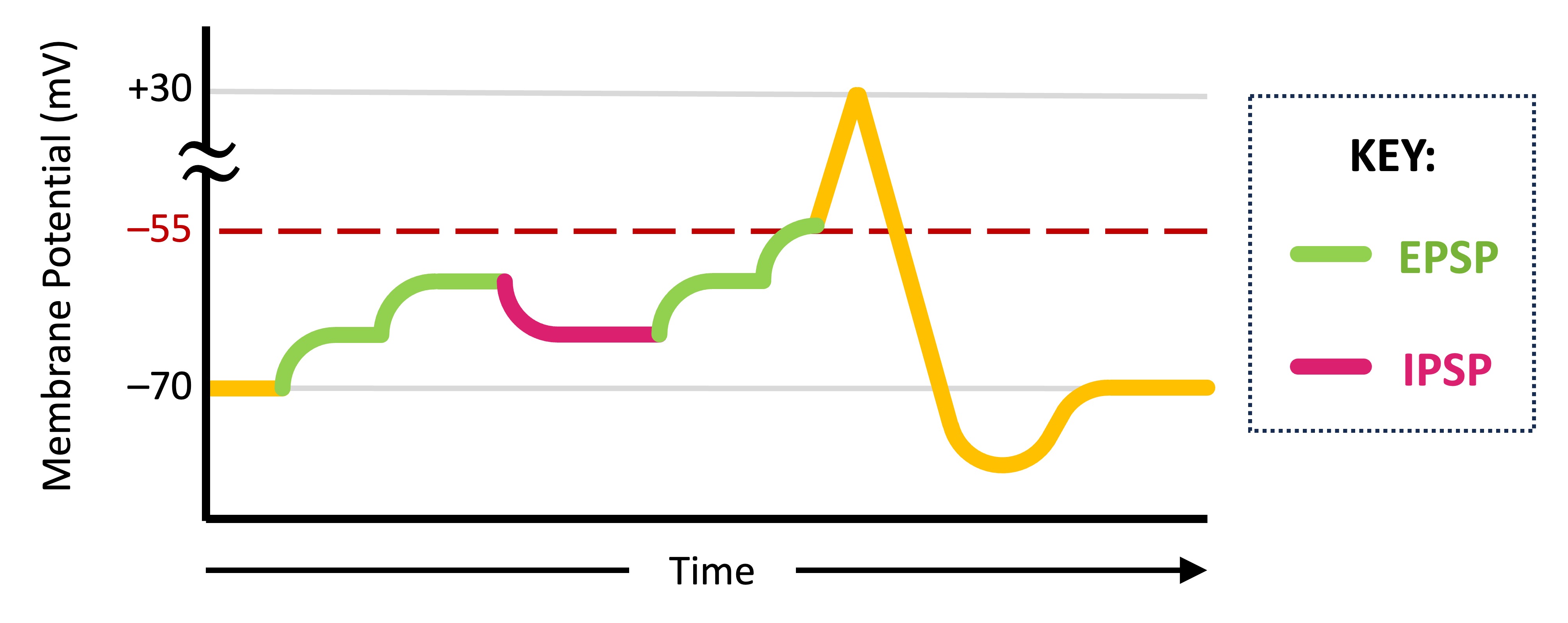
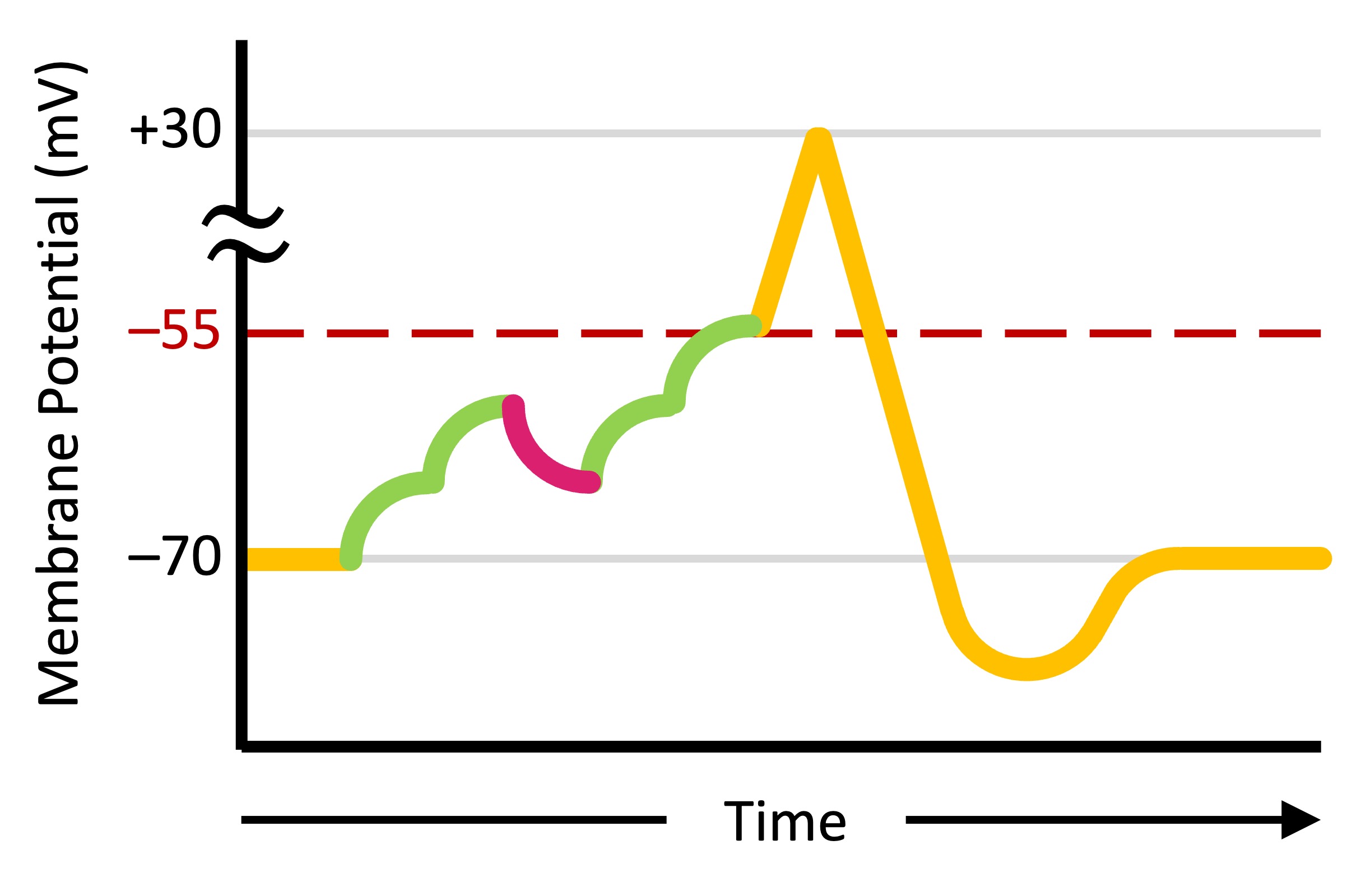
The combination of graded potentials in the post-synaptic neuron is known as summation
-
Cancellation occurs when excitatory and inhibitory graded potentials cancel each other out (no threshold potential reached)
-
Spatial summation occurs when EPSPs are generated from multiple presynaptic neurons simultaneously to reach threshold
-
Temporal summation occurs when multiple EPSPs are generated from a single presynaptic neuron in quick succession
These summative effects determine whether specific neurons are activated and hence may lead to alternative neural pathways
Summation