Solvent Properties
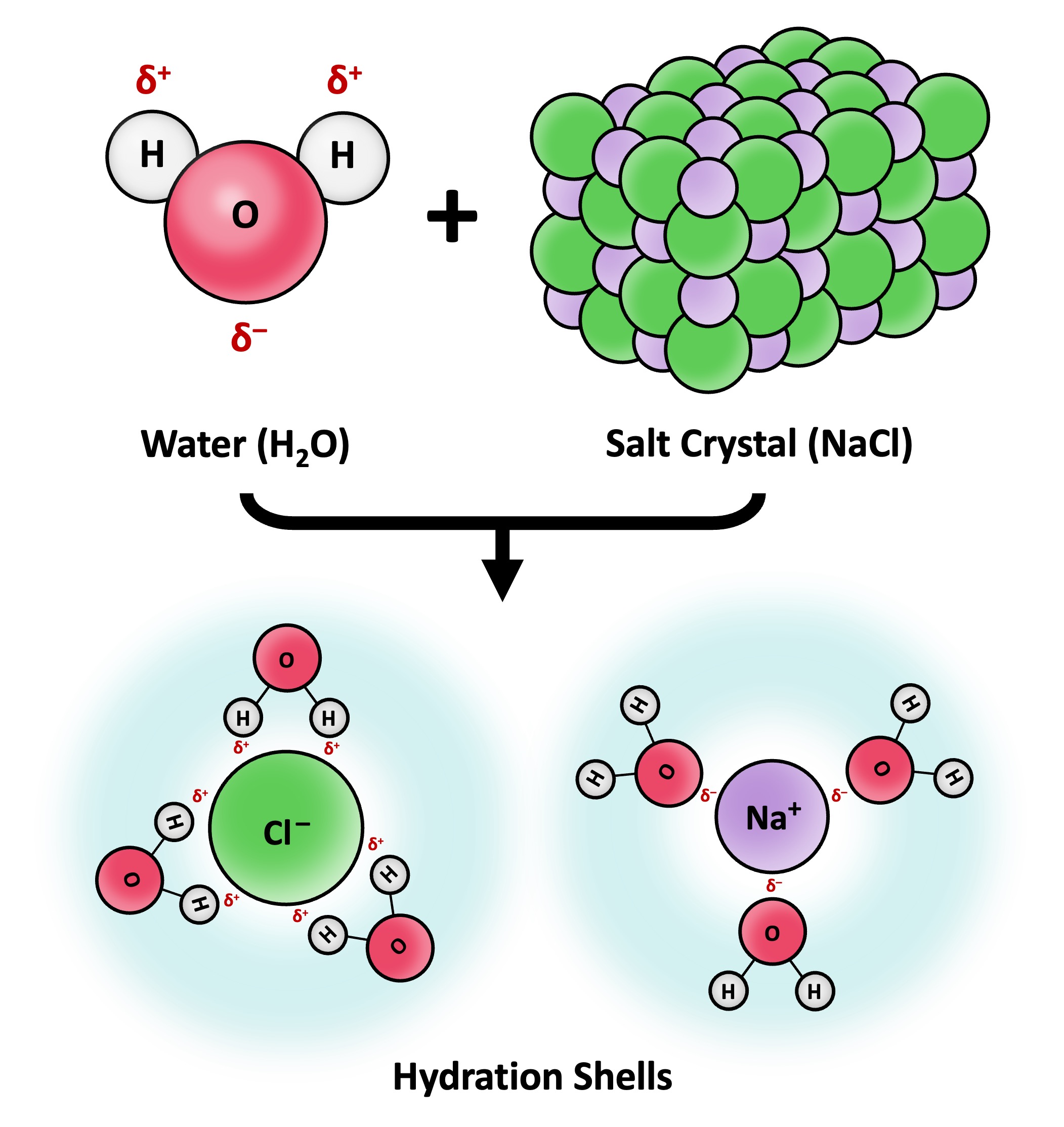
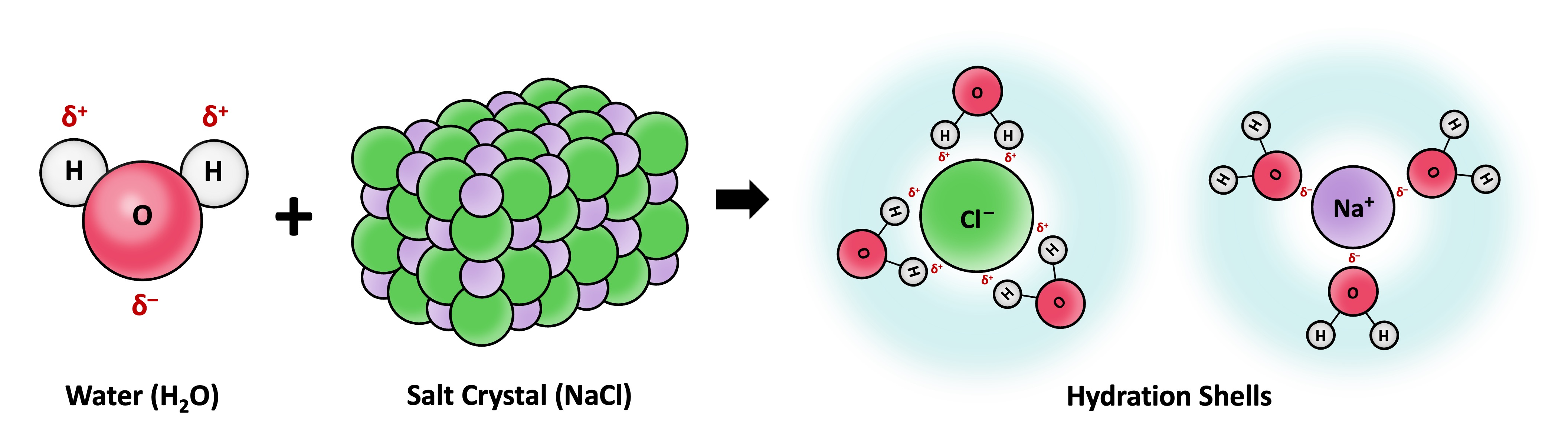
Solvation is the process by which solvent molecules surround and interact with solute molecules
-
A solute is any substance (usually a solid) that is dissolved by a solvent molecule to form a solution
-
Solutes that are able to be dissolved by a solvent are considered to be soluble (insoluble substances will not form a solution)
Water is commonly referred to as the universal solvent due to its capacity to dissolve a large number of substances
-
Water can dissolve any substance that contains charged particles (ions) or electronegative atoms (polarity)
-
The polar regions of the water molecule associate with molecular surfaces that have an opposing charge, forming dispersive hydration shells
Solvation
Metabolic Medium
The capacity of water to dissolve a large variety of substances makes it an important medium for metabolic reactions
-
Solutes dissolved into aqueous solutions are more likely to collide with enzymes and undergo necessary chemical reactions
-
Water can also promote enzyme activity by absorbing heat from exothermic reactions and maintain acid-base neutrality
Substances that are involved in metabolic reactions can be described as being either hydrophilic or hydrophobic
-
Substances that freely associate and readily dissolve in water are characterised as hydrophilic (‘water loving’) – this includes all polar molecules and ions
-
Substances that do not freely associate or dissolve in water are characterised as hydrophobic (‘water-hating’) – this includes all large non-polar molecules (lipids)
Transport Medium
The movement of water-soluble substances in plants and animals involves different transport systems
-
In animals, the blood plasma transports dissolved solutes – including amino acids, simple sugars, wastes (urea) and a small amount of gases (O2 and CO2)
-
In vascular plants, mineral ions are transported via xylem vessels while dissolved nutrients are transported via the phloem
Certain substances are not water-soluble and cannot be freely transported within an aqueous environment
-
In animals, lipids are packaged with proteins to form water-soluble lipoproteins that can be transported via the blood
-
The mechanism of lipid transport is not well understood in plants, but may involve conjugation to amino acids and transport via the phloem