Sexual Life Cycle
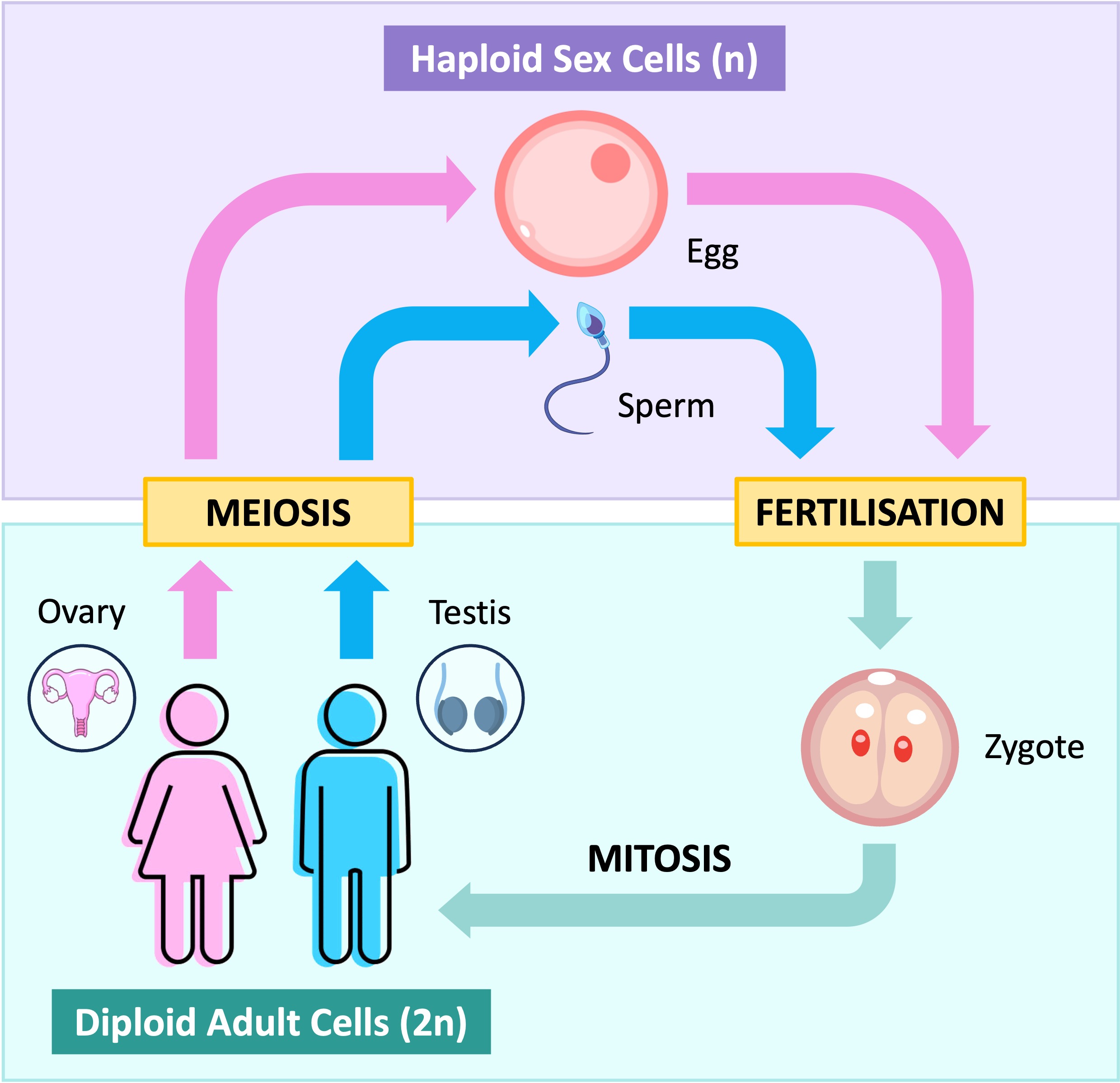
The life cycle of a sexually reproducing organism requires the formation of haploid sex cells (gametes) and their subsequent fusion to form a new organism
-
Sex cells are produced via meiosis, which functions to separate the parental combination of alleles to create cells with half the number of chromosomes
The fusion of two haploid gametes via fertilisation will result in the formation of a new diploid cell (called a zygote)
-
Because the zygote has genetic material from two different sources, it is genetically distinct from both of the parents
The zygote is able to undergo asexual reproduction (i.e. mitosis) to form a multicellular organism
-
Differentiation of these genetically identical cells will result in the formation of distinct tissues with specific functions
Sexual Life Cycle