Semi-Conservative
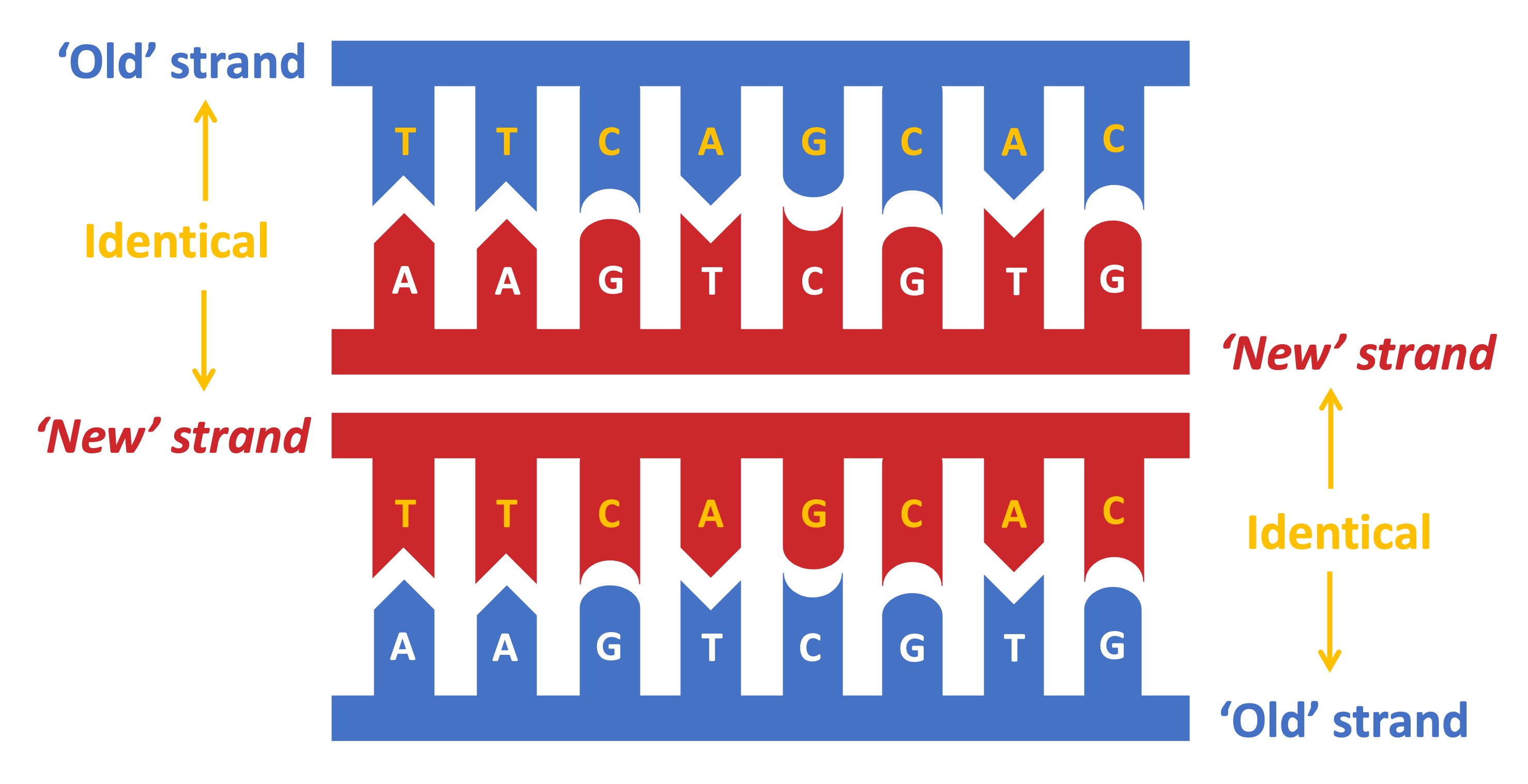
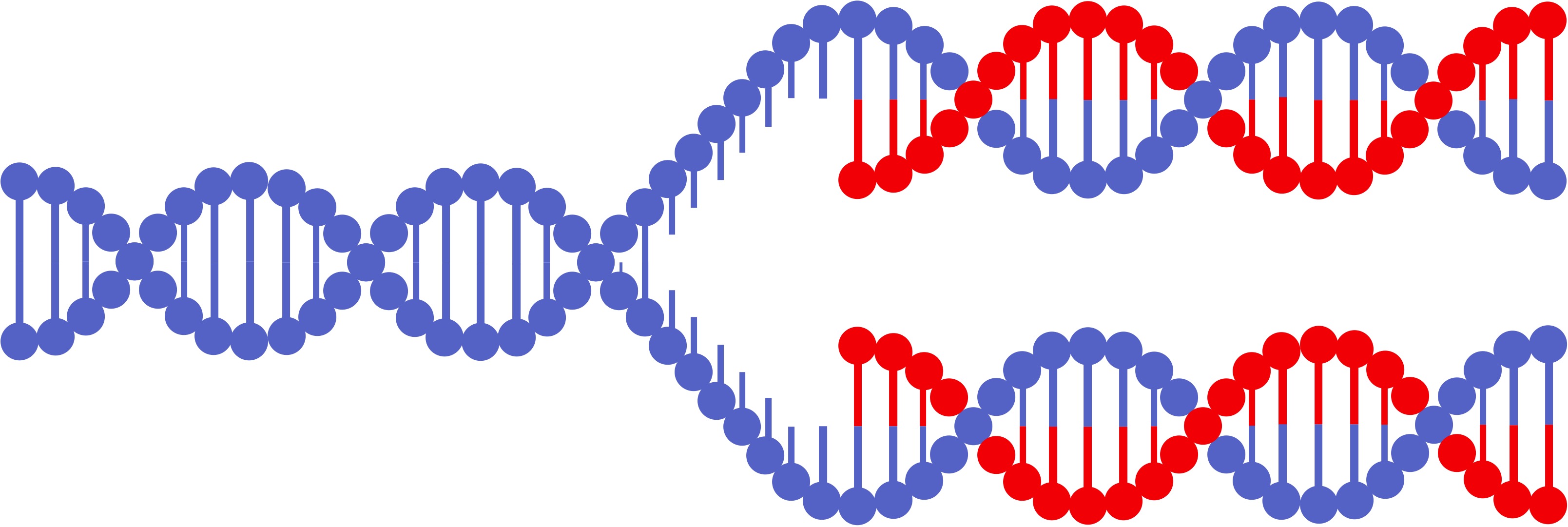
DNA replication is a semi-conservative process, because when a new double-stranded DNA molecule is formed:
-
One strand will be from the original template molecule (conserved)
-
One strand will be newly synthesised (not conserved)
Semi-Conservative Replication
The DNA is copied with a high degree of accuracy because each nitrogenous base can only pair with its complementary partner
-
Adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) – via two hydrogen bonds
-
Cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G) – via three hydrogen bonds
Consequently, when DNA is replicated:
-
Each new strand formed will be identical to the original strand that was separated from the template
-
The two semi-conservative molecules formed will have an identical base sequence to the original molecule
Conservation of Base Sequence