Self Replication
The capacity for certain organic compounds to self-replicate is considered to be a fundamental requirement in the initial formation of cells
-
This allows for chemical processes to be reproduced in successive cells as the necessary organic compounds are effectively inherited
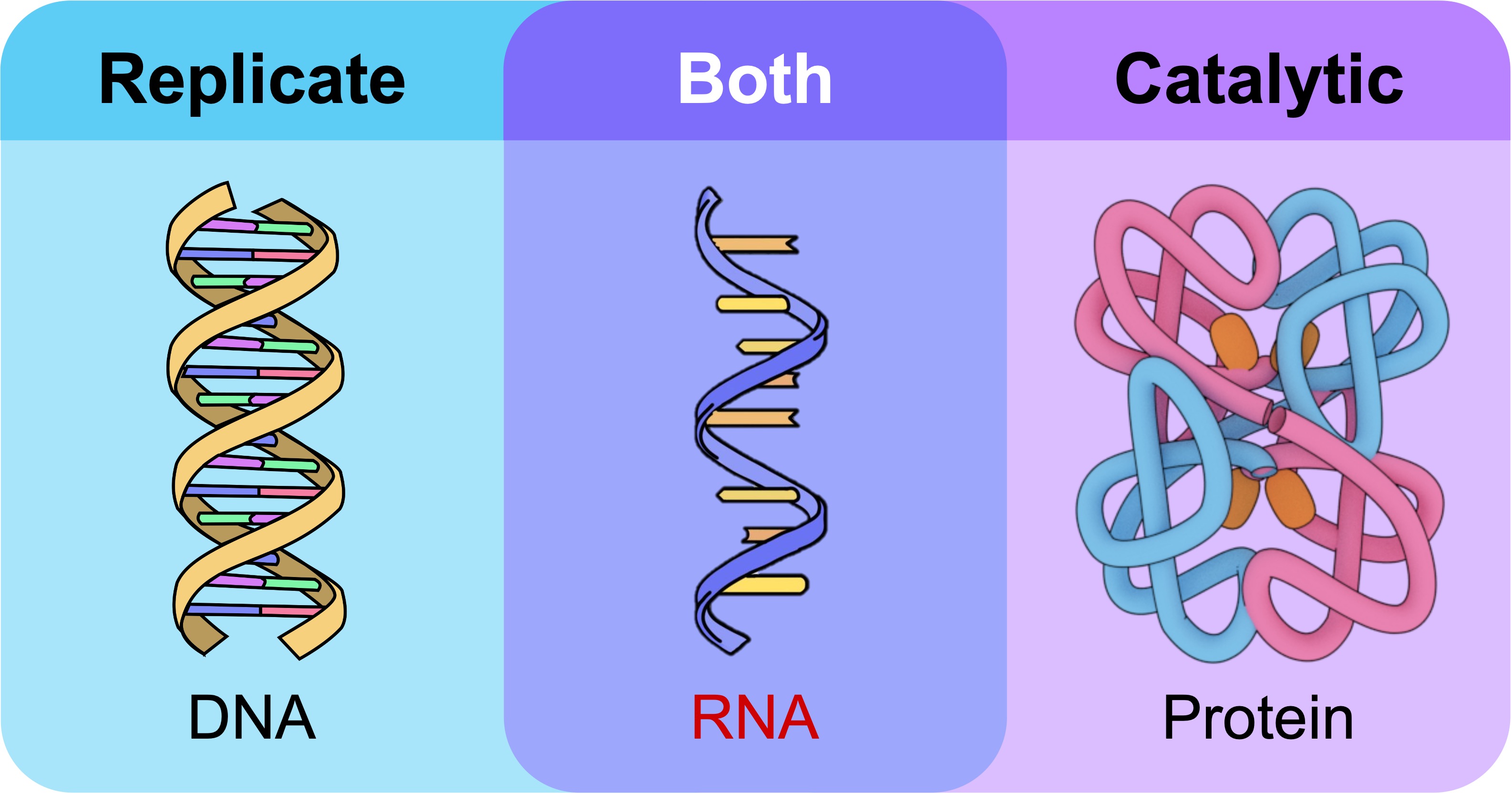
RNA is presumed to have been the first genetic material due to two key qualities:
-
RNA can self replicate: RNA can form a complementary template sequence that can be used to produce new identical molecules
-
RNA can act as a catalyst: RNA catalysts (ribozymes) are involved in peptide bond formation and intron splicing in modern cells
RNA is the only molecule that is capable of both self-replication and catalytic functioning, but has since been superseded:
-
DNA, through its superior chemical stability (double helical structure), has taken over as the data storage form
-
Protein, through its greater variability (20 amino acids as opposed to 4 bases), has taken over as the catalytic form
RNA remains as a transitional form between DNA and protein in modern cells, suggestive of its multi-faceted origins
RNA Hypothesis