RNA Synthesis
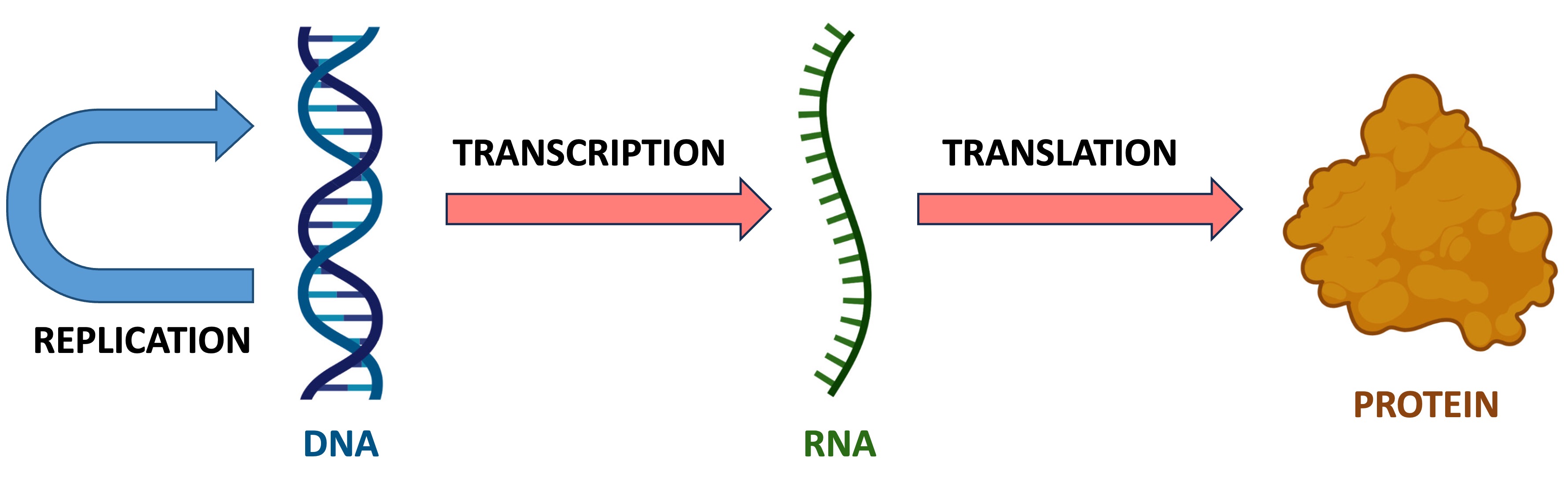
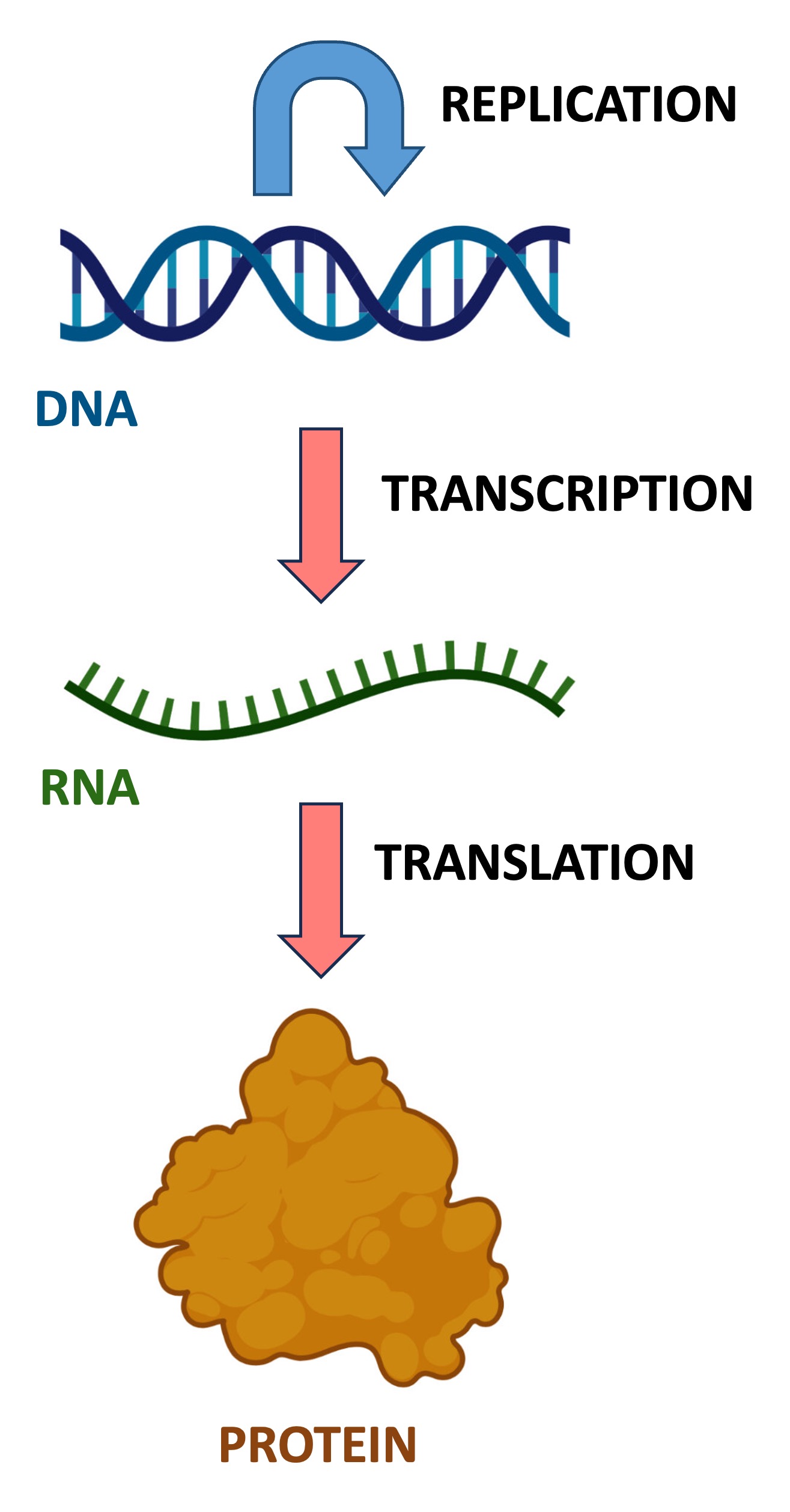
The central dogma of molecular biology explains the flow of genetic information within a cell
-
DNA is the master set of instructions for all cell activities (i.e. the genetic ‘blueprint’ of the cell)
-
RNA (messenger RNA) is a temporary ‘photocopy' of specific genetic instruction (gene)
-
Proteins are the products created from these instructions that carry out the cellular functions
DNA → RNA
The genetic instructions of a cell are stored within the sequences of double-stranded DNA molecules
-
Double stranded molecules are more stable and help to ensure the conservation of the base sequence
-
In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is stored within a membrane-bound nucleus – providing a further level of protection for the master sequence
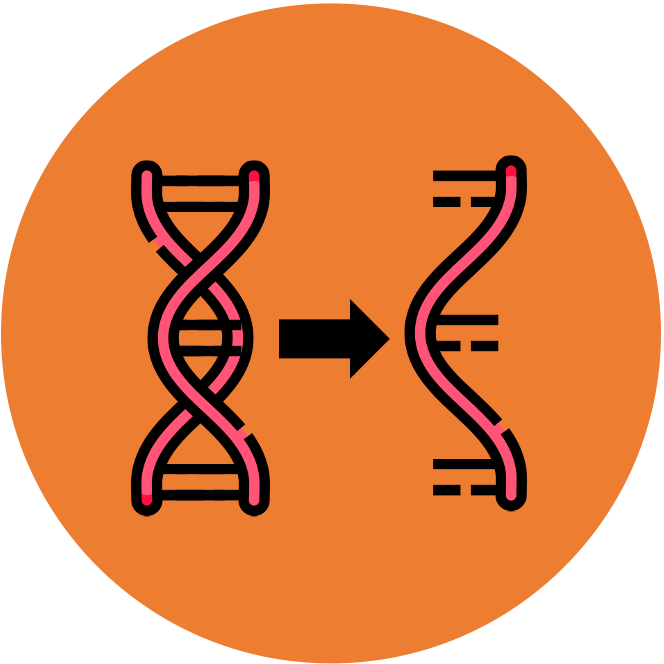
When a genetic instruction needs to be expressed, a single-stranded RNA copy of that particular sequence is made (via transcription)
-
The RNA molecule is a temporary copy that is complementary to the sequence on the template strand of DNA
-
Once synthesised, the RNA will interact with ribosomes in the cytoplasm, which are responsible for synthesising proteins according to the genetic instructions
Central Dogma