RNA Processing
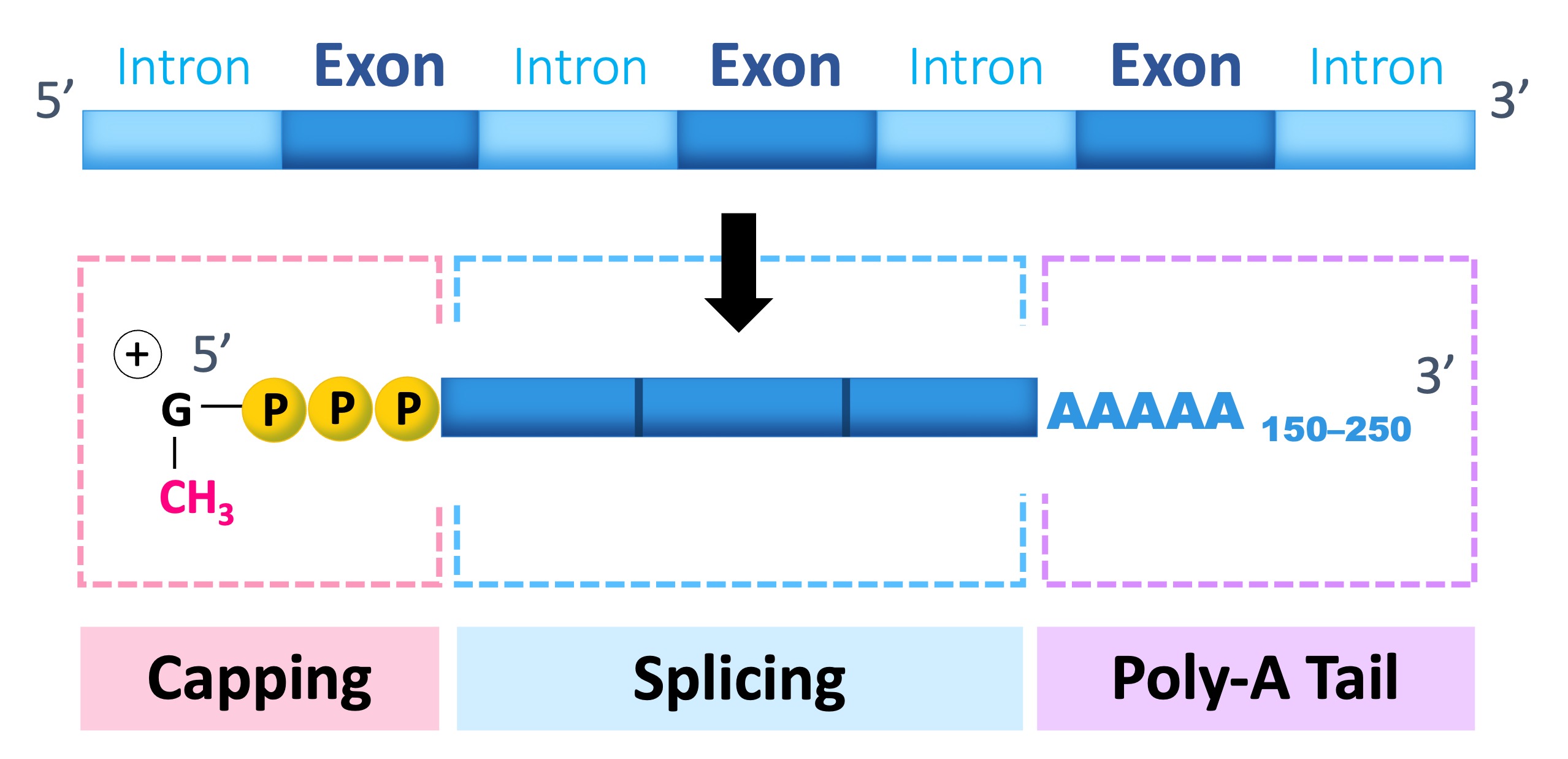
In eukaryotes, there are three post-transcriptional events that must occur in order to form messenger RNA (mRNA)
-
Prokaryotic cells do not undertake these events due to their lack of compartmentalisation and more compact genomes
Capping
-
Capping involves the addition of a methyl group to the 5’-end of the transcribed RNA
-
The methylated cap provides protection against degradation by exonucleases and also allows the transcript to be recognised by the cell’s translational machinery (nuclear export proteins and ribosome)
Polyadenylation
-
Polyadenylation describes the addition of a long chain of adenine nucleotides (a poly-A tail) to the 3’-end of the transcript
-
The poly-A tail improves the stability of the RNA transcript and facilitates its export from the nucleus
Splicing
-
Within eukaryotic genes are non-coding sequences called introns, which must be removed (via splicing) prior to forming mature mRNA
-
The coding regions are called exons and these are fused together when introns are removed to form a continuous sequence
-
In other words, introns are intruding sequences whereas exons are expressing sequences
-
RNA Processing