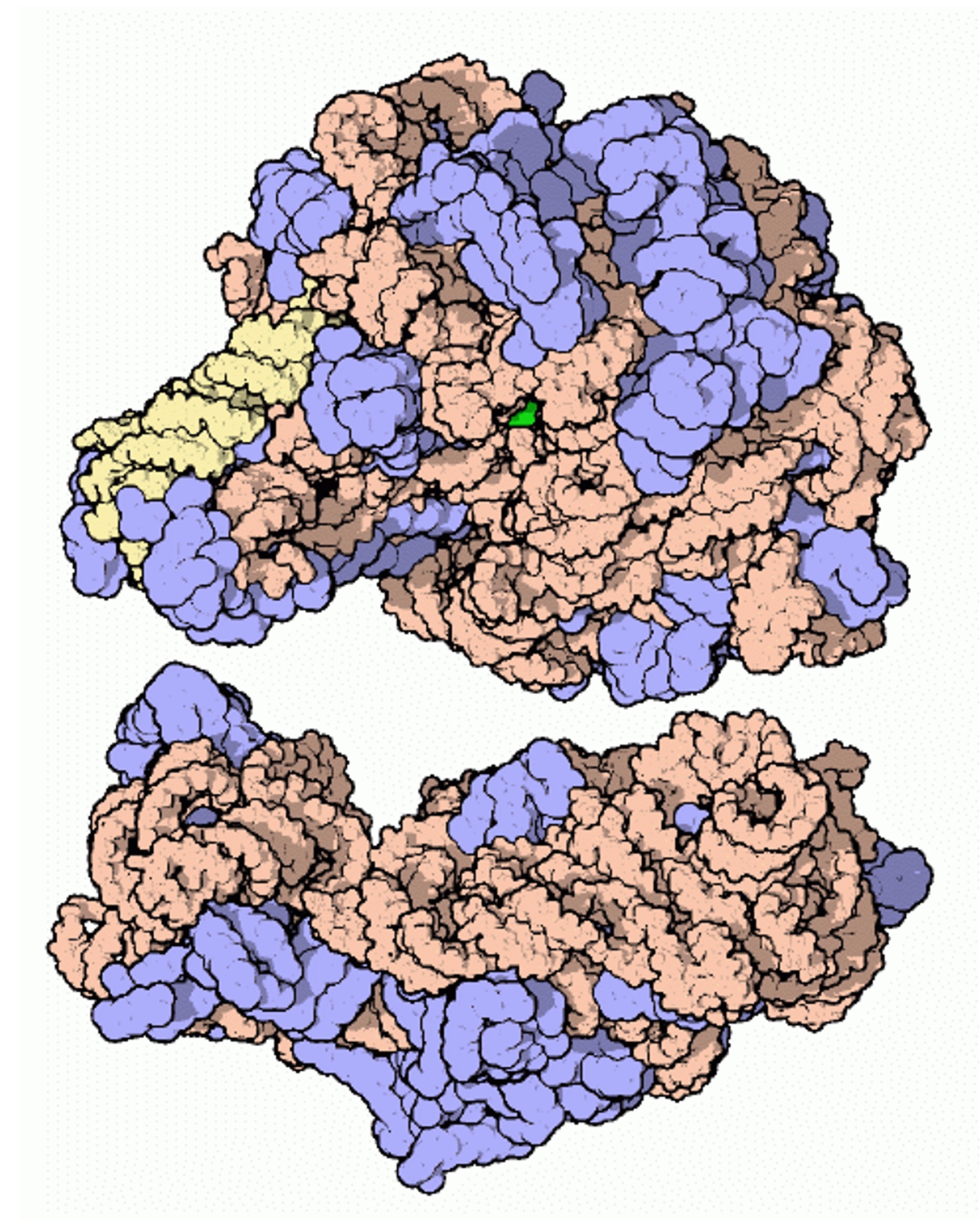
Ribosomes
The ribosome is the site of polypeptide synthesis (protein assembly) within the cell
-
It is composed of protein (provides stability) and ribosomal RNA (responsible for catalytic activity)
-
Eukaryotic ribosomes are larger in size (80S) compared to prokaryotic ribosomes (70S)
Ribosomes are comprised of two distinct subunits:
-
The small subunit is responsible for binding to mRNA, while the large subunit binds to tRNA
-
When the two subunits form a complex, translation of an mRNA sequence can occur
In eukaryotes, ribosomes can either be located freely within the cytosol or embedded within the rough endoplasmic reticulum
-
Free ribosomes synthesise proteins for use within the cytosol (i.e. intracellular proteins)
-
Ribosomes embedded within the rough ER synthesise proteins that will be packaged into vesicles and transported to other organelles
-
If the vesicles are transported to the Golgi apparatus, then the proteins will be secreted from the cell for extracellular use
Structure of the Ribosome

Simple Diagram