Protein Synthesis
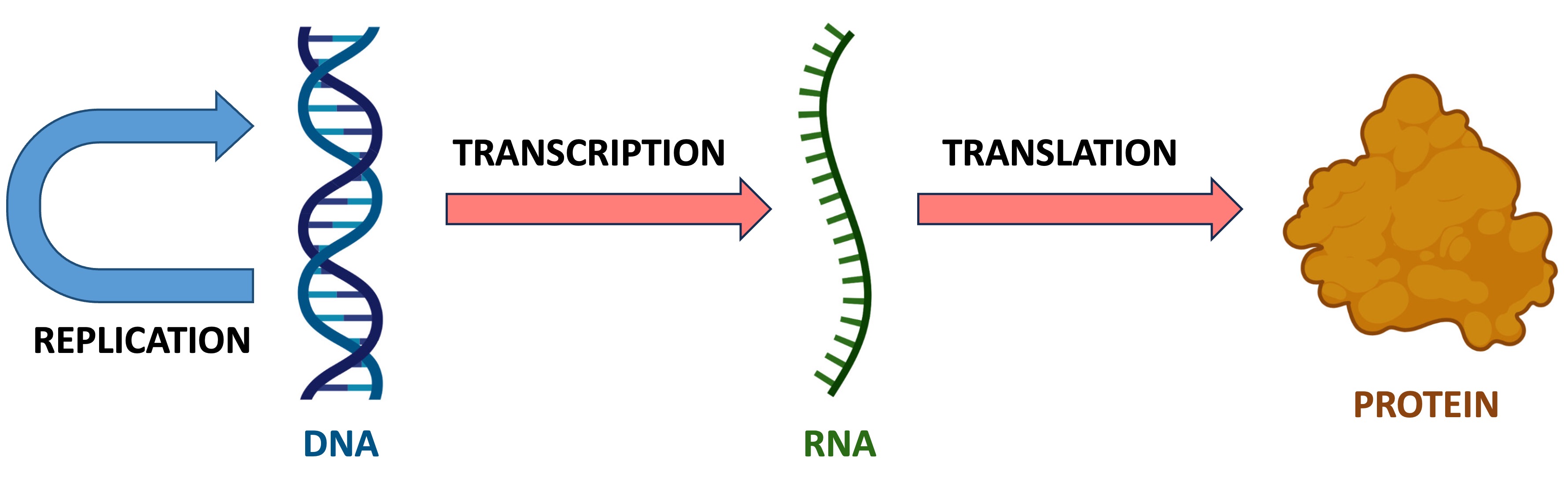
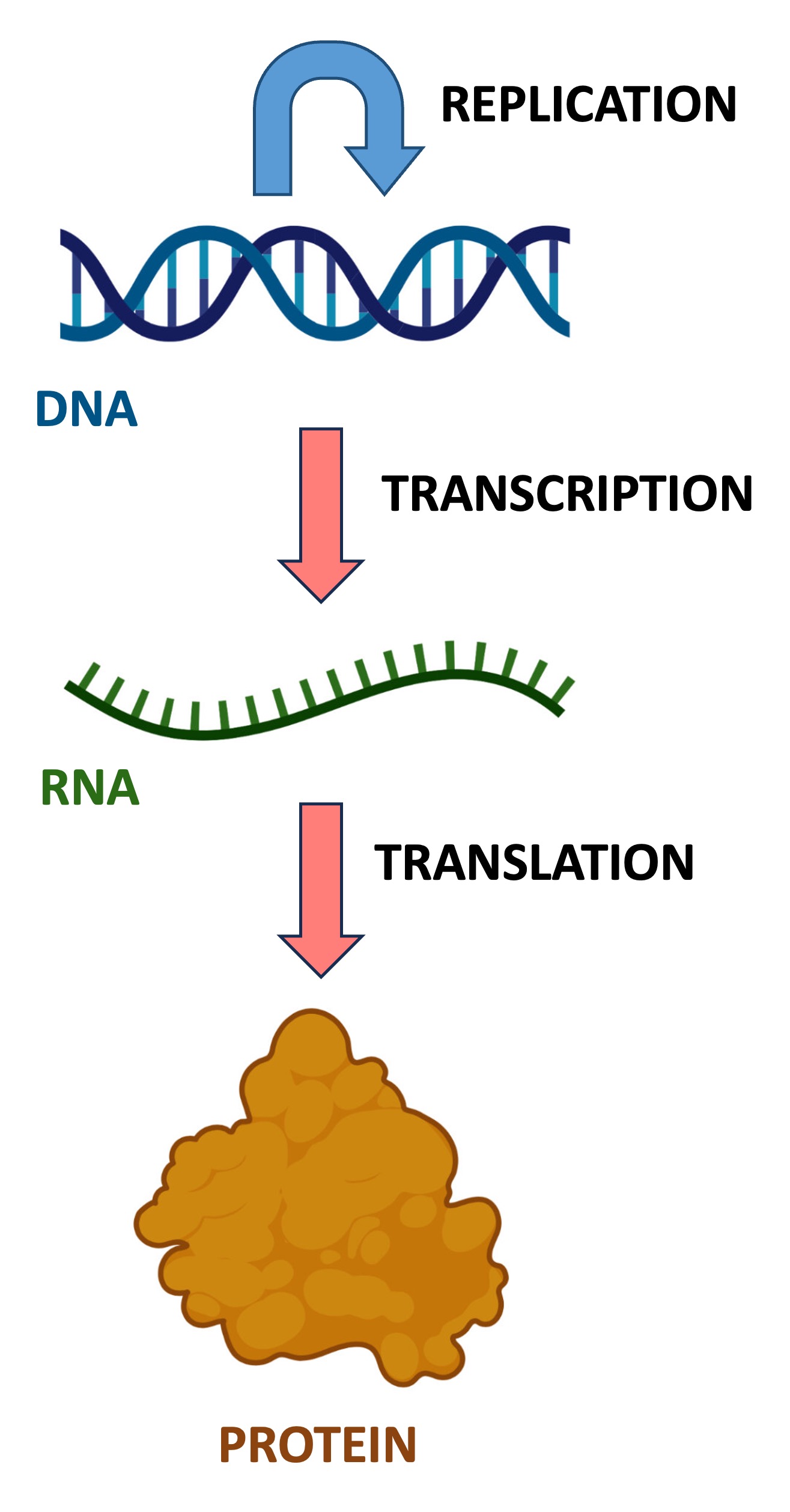
The central dogma of molecular biology explains the flow of genetic information within a cell
-
DNA is the master set of instructions for all cell activities (i.e. the genetic ‘blueprint’ of the cell)
-
RNA (messenger RNA) is a temporary ‘photocopy' of specific genetic instruction (gene)
-
Proteins are the products created from these instructions that carry out the cellular functions
RNA → Protein
The genetic instructions of a cell encode the amino acid sequences of polypeptide chains (proteins)
-
DNA instructions can be selectively transcribed into mRNA sequences to allow for the variable expression of proteins
-
The differential expression of proteins within a cell will determine its functional activity
The process of protein synthesis is called translation and occurs at the ribosomes
-
Proteins can be synthesised by cytosolic ribosomes or by ribosomes embedded to the rough endoplasmic reticulum
-
Cytosolic ribosomes produce intracellular proteins, while the rough ER synthesises proteins for specific organelles or extracellular use
Central Dogma