Polymers
Polymers
Polymers are large macromolecules composed of smaller repeating subunits (called monomers) via condensation reactions
-
Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides are joined together to form polysaccharides via glycosidic linkages
-
Nucleic Acids: Nucleotides are connected by phosphodiester bonds to form polynucleotide chains (DNA or RNA)
-
Proteins: Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds to form polypeptide chains (proteins can possess multiple chains)
-
Lipids: Do not possess monomers but fatty acid chains can be connected by ester linkages to form triglycerides and phospholipids
Types of Polymers
Carbohydrates
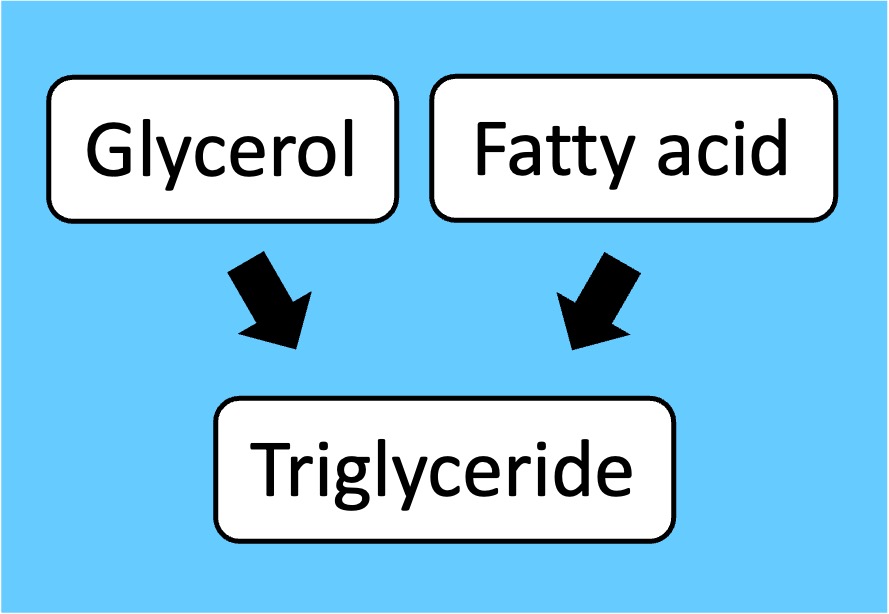
Lipids*
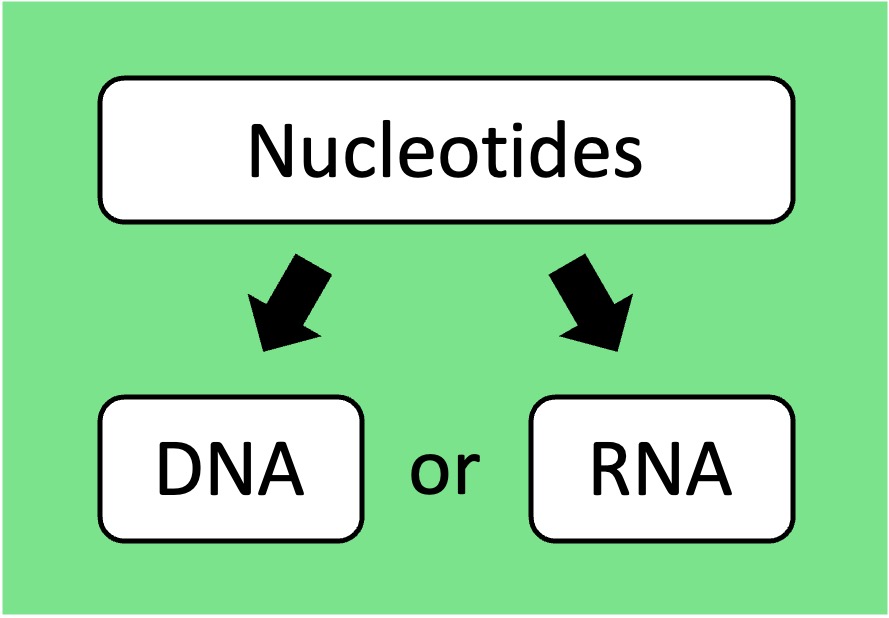
Nucleic Acids
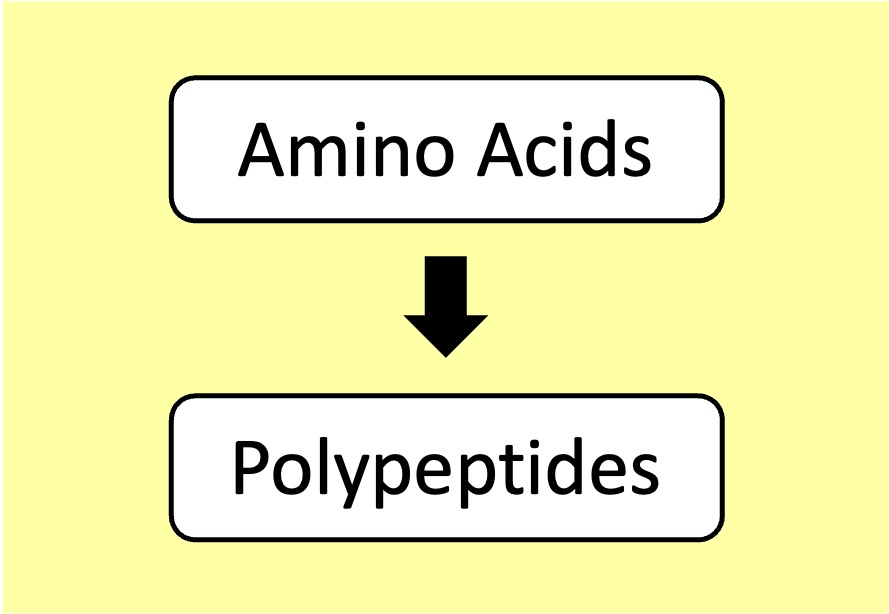
Proteins
Digestion
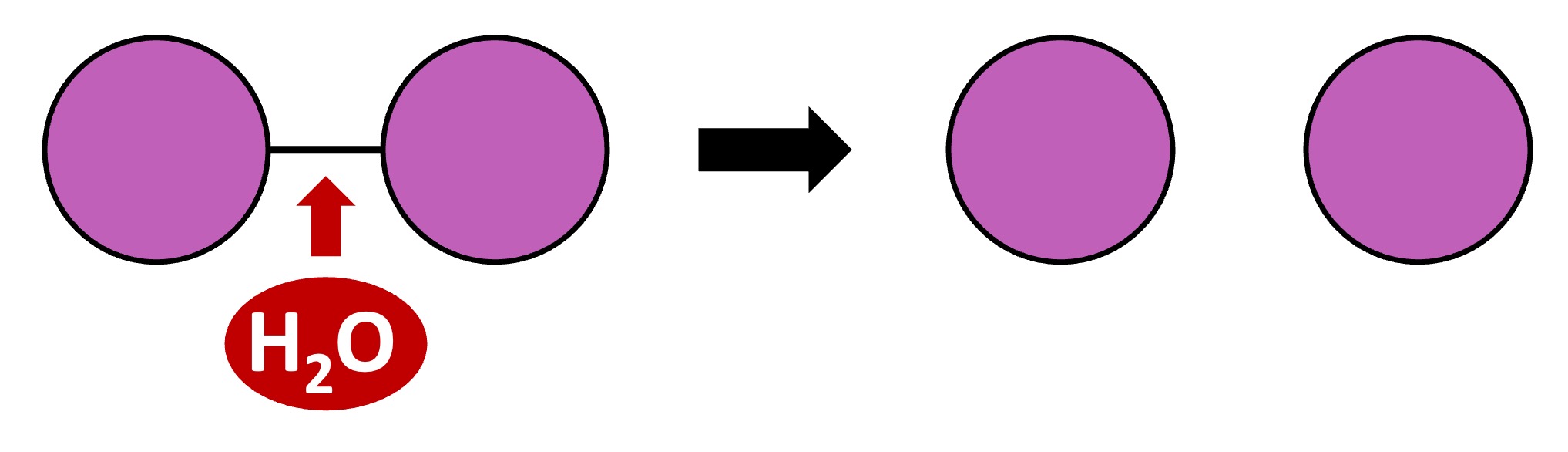
Polymers can be broken down into their monomeric subunits via hydrolysis reactions
-
A water molecule is split to provide the -H and -OH groups required to break the covalent bond between two monomers
Hydrolysis Reaction
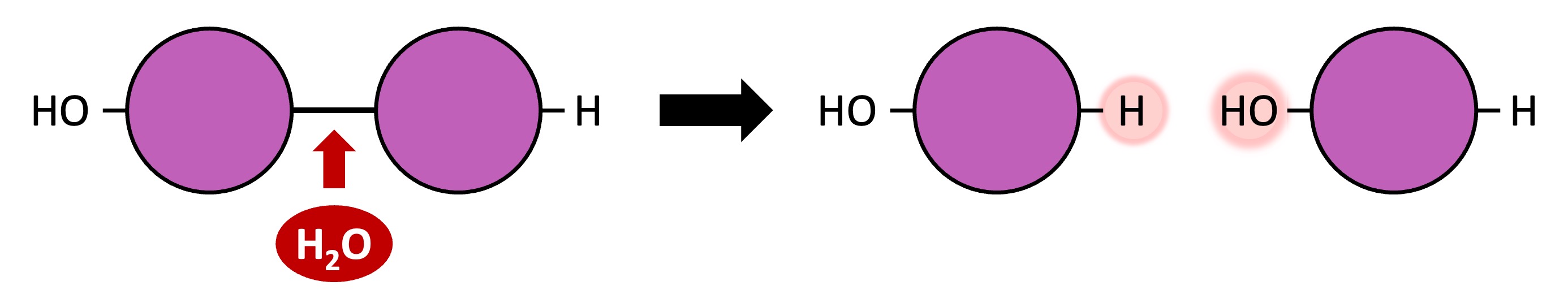
Hydrolysis Reaction