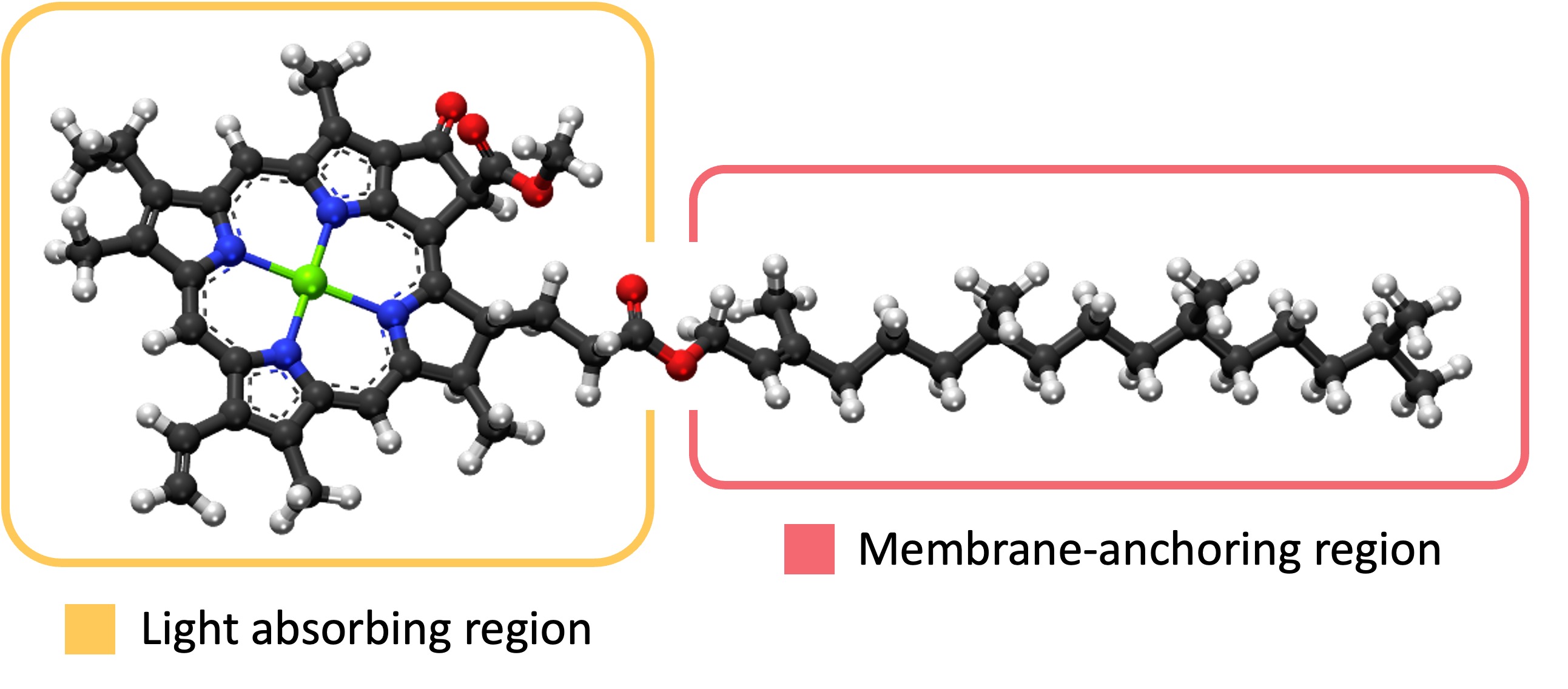
Pigments
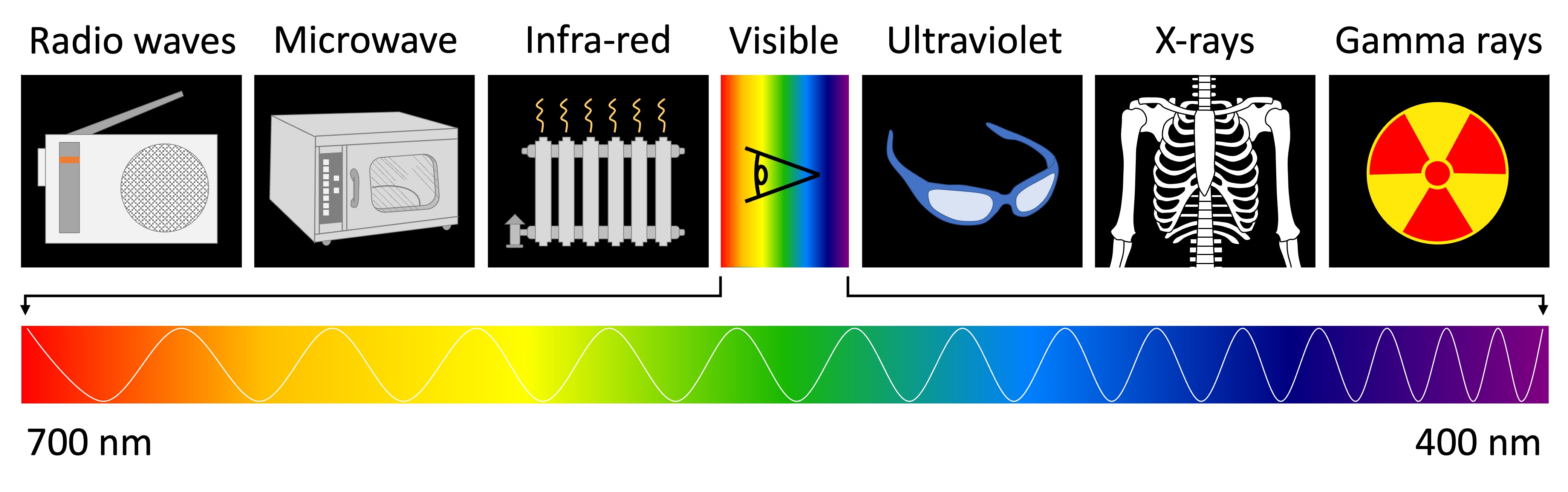
Light Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum comprises the full range of all types of radiation energy (travels through space in particles or waves)
-
The sun emits its peak power in the visible region of this spectrum (white light = 400nm – 700nm)
-
Colours represent different wavelengths of visible light and range from red (longest) to violet (shortest)
-
The colours of the visible spectrum (from longest to shortest) are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet



Pigment Molecules
In photosynthetic organisms, the absorption of light is mediated by specific pigment molecules (e.g. chlorophyll)
-
Each pigment molecule contains electrons at discrete and specific energy levels (according to the pigment’s atomic configuration)
-
These electrons can absorb light at specific frequencies (or wavelengths) and become energised and delocalised (ionised)
-
The energy from these excited electrons can be harnessed by the cell to make chemical energy (ATP – via photophosphorylation)