Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which cells synthesise organic compounds (e.g. glucose) from inorganic molecules (CO2 and H2O) in the presence of sunlight
-
This process requires a photosynthetic pigment (chlorophyll) and can only occur in certain organisms (plants, certain bacteria)
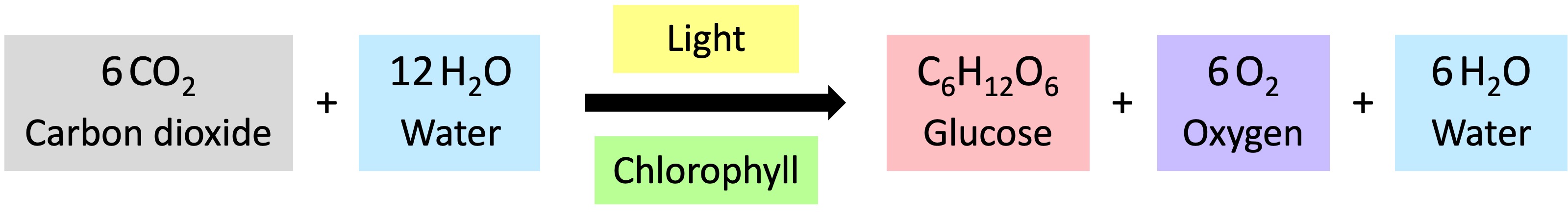
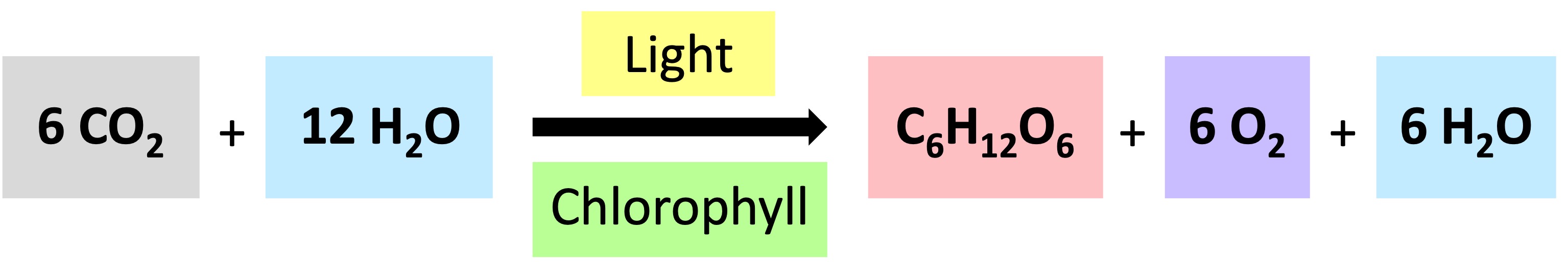

Photosynthetic organisms contain pigments that capture the light energy from the sun to create chemical energy (ATP)
-
This chemical energy can then be used to synthesise organic compounds (e.g. glucose) via anabolic reactions
-
The organic compounds can either contribute to cellular structure or be catabolically digested as an energy source (cell respiration)