Pathogens
A pathogen is a disease causing agent that disrupts the normal physiology of the infected organism
-
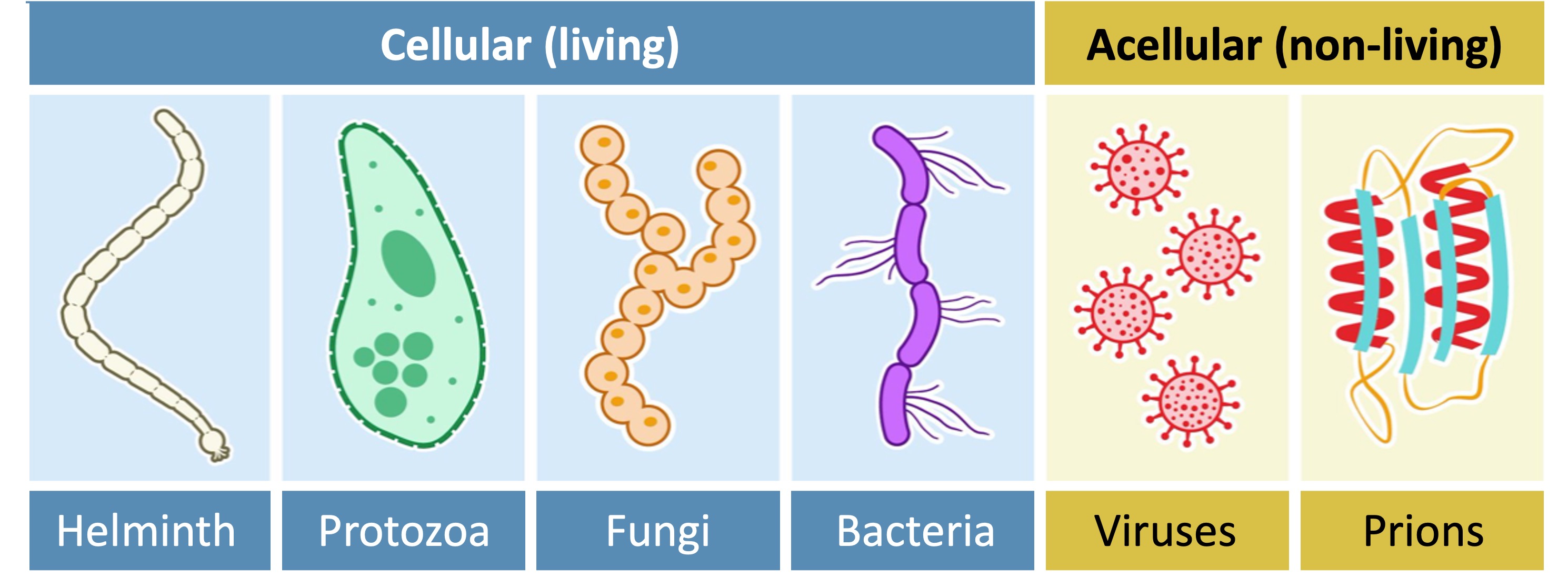
Pathogens can be cellular (e.g. fungi, protozoa, bacteria) or acellular (viruses and prions)
Cellular pathogens typically cause disease by acting as parasites – cannabilising the host resources and disturbing homeostasis
-
Bacteria: Prokaryotic cells that can reproduce quickly and may compete with host cells for space and nutrition
-
Pathogenic bacteria can potentially cause disease by releasing damaging compounds (exotoxins or endotoxins)
-
-
Fungi: Fungal infections typically affect body surfaces and are more common in tropical regions (moist environments)
-
Fungi can be either unicellular (yeasts) or multicellular (moulds) and most pathogenic species are opportunistic (require susceptibility)
-
-
Protozoa: A diverse group of unicellular eukaroytes that sometimes rely on host organisms to complete part of their life cycle
-
Helminths: Multicellular worms that live within, and feed on, living hosts (they are endoparasites)
Acellular pathogens consist of non-living compounds that are capable of replication (resulting in uncontrolled proliferation)
-
Viruses: A virus typically consists of an inner core of nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat (capsid)
-
Viruses invade and then commandeer host cells, using the hijacked cellular machinery to reproduce and spread
-
-
Prions: An infectious protein that has folded abnormally into a structure capable of causing disease
-
Prions can cause normally folded proteins to refold into the abnormal form (which then aggregate to form amyloid fibres)
-
Types of Pathogens