Osmotic Effects
No Cell Wall
In cells that lack a cell wall, uncontrolled osmosis will have negative effects with regards to cell viability:
-
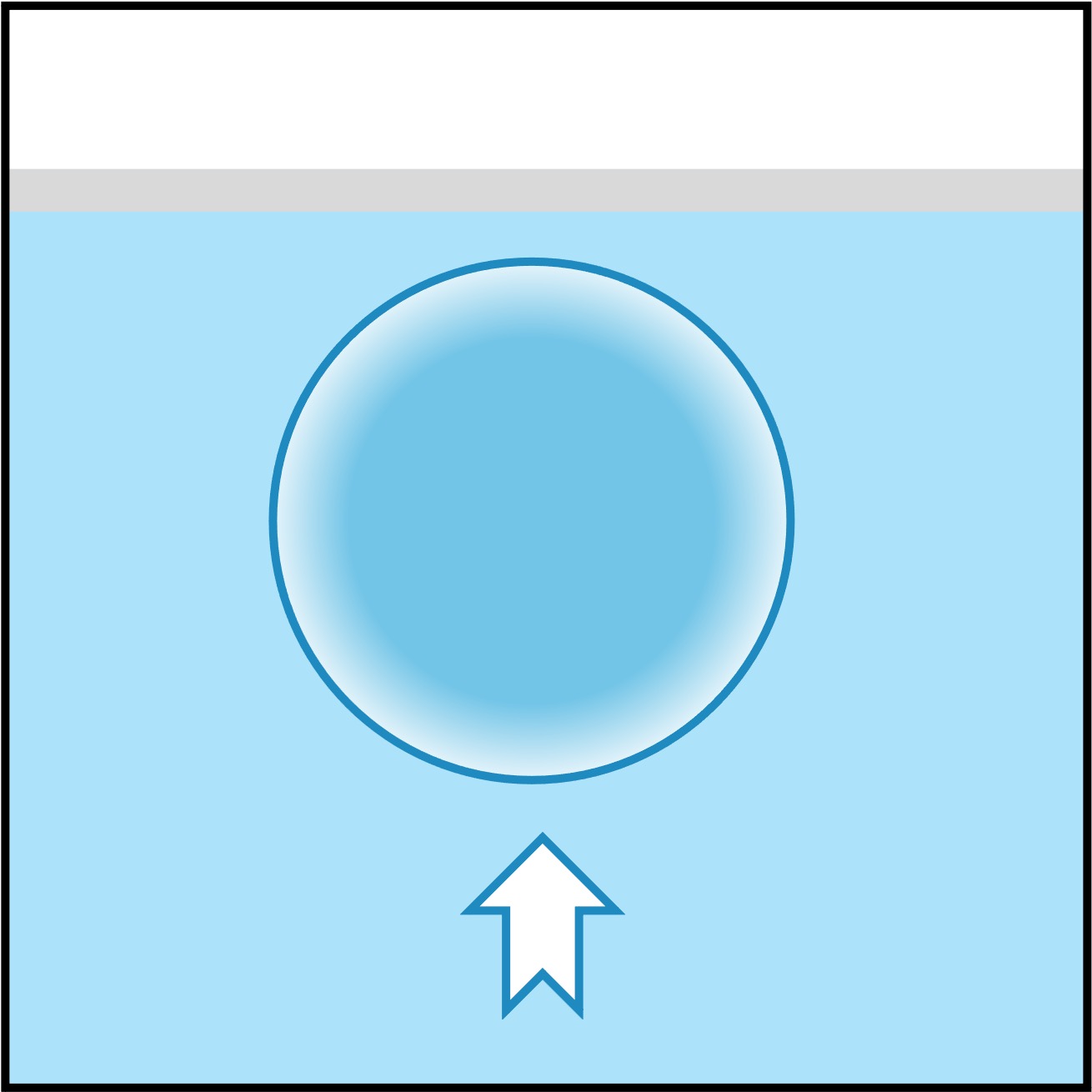
In hypertonic solutions, water will leave the cell causing it to shrivel (crenation)
-
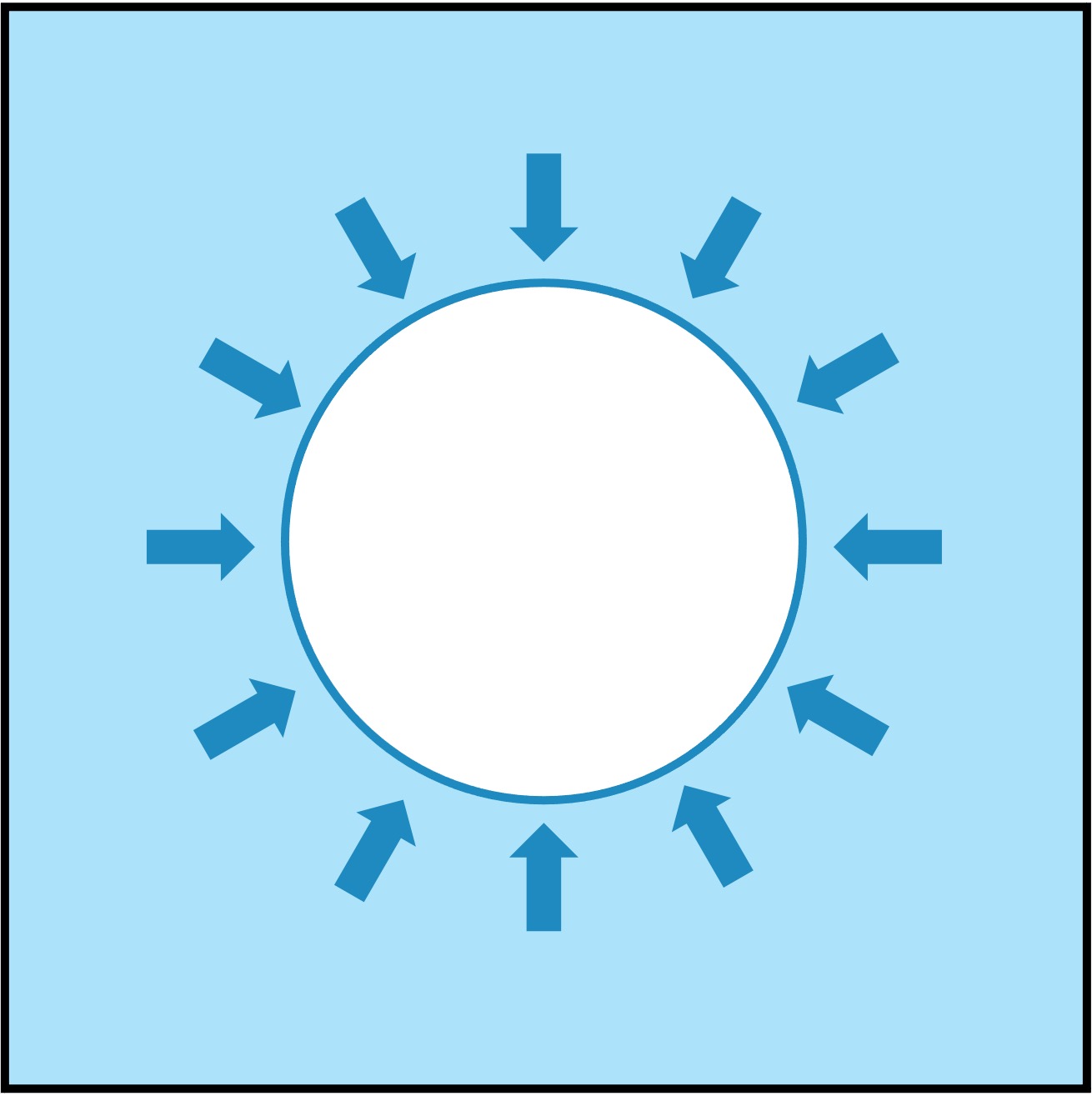
In hypotonic solutions, water will enter the cell causing it to swell and potentially burst (lysis)
-
In multicellular organisms, it is therefore important that tissue fluid remains isotonic to prevent harmful changes
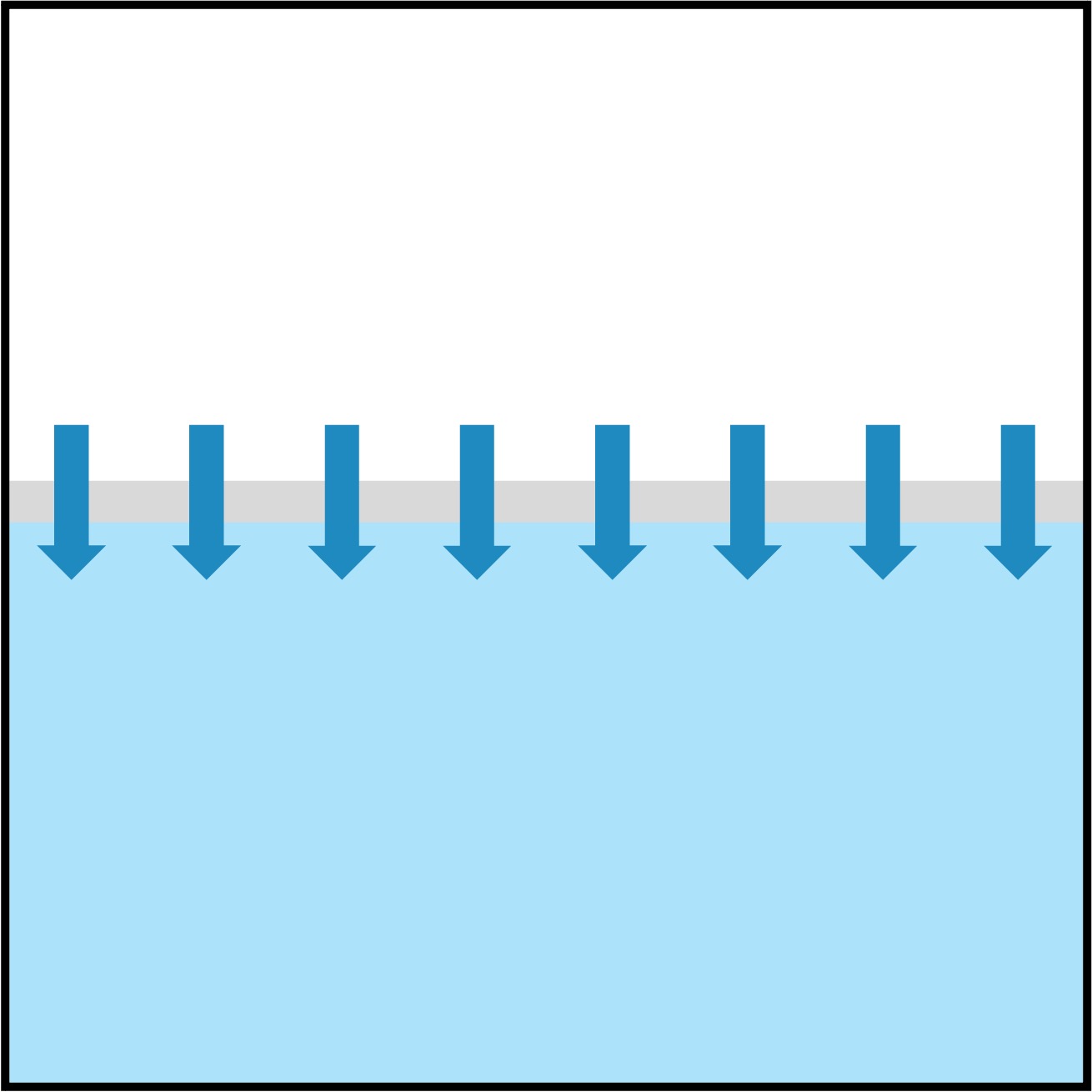
Osmosis in Erythrocytes
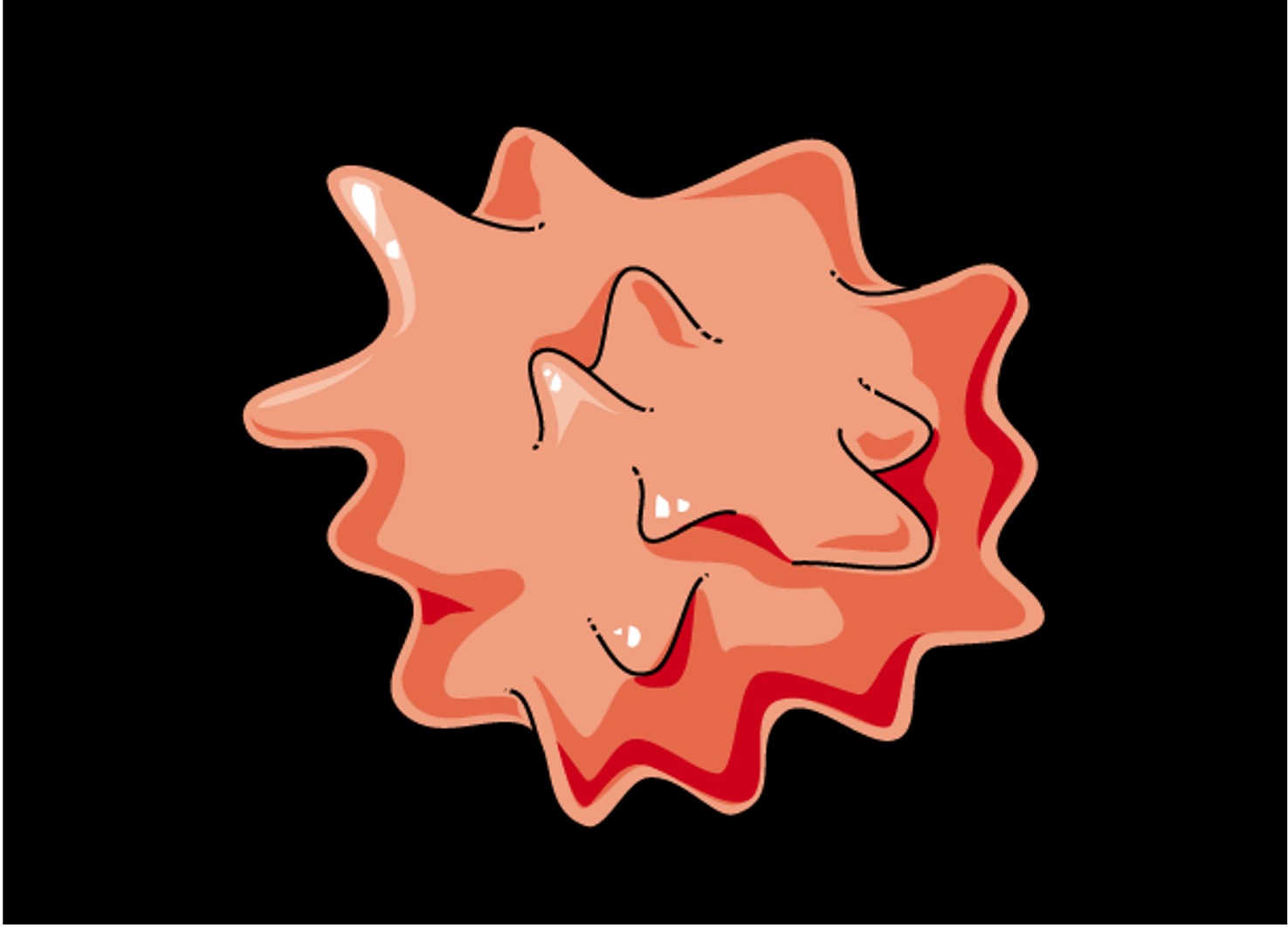
Hypertonic
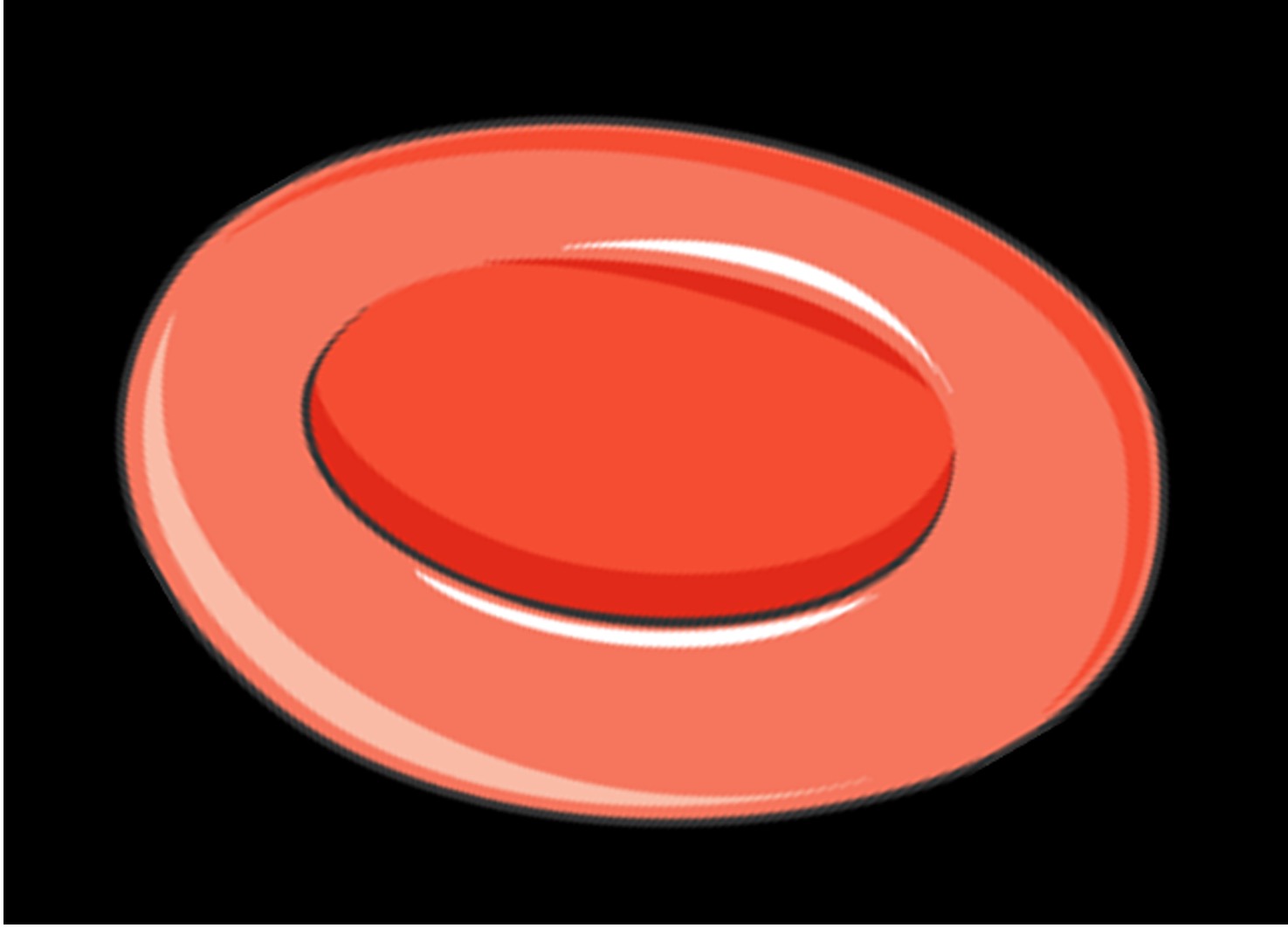
Isotonic
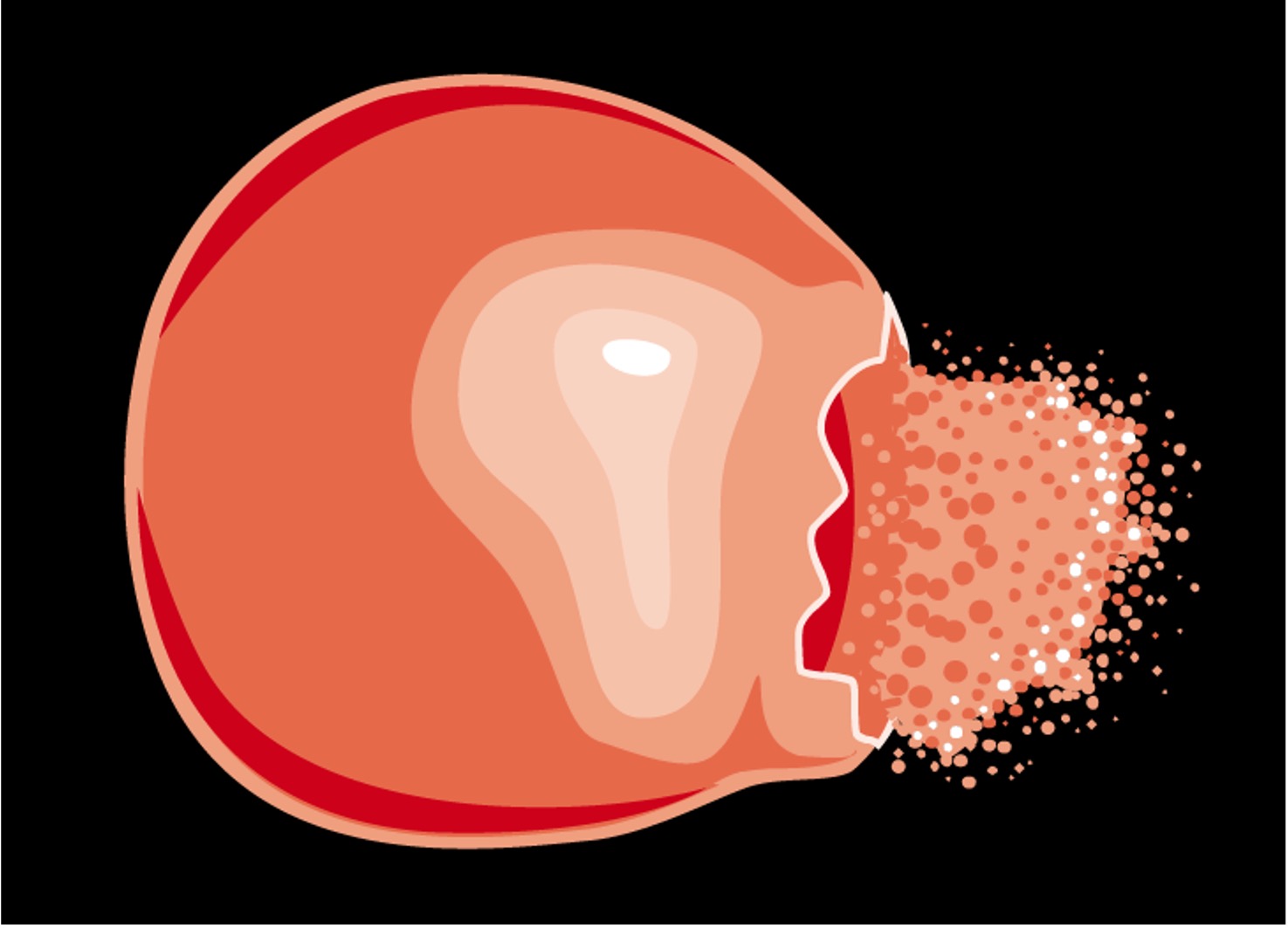
Hypotonic
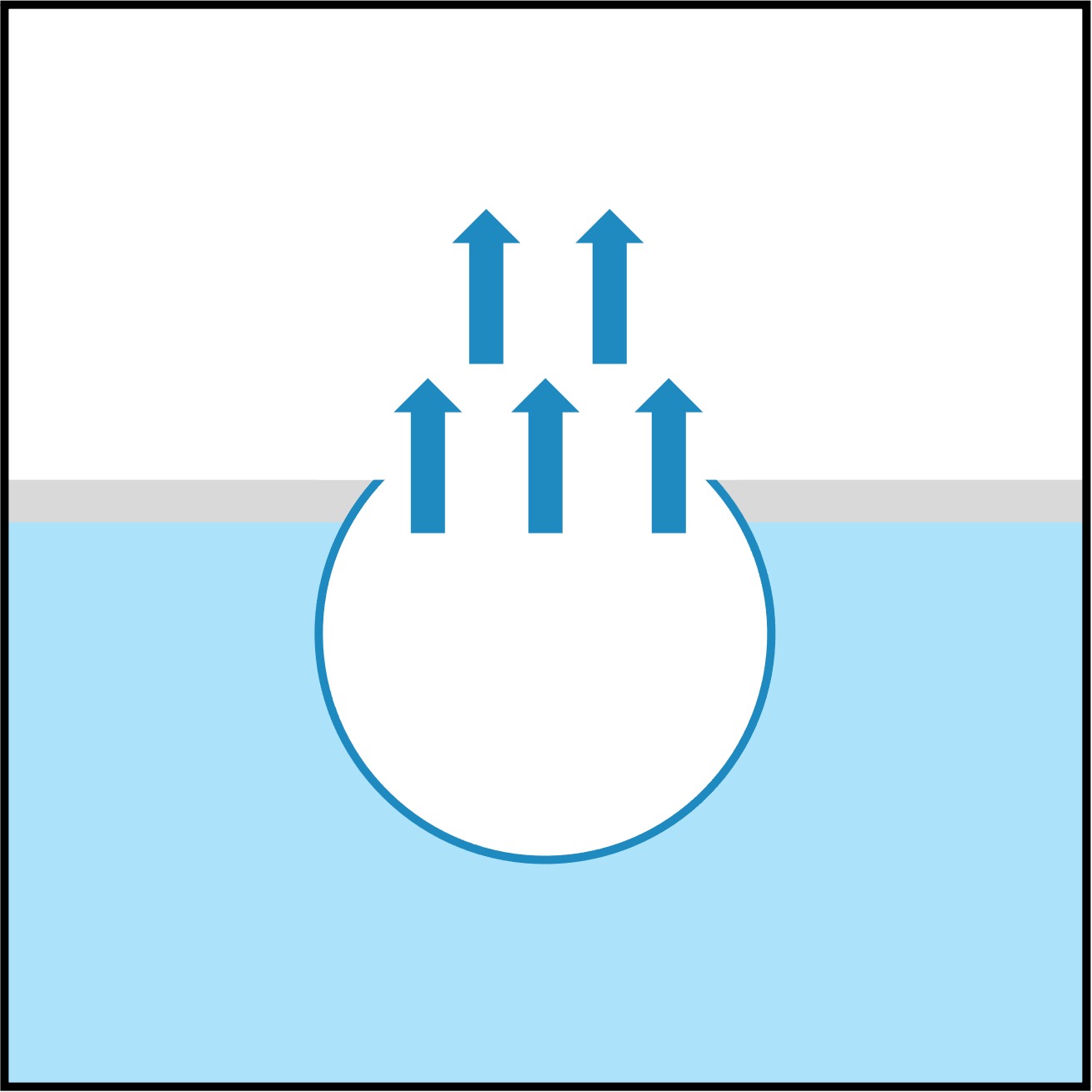
Contractile Vacuoles
Unicellular organisms (such as protists) may possess a contractile vacuole to regulate the osmotic conditions within the cell
-
Excess water is absorbed into the contractile vacuole, causing it to swell (this is called diastole)
-
The vacuole then fuses to the plasma membrane and contracts, expelling the water (this is systole)
-
The amount of water expelled and the rate of contractions are determined by the extracellular conditions

Water enters cell (osmosis)

Water moves into vacuole

Vacuole goes to membrane

Contraction expels water
With a Cell Wall
In plants and fungi, the effects of uncontrolled osmosis are moderated by the presence of an inflexible cell wall
-
In hypertonic solutions, the cytoplasm will shrink (plasmolysis) but the cell wall will maintain a structured shape
-
In hypotonic solutions, the cytoplasm will expand but be unable to rupture within the constraints of the cell wall (turgor)
-
Excess water may be stored in a large, central vacuole that has its own membrane called the tonoplast
Osmosis in Plants
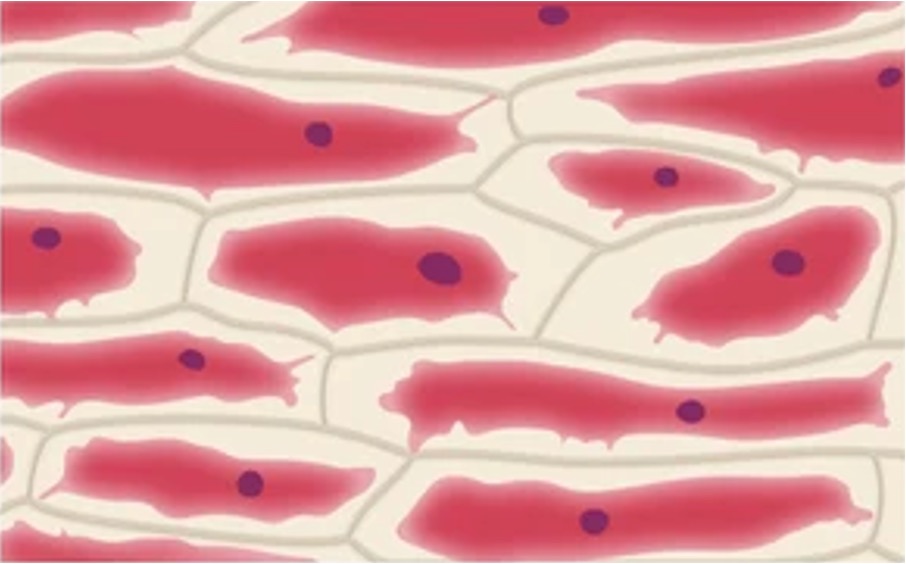
Hypertonic
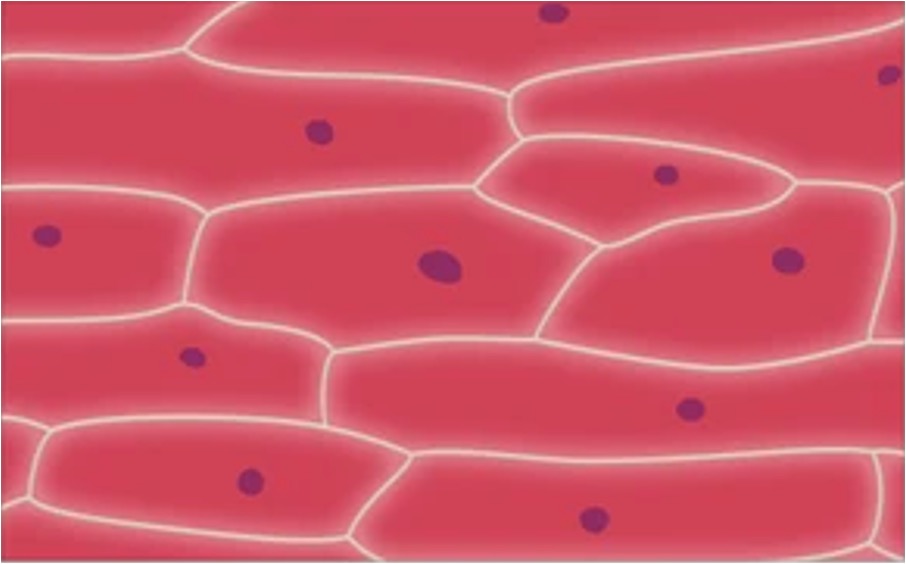
Hypotonic
Isotonic Solutions
Tissues or organs to be used in medical procedures must be kept in solution to prevent cellular dessication
-
This solution must share the same osmolarity as the tissue / organ (i.e. isotonic) in order to prevent osmosis from occurring
Isotonic solutions can also be delivered intravenously to restore fluid levels to patients with hypovolemia
-
Hypovolemia (low blood plasma levels) can occur due to dehydration or trauma (excessive blood loss)