Organelles
Organelles are the discrete subunits of a cell that are adapted to perform specific functions
-
The plasma membrane and ribosomes are universal organelles that are present in every living cell
-
Complex cells (eukaryotes) possess additional membrane-bound organelles that provide further functionality
Types of Organelles
-
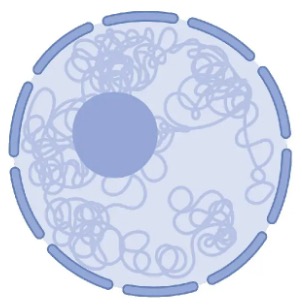
Nucleus
-

-
The nucleus is a double membrane structure with pores that stores the genetic material (DNA)
-
Within the nucleus, a specific region called the nucleolus is responsible for ribosome assembly
-
-
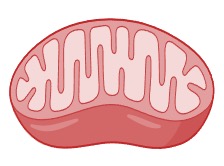
Mitochondria
-

-
Mitochondria are responsible for ATP production via the process of aerobic cell respiration
-
It has an inner membrane that is highly folded into cristae in order to increase the SA:Vol ratio
-
-
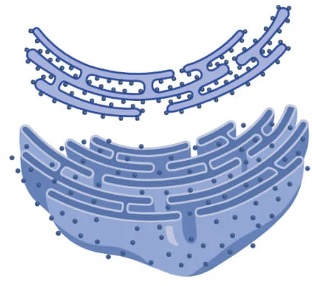
Endoplasmic Reticulum
-

-
The ER is a membranous network that synthesises and transports materials via vesicles
-
The smooth ER synthesises lipids, while the rough ER synthesises proteins (via ribosomes)
-
-
Golgi Complex
-

-
The golgi apparatus is an assembly of folded membranes responsible for material secretion
-
Material is sorted, stored, modified and exported from the cell within vesicles (exocytosis)
-
-
Vesicles
-

-
Vesicles are membranous containers involved in the transport and storage of materials
-
Peroxisomes are involved in the oxidation of lipids and the digestion of toxic metabolites
-
Lysosomes are responsible for the breakdown of cellular wastes and pathogenic debris
-
Vacuoles are comparatively larger containers that store excess fluid and regulate pH
-
-
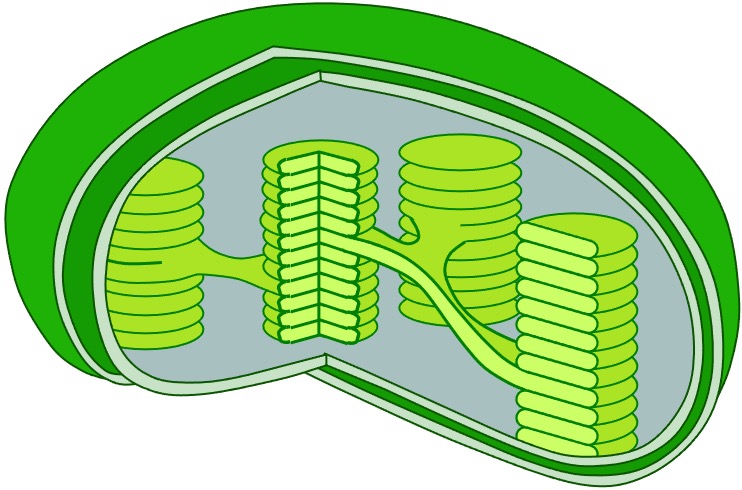
Chloroplast (plants)
-

-
An organelle responsible for photosynthesis (converting light energy into chemical energy)
-
Chloroplasts use the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll to absorb and utilise light energy
-
-
Centrosome (animals)
-

-
Centrosomes function as microtubule-organising centres composed of paired centrioles
-
They contribute towards cell division in animal cells (plants and fungi use other structures)
-
-
Nucleus
-

-
Double membrane structure that stores genetic material / DNA
-
A nucleolus is a dark region in a nucleus that makes ribosomes
-
-
Mitochondria
-

-
Responsible for ATP production (via aerobic cell respiration)
-
The inner membrane is highly folded to increase SA:Vol ratio
-
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum
-

-
A membranous network that transports materials via vesicles
-
Smooth ER synthesises lipids ; rough ER synthesises proteins
-
-
Golgi Complex
-

-
An assembly of folded membranes used for material secretion
-
Material is sorted, stored, modified and exported from the cell
-
-
Vesicles
-

-
Membrane sacs involved in transport and storage of material
-
Peroxisomes are involved in the digestion of toxic metabolites
-
Lysosomes are responsible for breaking down cellular wastes
-
Vacuoles are comparatively larger sacs that store excess fluid
-
-
Chloroplast (plants)
-

-
Structure responsible for photosynthesis (in plant cells only)
-
Uses the pigment chlorophyll to absorb and utilise sunlight
-
-
Centrosome (animals)
-

-
Microtubule-organising centre composed of paired centrioles
-
Contributes towards mitotic cell division (in animal cells only)
-
Exceptions
Certain cellular components are not considered to be organelles:
-
Cell walls are not considered organelles as they are extracellular components
-
Cytoskeletons and cytosol are categorised as structural elements as opposed to distinctive organelles