Nucleosomes
In eukaryotic organisms, DNA is packaged into a compact structure for more effective storage within the nucleus
-
The DNA is associated with histone proteins to form a condensed complex known as a nucleosome
Nucleosome Structure
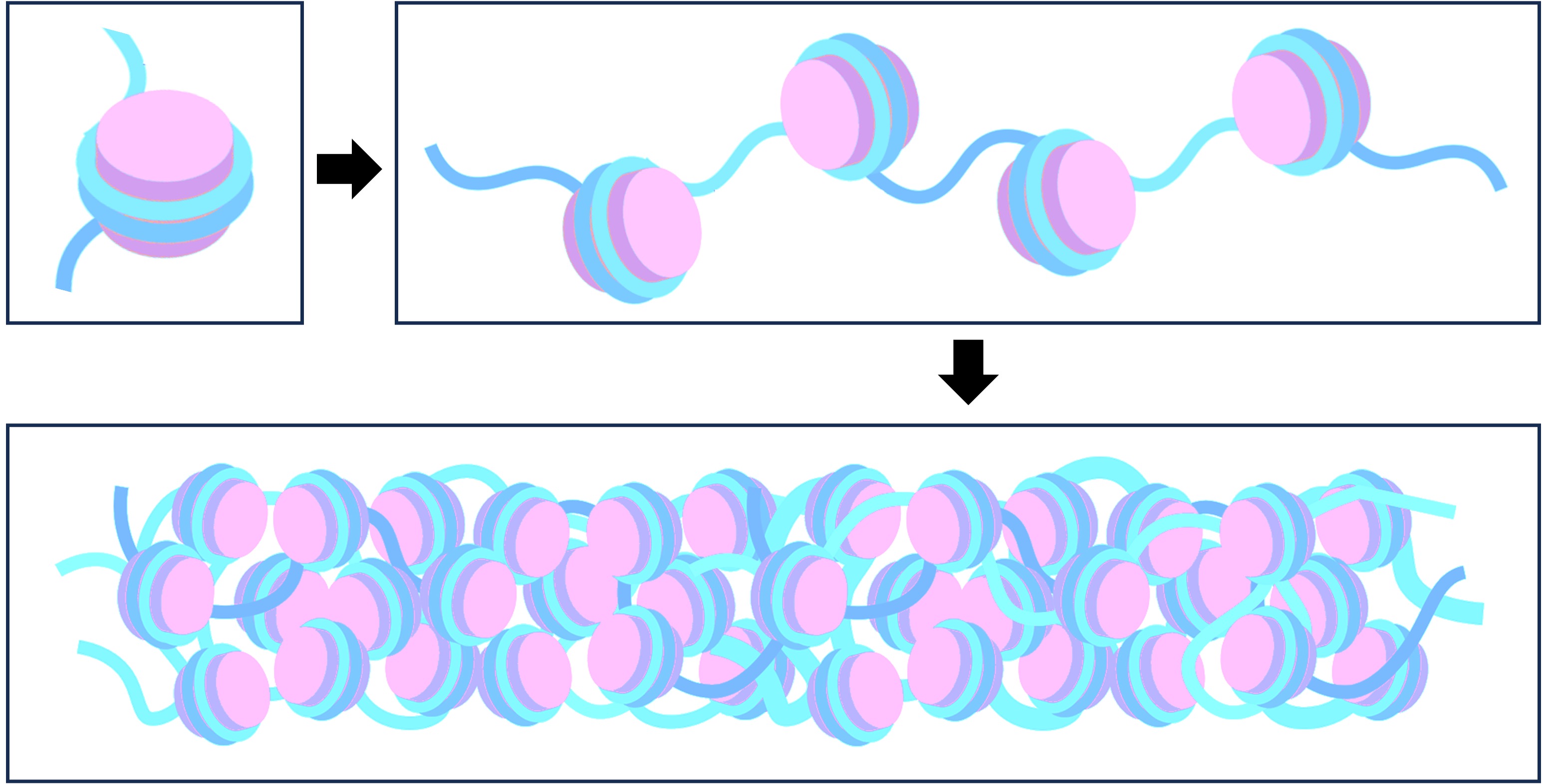
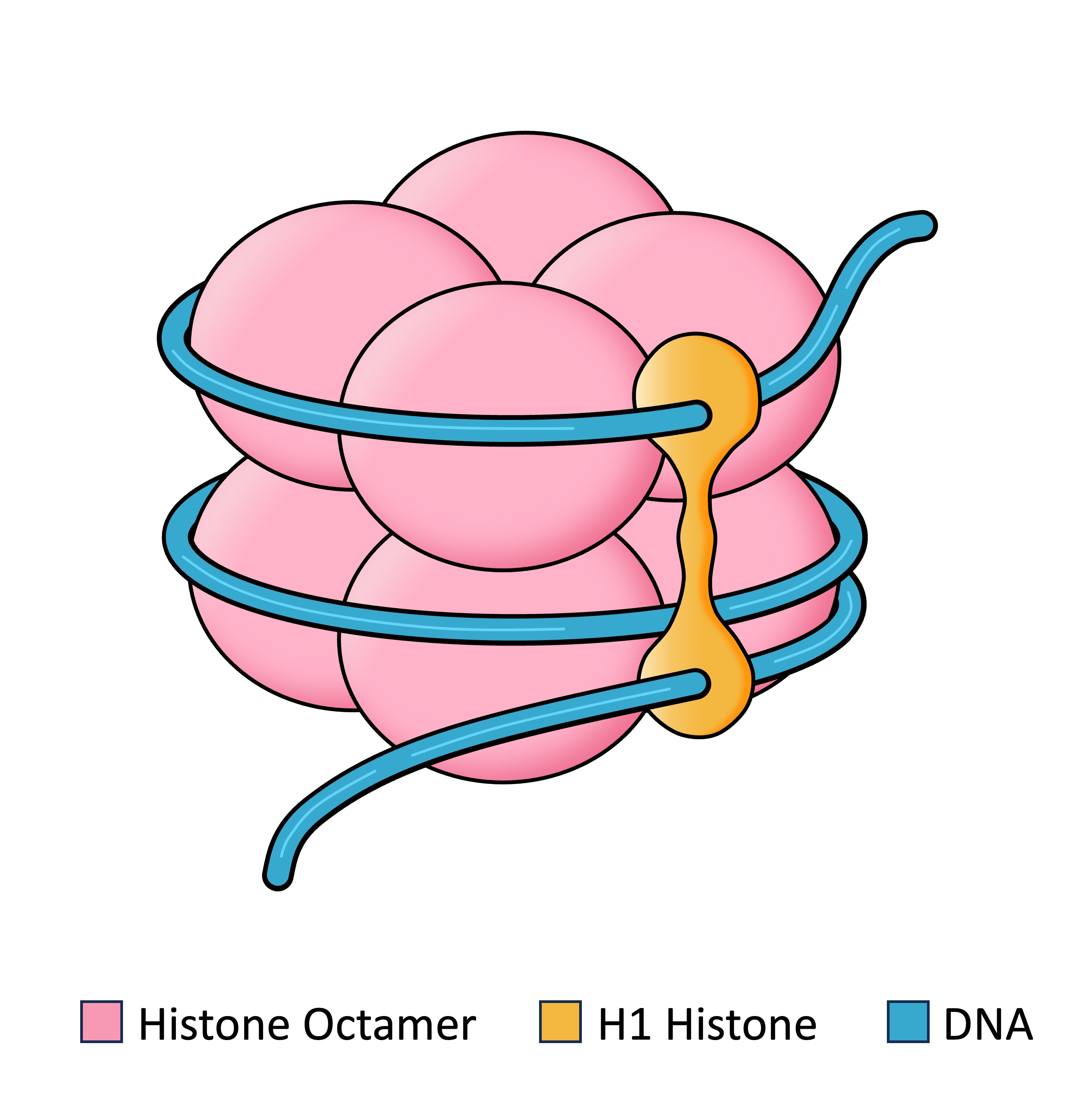
A nucleosome consists of a molecule of DNA wrapped around a core of eight histone proteins (an octamer)
-
The negatively charged DNA associates with the positively charged amino acids on the surface of the histone proteins
-
The DNA is coiled around the histone octamer in a manner that resembles thread being wrapped around a spool
-
Individual nucleosomes are together linked by an additional histone protein (H1 histone) attached to linker DNA
-
The nucleosomes are then folded into increasingly more complicated structures, eventually forming chromatin
Nucleosome
Diagram
Molecular Model
Nucleosome Function
Nucleosomes help to supercoil the DNA, which protects the DNA from damage and regulates the level of transcriptional activity
-
The histone proteins have N-terminal tails which extrude outwards from the nucleosome – these tails determine how tightly the DNA is packaged
-
When the DNA is more tightly packaged, the genetic instructions are less accessible to the transcriptional machinery of the cell
Nucleosome Packaging