Neurons
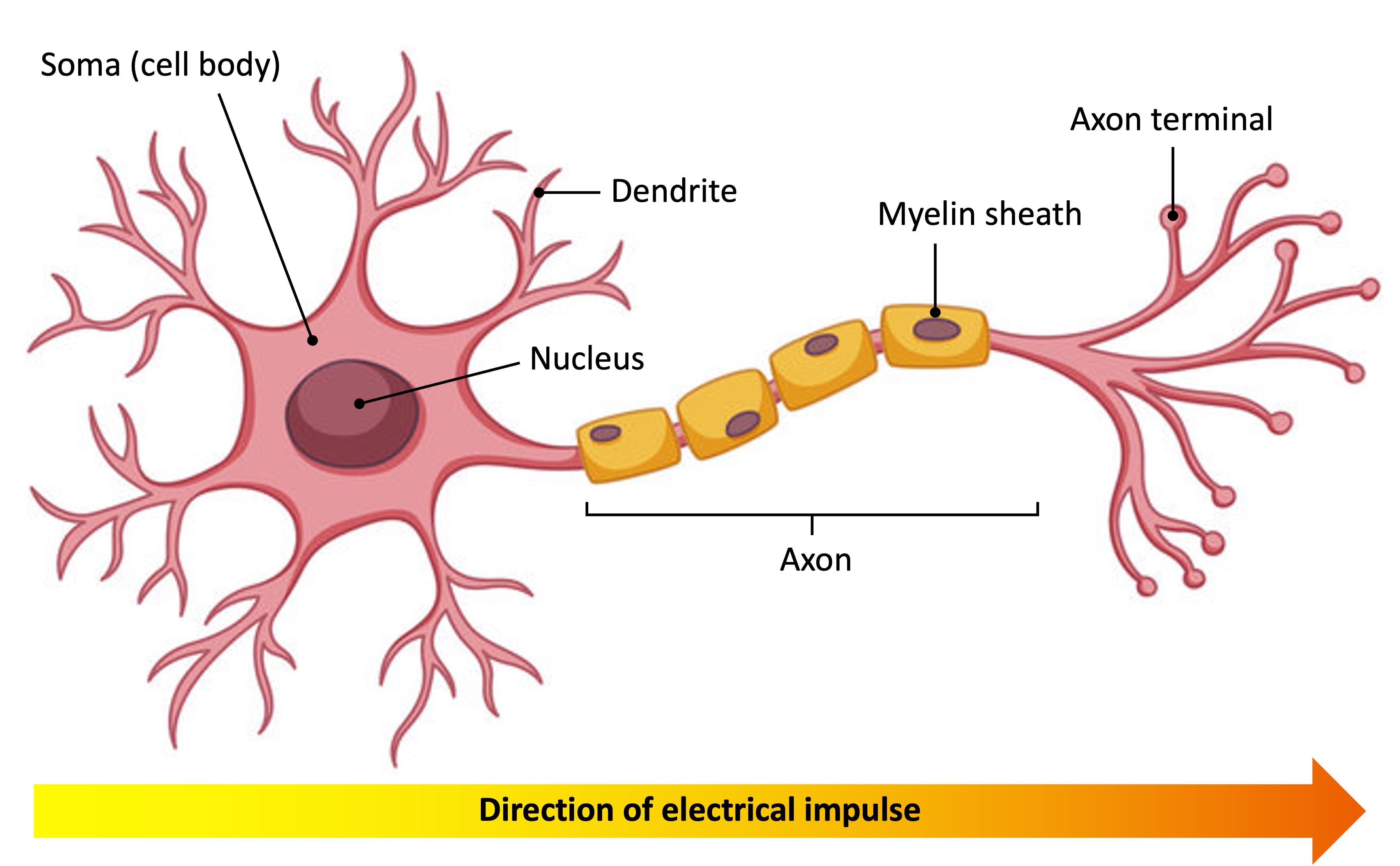
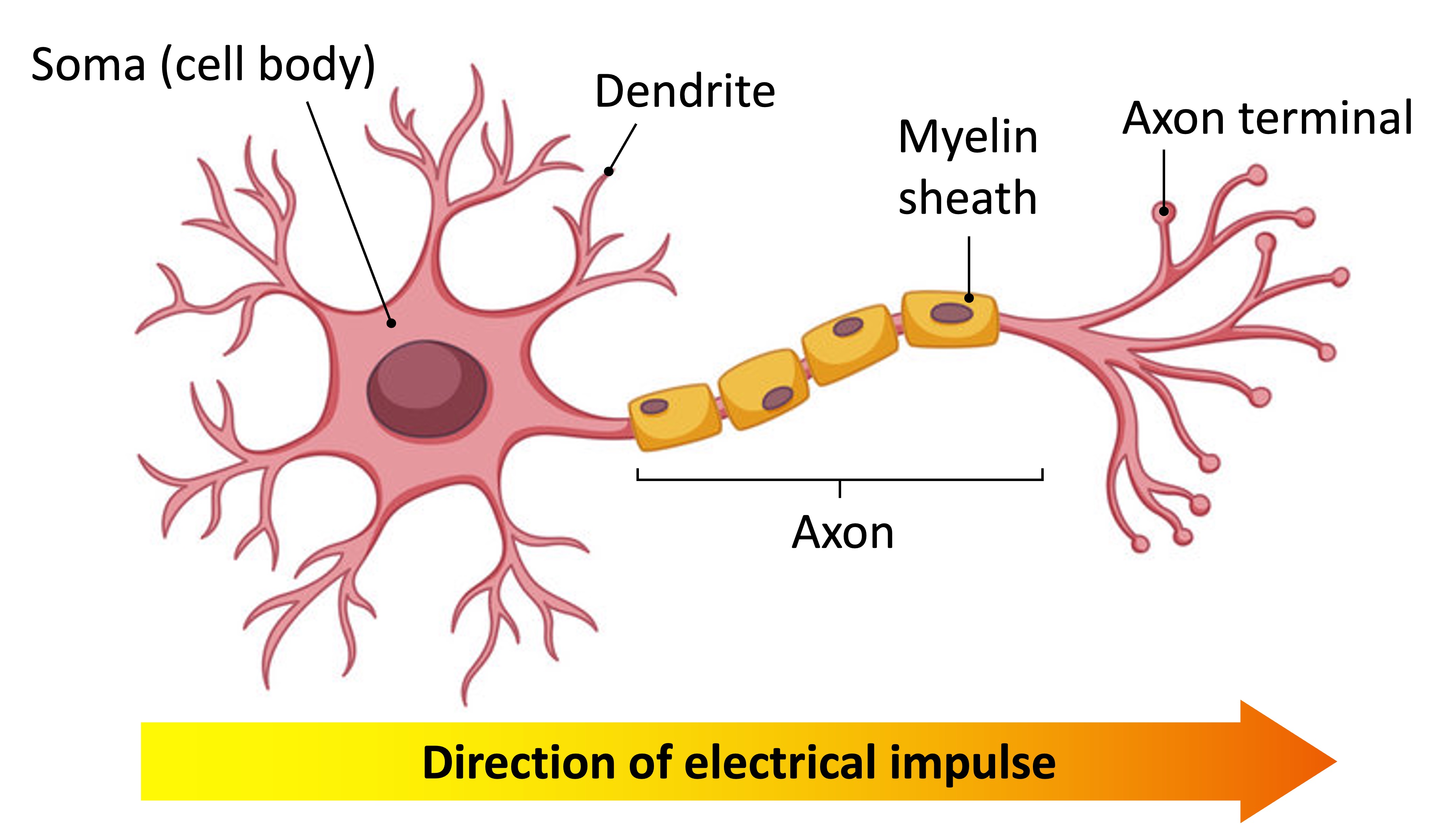
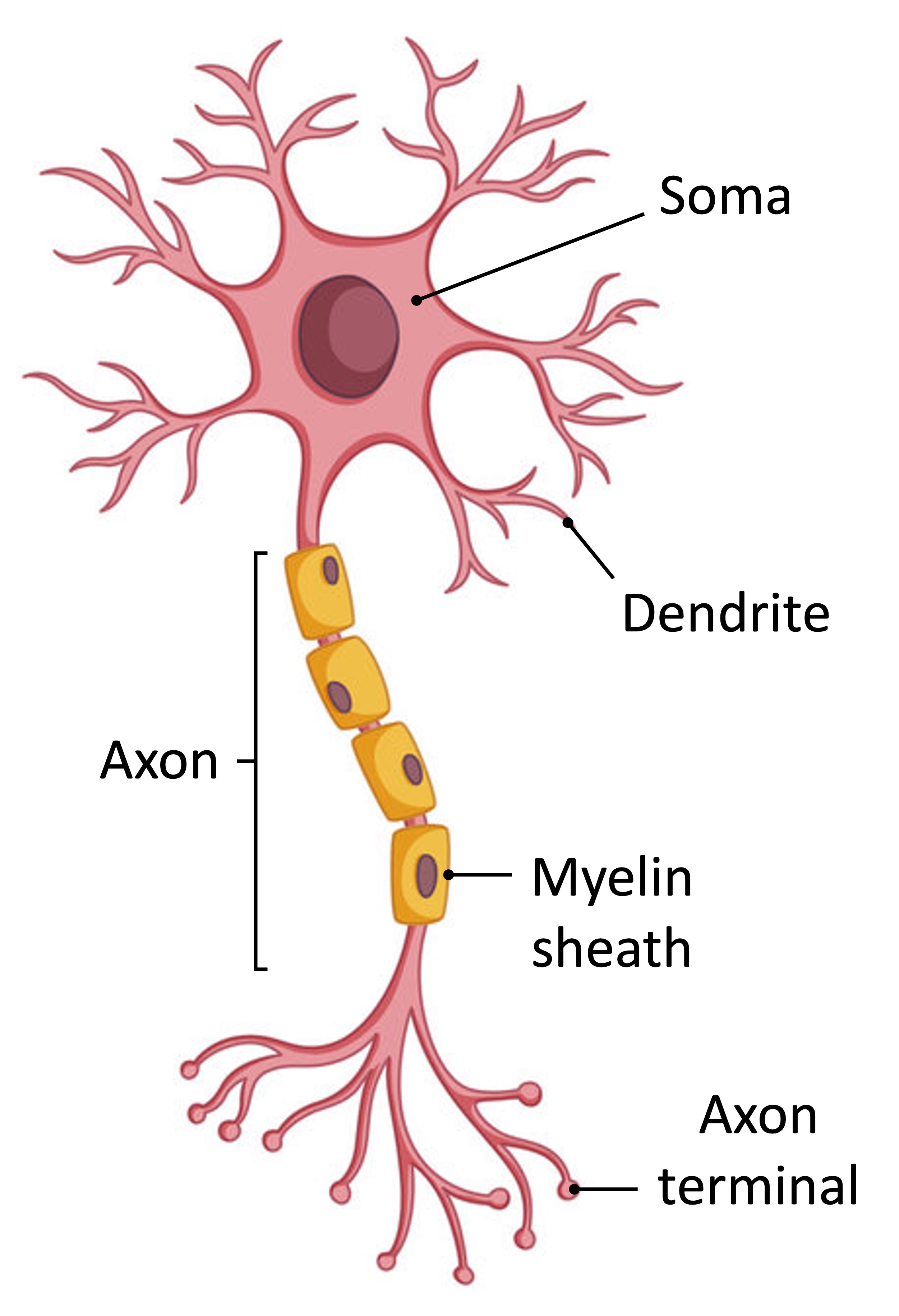
Neurons are specialised cells that function to transmit electrical impulses within the nervous system
-
Sensory receptors convert a range of stimuli into electrical signals, which are converted by effectors into specific responses
While neurons may differ according to role (sensory, relay or motor), most share three basic components:
-
Dendrites – Short-branched fibres that convert chemical information from other neurons or receptor cells into electrical signals
-
Axon – An elongated fibre that transmits the electrical signals to terminal regions for communication with other neurons or effectors
-
Soma – A cell body containing the nucleus and organelles, where essential metabolic processes occur to maintain cell survival
In some neurons, the axon may be surrounded by an insulating layer known as a myelin sheath
-
The myelin sheath improves the conduction speed of electrical impulses along the axon, but require additional space and energy
Structure of a Neuron