Natural Selection
Charles Darwin proposed the theory of evolution via natural selection, whereby a change in characteristics was driven by environmental selection pressures influencing survival and reproduction rates
-
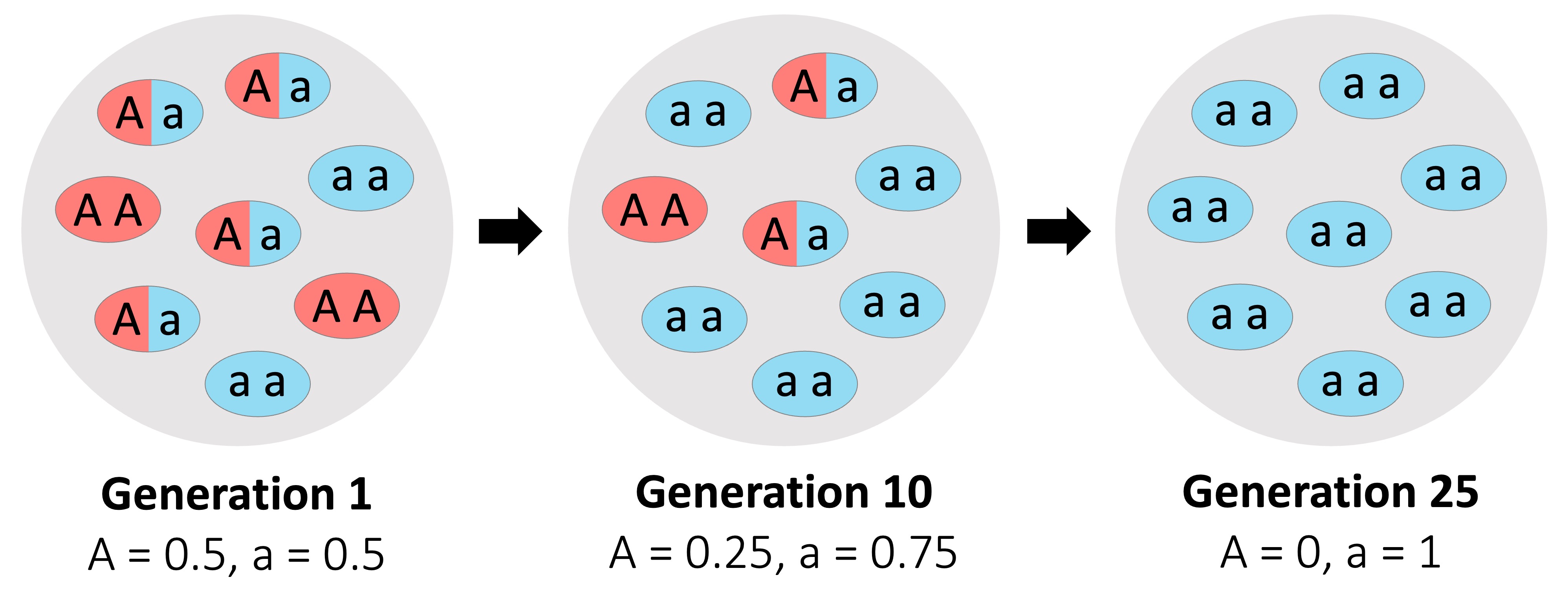
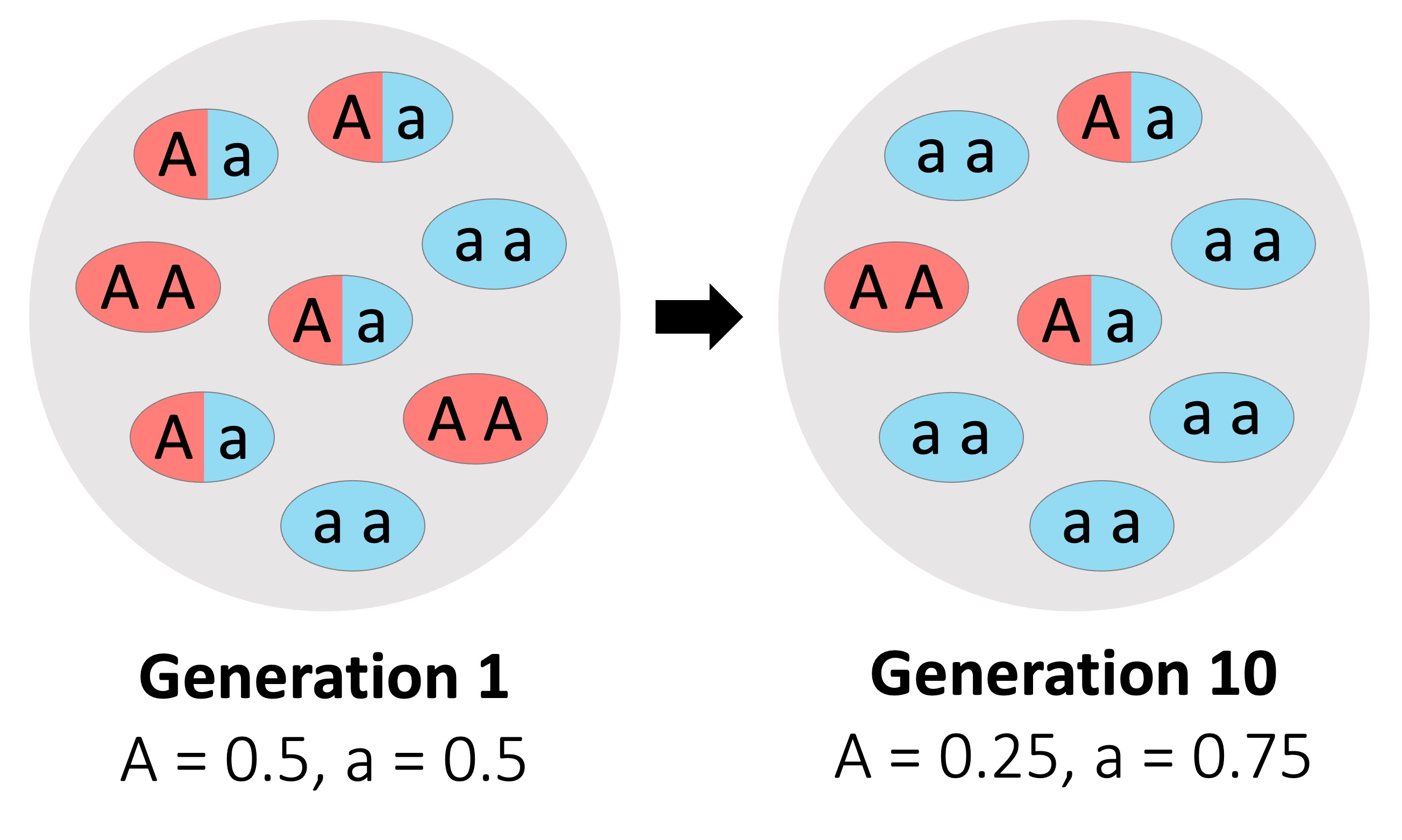
Evolution was described as the change in heritable characteristics of a population across successive generations
Neo-Darwinism involves the synthesis of Darwin’s ideas concerning natural selection with a modern understanding of genetics
-
It combines an awareness of Mendelian inheritance and knowledge of molecular biology (DNA structure and function)
-
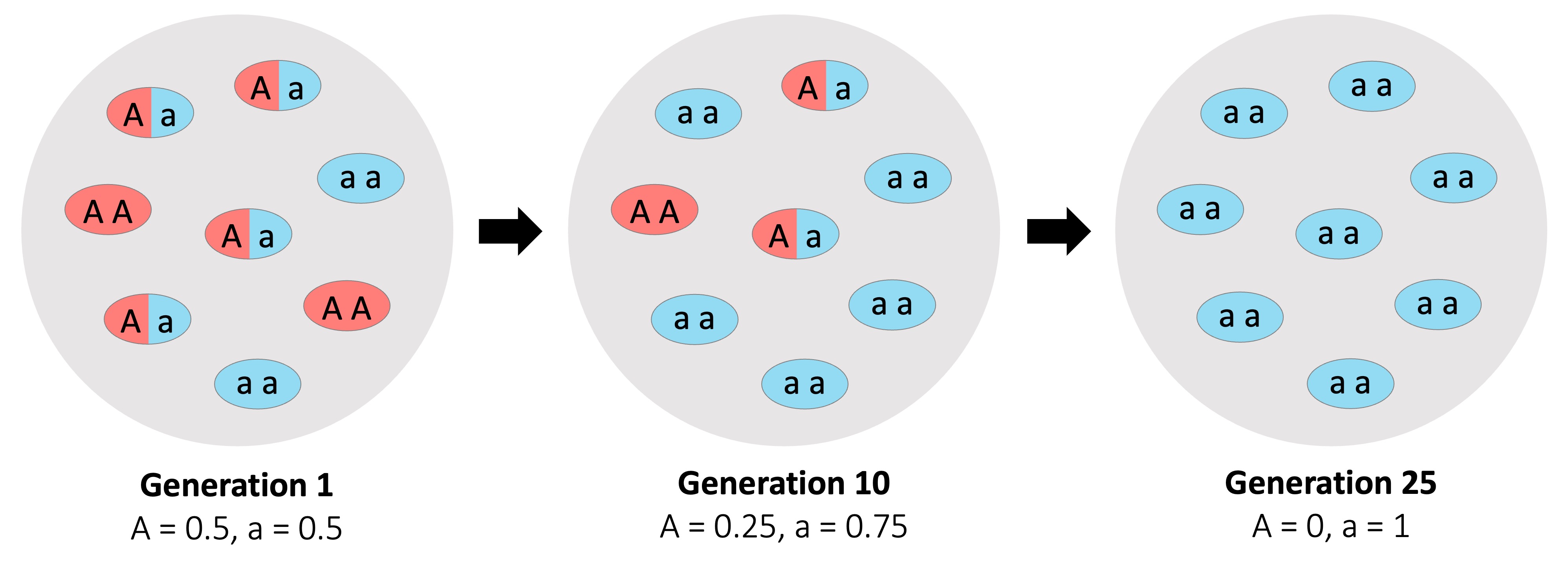
Evolution is now described as a change in the allele frequency of a gene pool over many generations
Neo-Darwinian Evolution
Types of Selection
Natural selection changes the composition of a gene pool in response to a differentially selective environmental pressure
-
The frequency of one particular allele in relation to another will be a product of the type of selection that is occurring
-
Types of selection include directional selection, stabilising selection and disruptive selection
Directional Selection
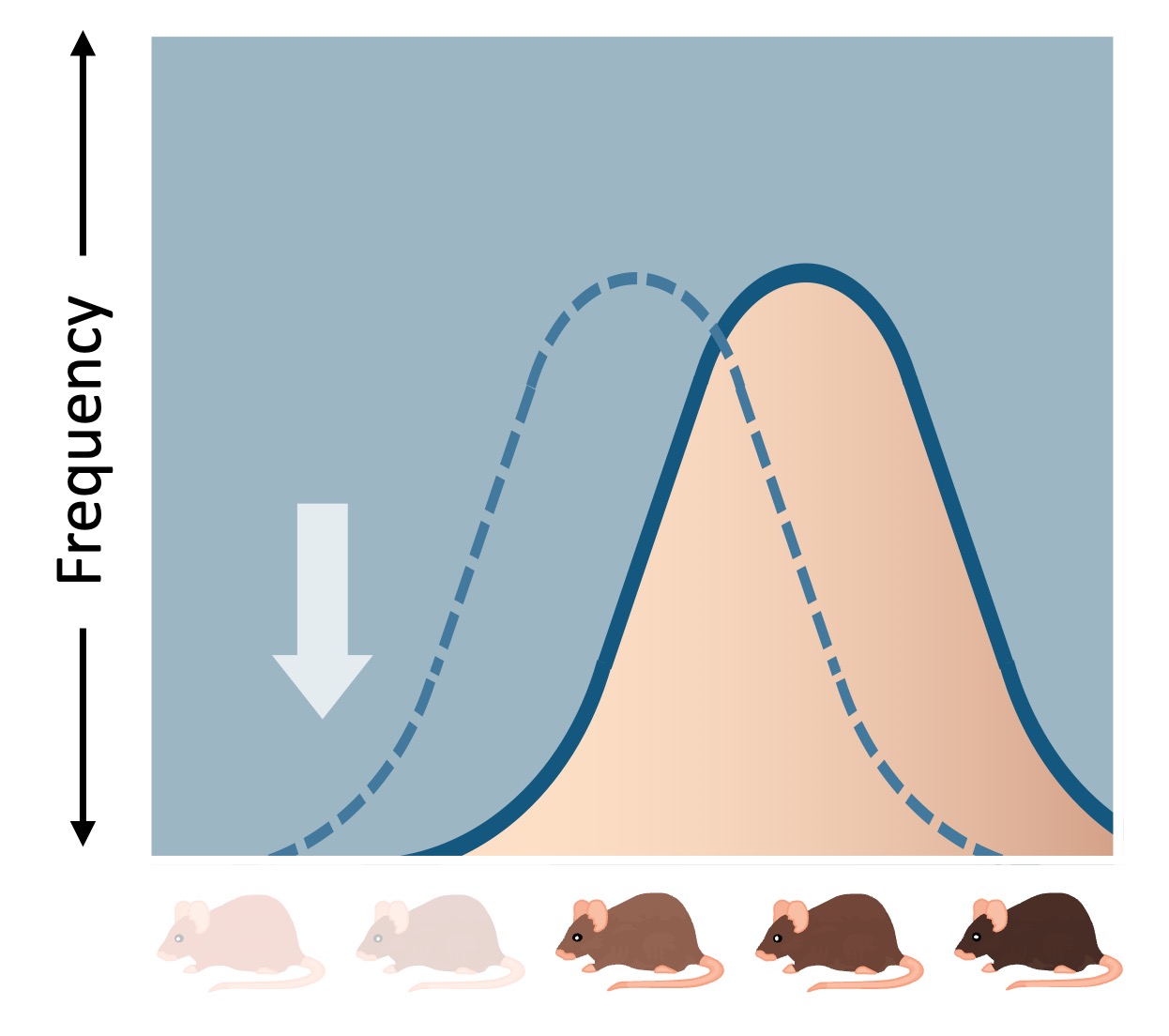
Directional selection occurs when one phenotypic extreme is selected at the cost of the other phenotypic extreme
-
This causes the phenotypic distribution to clearly shift in one direction (towards the beneficial extreme)
-
This type of selection occurs in response to gradual or sustained changes in environmental conditions
-
Directional selection will typically be followed by stabilising selection once an optimal phenotype has been normalised
-
An example of directional selection is the development of antibiotic resistance in bacterial populations
Stabilising Selection
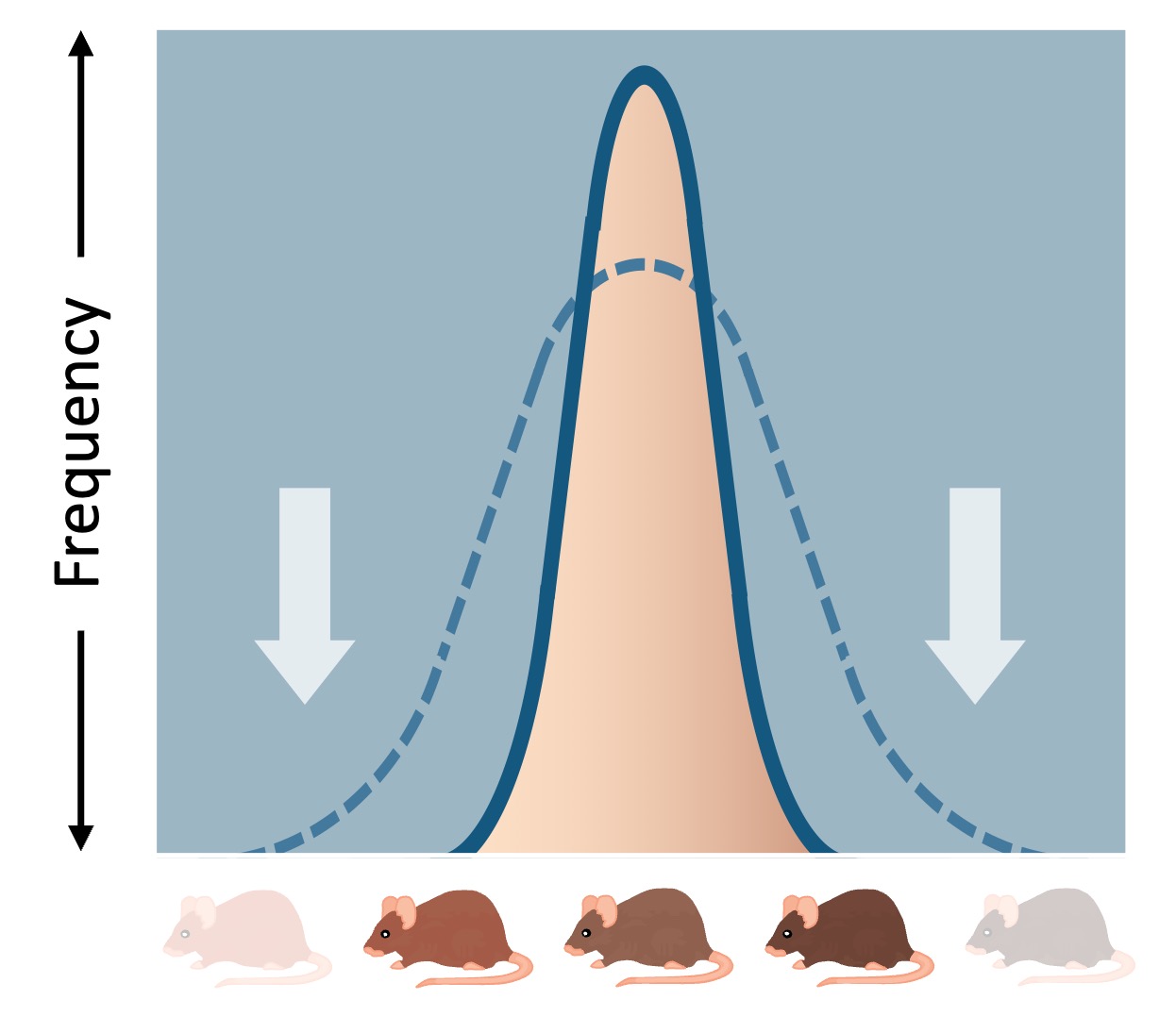
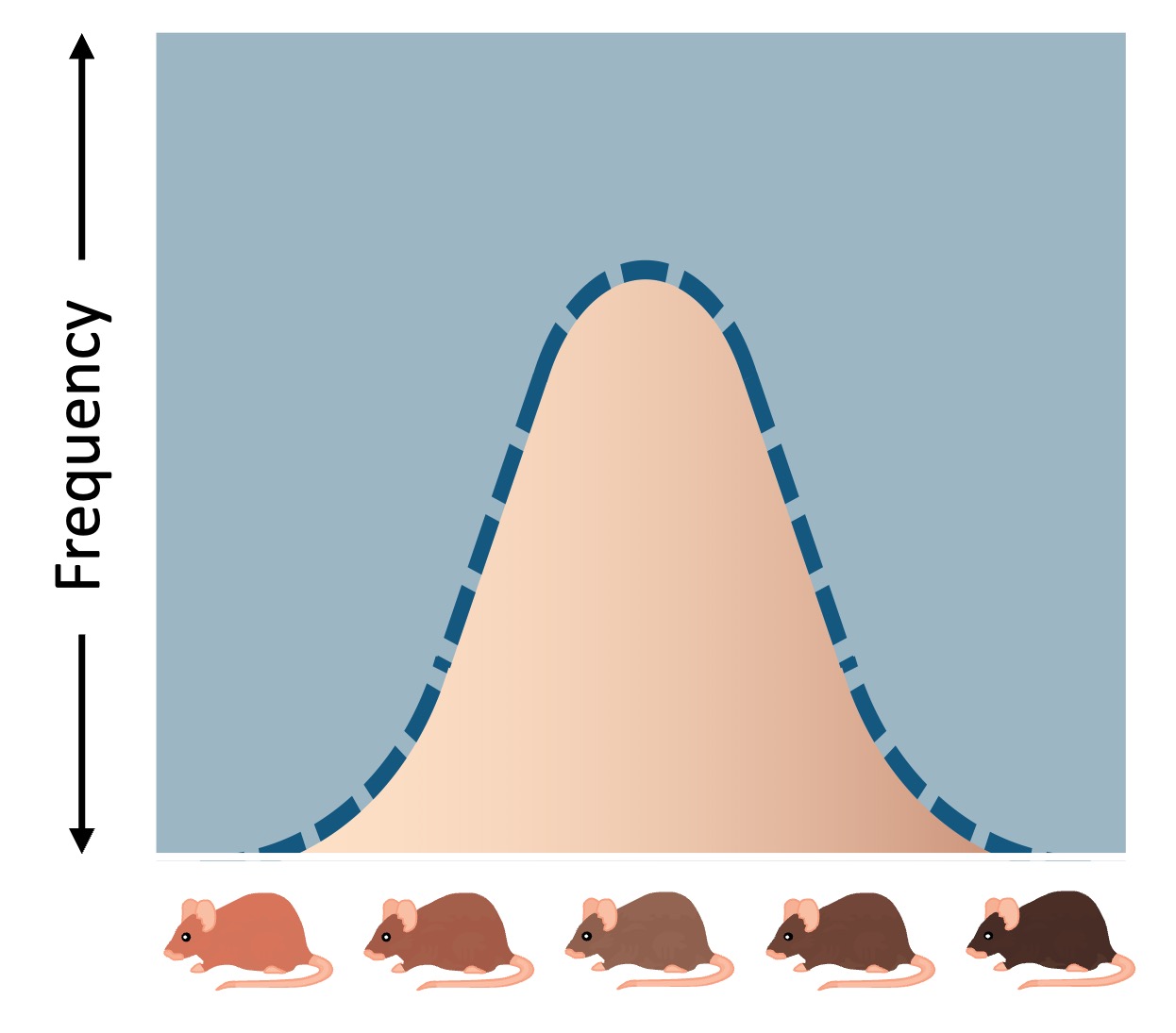
Stabilising selection occurs when an intermediate phenotype is favoured at the expense of both phenotypic extremes
-
This results in the removal of extreme phenotypes (phenotypic distribution becomes centrally clustered to reflect homogeneity)
-
This type of selection occurs when environmental conditions are stable and competition is low
-
An example of stabilising selection is human birth weights (too large = birthing complications ; too small = risk of infant mortality)
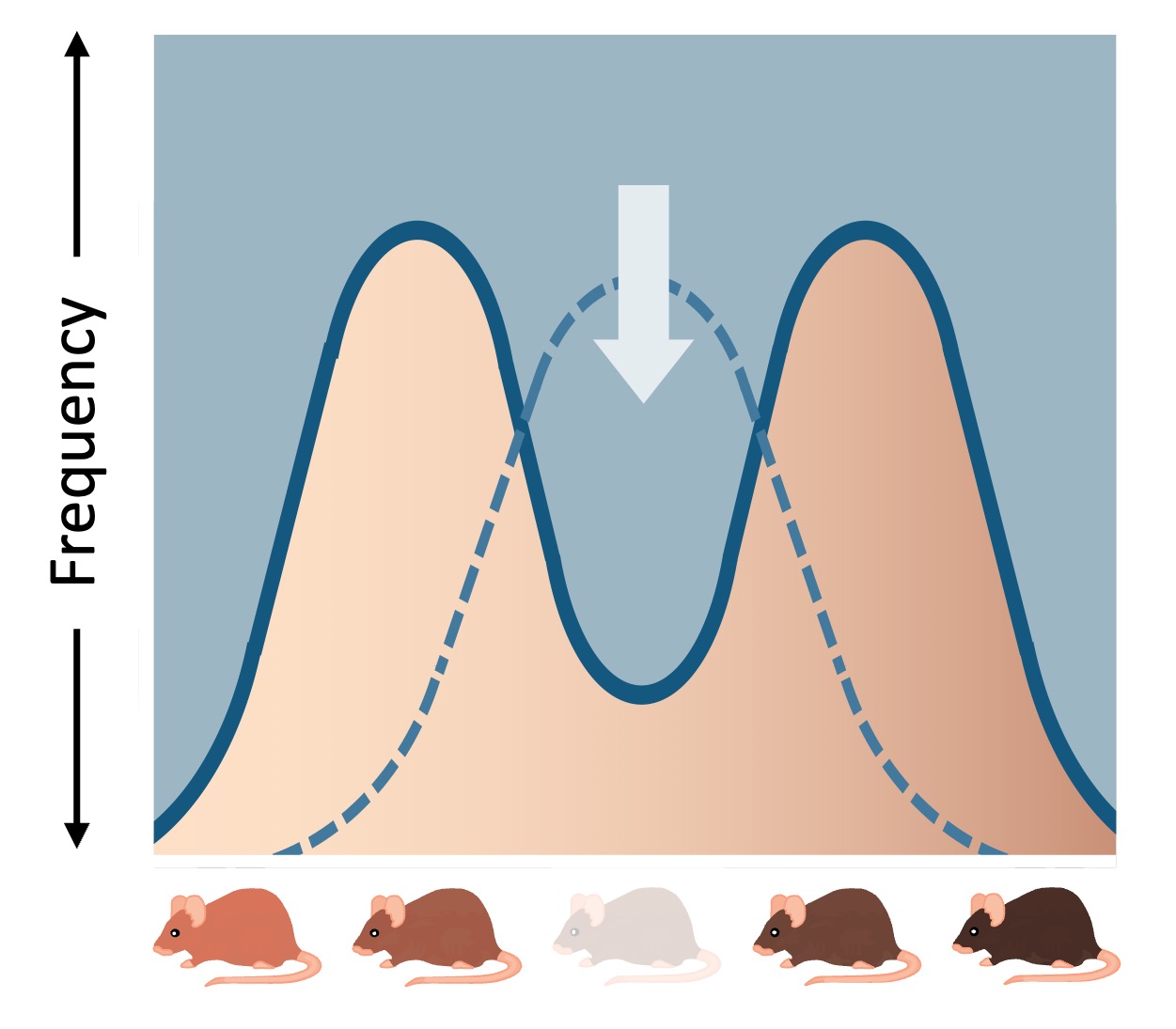
Disruptive Selection
Disruptive selection occurs when both phenotypic extremes are favoured at the expense of the intermediate phenotypic ranges
-
This causes the phenotypic distribution to deviate from the centre and results in a bimodal spread
-
This type of selection occurs when fluctuating environmental conditions (e.g. seasons) favour the presence of two different phenotypes
-
Continued separation of phenotypic variants may eventually split the population into two distinct sub-populations (speciation)
-
An example of disruptive selection is the proliferation of black or white moths in regions of sharply contrasting colour extremes
Types of Selection
No Selection

Directional

Stabilising