Monomers
Monomers
Organic compounds are typically composed of recurring subunits (monomers) which are covalently joined to form polymers
-
The monomeric subunit of carbohydrates is a monosaccharide (single sugar unit)
-
Nucleic acids are composed of repeating nucleotides (containing a sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous base)
-
Proteins consist of linked chains of amino acids which differ according to a variable side chain (‘R’ group)
-
Lipids do not contain monomers but certain types may be composed of distinct subunits (fatty acid chains)
Types of Monomers / Subunits
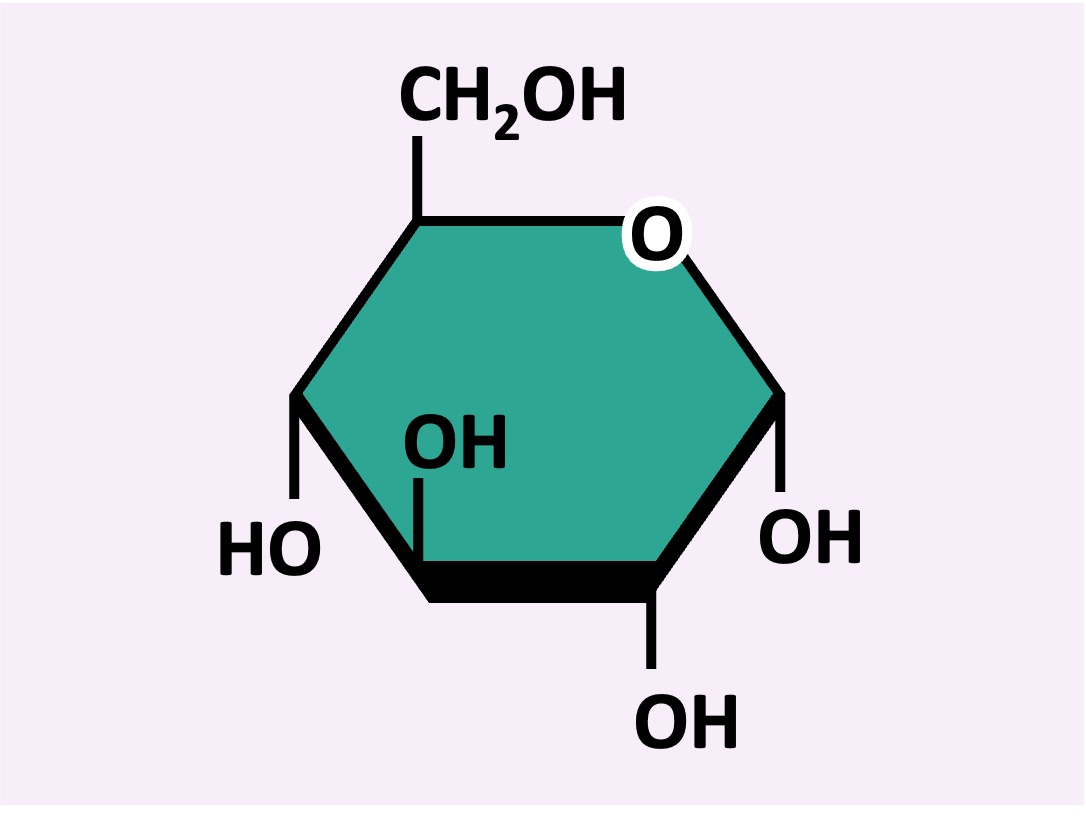
Monosaccharide
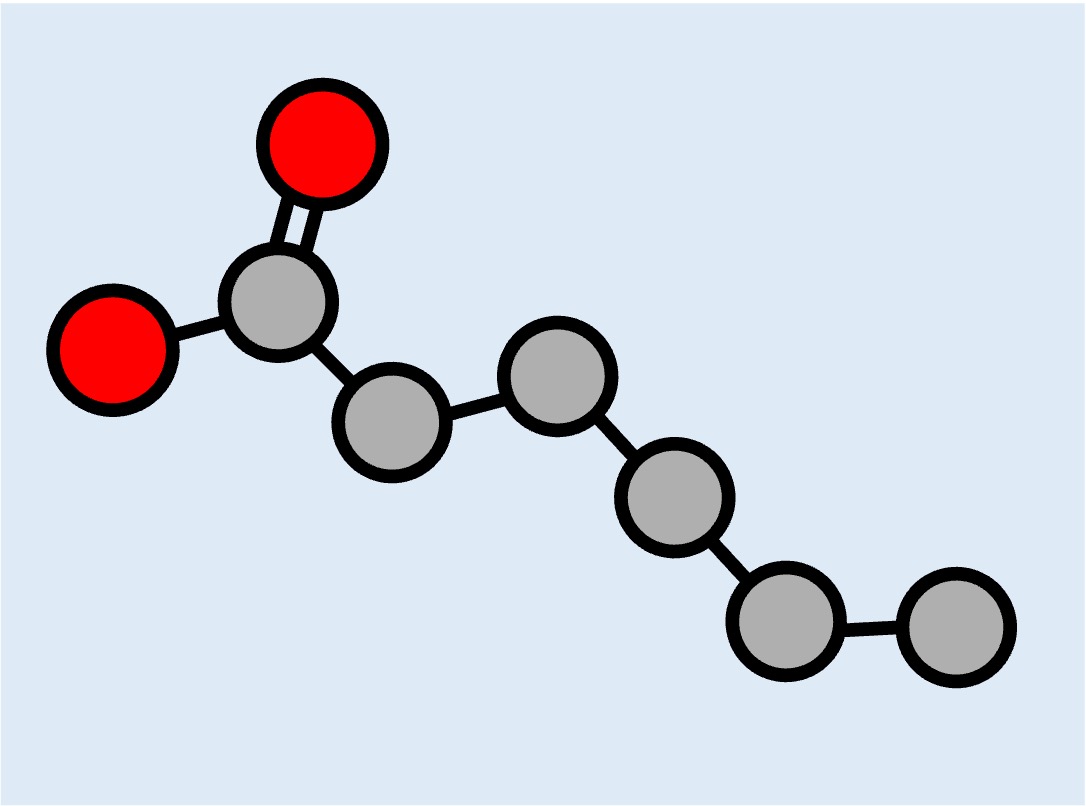
Fatty Acid
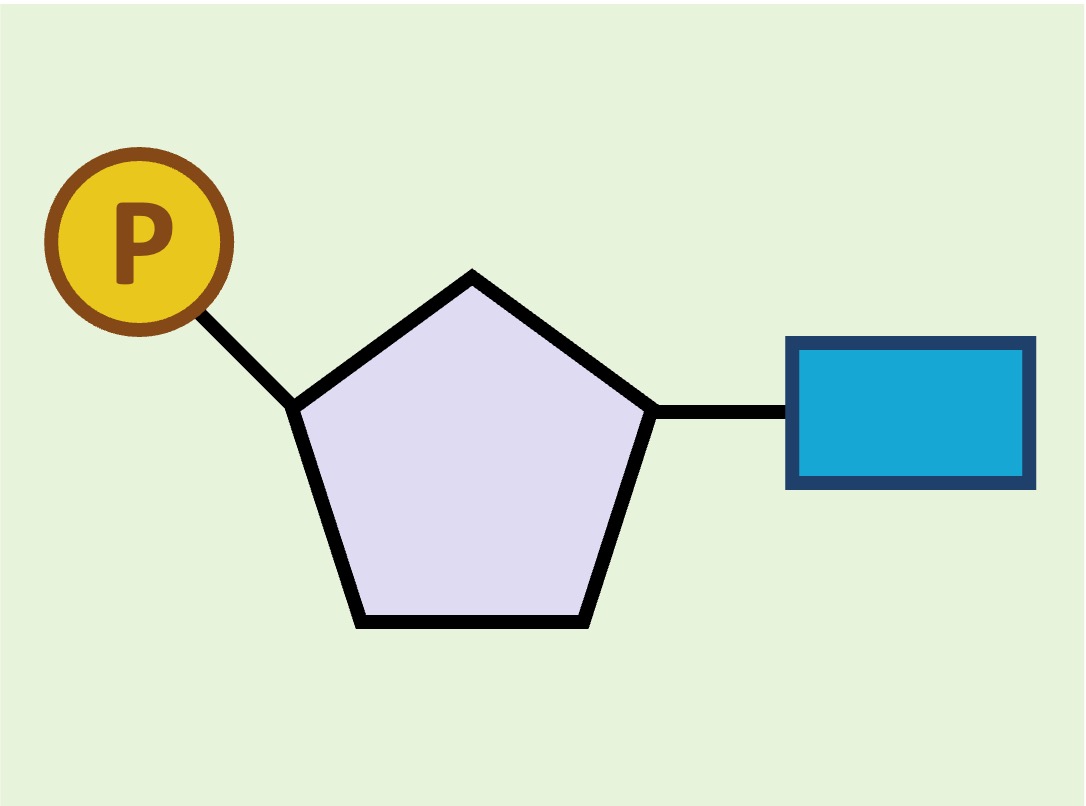
Nucleotide
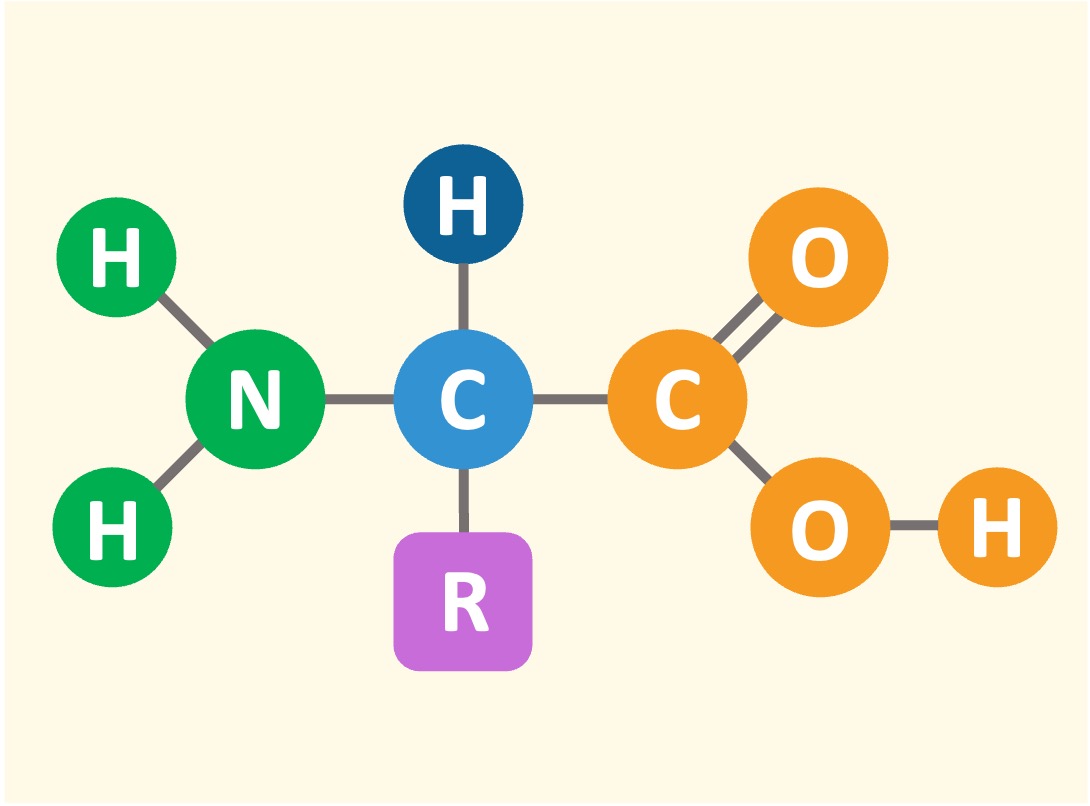
Amino Acid
Polymerisation
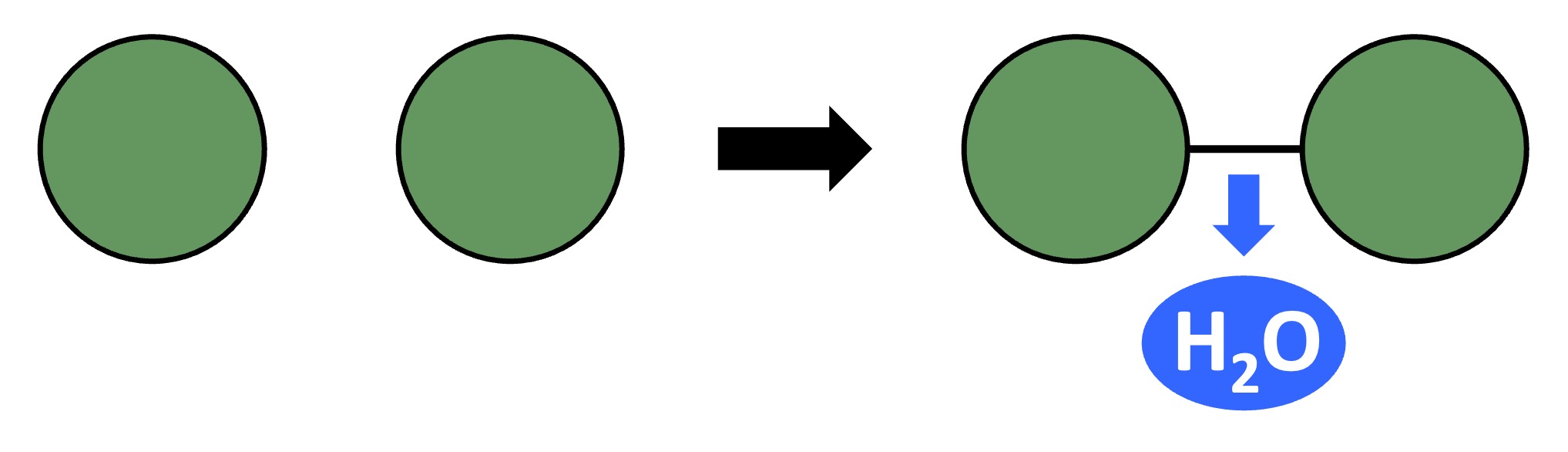
Polymers can be formed from monomeric subunits via condensation reactions
-
A hydroxyl group (-OH) on one monomer is combined with a hydrogen atom (-H) on another monomer
-
The two monomers become covalently bonded and a water molecule is produced as a by-product
Condensation Reaction
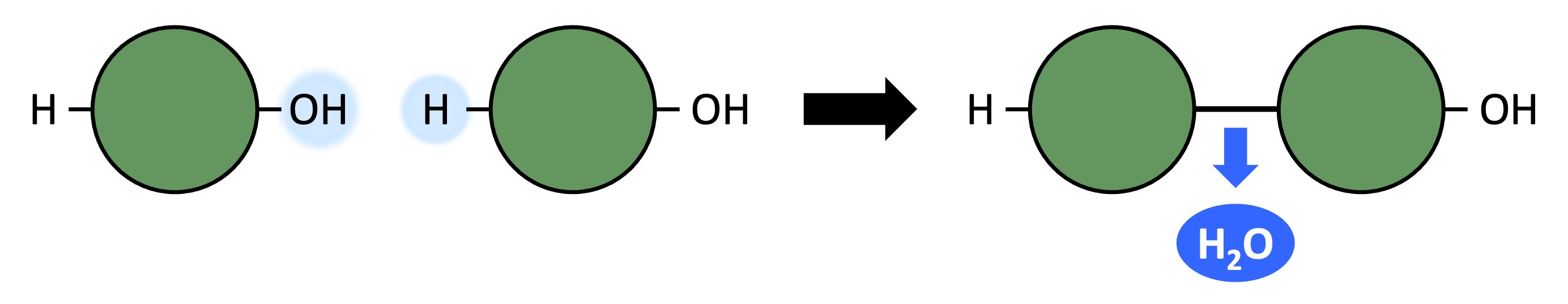
Condensation Reaction