Molecular Evidence
All organisms use DNA and RNA as genetic material to synthesise proteins according to an (almost) universal genetic code
-
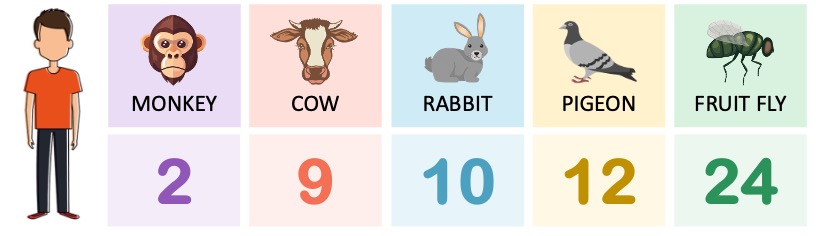
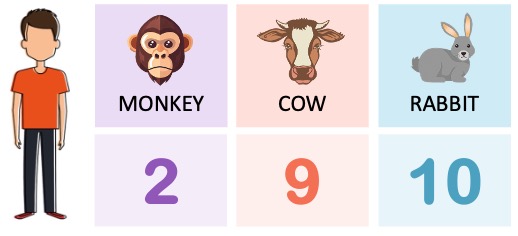
This shared molecular heritage means that base and amino acid sequences can be compared between species to ascertain levels of relatedness
Over the course of millions of years, mutations will accumulate within any given segment of DNA
-
The number of differences between comparable base sequences demonstrates the degree of evolutionary divergence
-
A greater number of differences between comparable base sequences suggests more time has past since two species diverged
-
Hence, the more similar the base sequences of two species are, the more closely related the two species are expected to be
When comparing molecular sequences, scientists may use non-coding DNA, gene sequences or amino acid sequences
-
Non-coding DNA provides the best means of comparison as mutations will occur more readily in these sequences
-
Gene sequences mutate at a slower rate, as changes to base sequence may potentially affect protein structure and function
-
Amino acid sequences may also be used for comparison, but will have the slowest rate of change due to codon degeneracy
Amino acid sequences are typically used to compare distantly related species (i.e. different taxa), while DNA or RNA base sequences are often used to compare closely related organisms
Molecular Homology