Mitosis vs Meiosis
After DNA has been replicated, the nucleus must first be divided before the cell can split into two
-
Nuclear division is necessary to ensure that both daughter cells have genetic material and are not anucleate
-
Anucleate cells are unable to synthesise proteins needed to maintain the structure and metabolic activities of a cell, resulting in an extremely limited lifespan (e.g. red blood cells)
There are two distinct ways the nucleus can be divided, according to the function of the daughter cell:
-
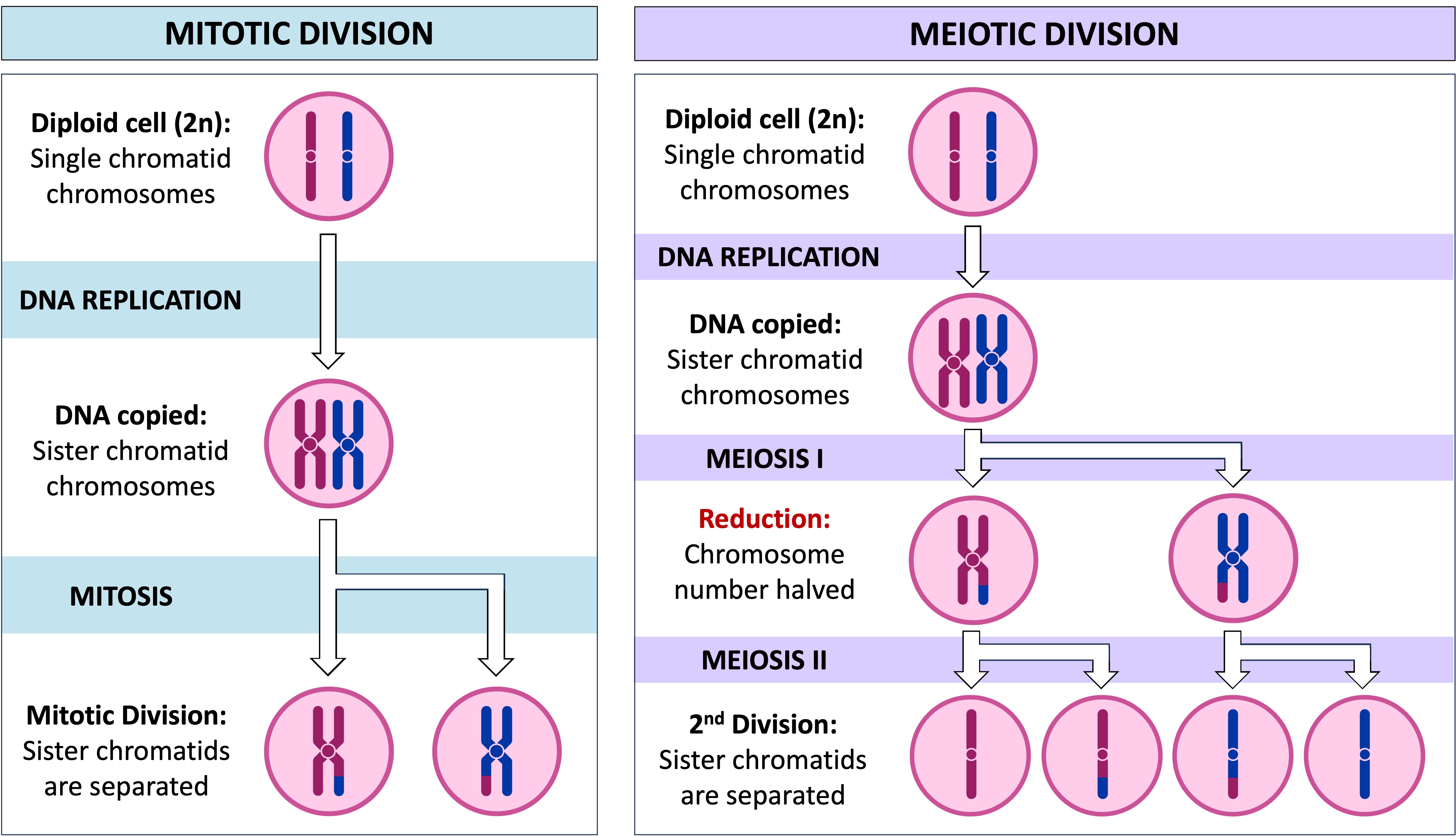
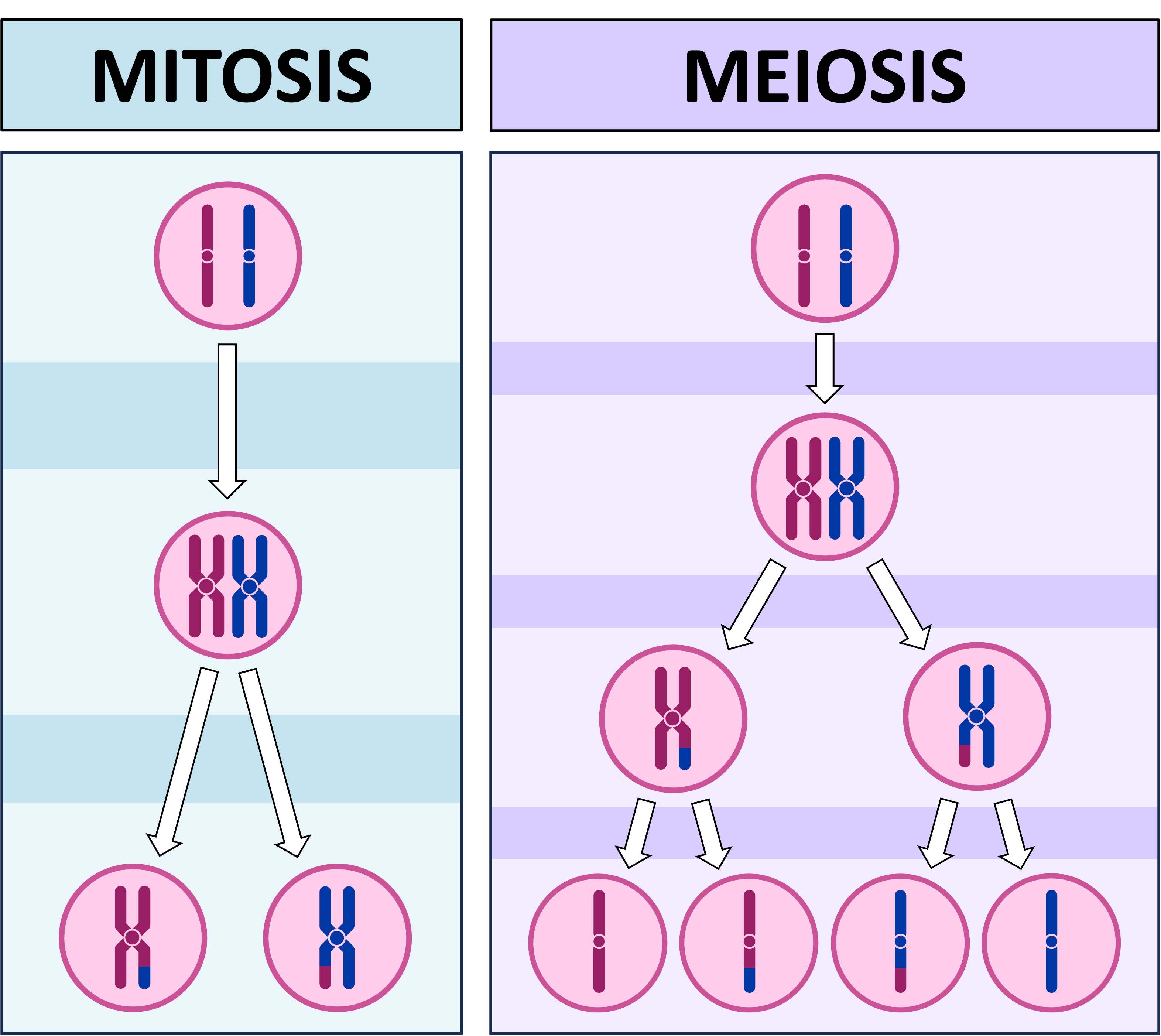
Mitosis: A single nuclear division that produces genetically identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell
-
Meiosis: A process of two nuclear divisions that produce genetically distinct daughter cells with only half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell
Mitosis
Mitosis is a process of asexual reproduction that results in the production of genetically identical daughter cells (clones)
-
It involves a single nuclear division that ultimately results in the production of two daughter cells
-
The single nuclear division separates the sister chromatids into two identical sets of chromosomes
-
-
The chromosome number and genome remains unchanged between the parent cell and daughter cells
-
In multicellular organisms, it is used for cell proliferation (generates new body cells for growth and tissue repair)
-
Malfunctions in mitosis can lead to the development of cancers (uncontrolled cell division of body cells)
Meiosis
Meiosis is a process of sexual reproduction that results in the production of genetically distinct daughter cells (promotes variation)
-
It involves two nuclear divisions that typically result in the production of four daughter cells
-
The first nuclear division divides the total number of chromosomes in two (reduction division)
-
The second nuclear division separates the sister chromatids that were produced by DNA replication
-
-
The chromosome number is halved from parent cell to daughter cell (diploid → haploid)
-
In multicellular organisms, it is used to create sex cells (gametes) in order to generate offspring that are genetically distinct
-
Malfunctions in meiosis can lead to aneuploidy conditions (offspring with an abnormal total number of chromosomes)
Mitosis versus Meiosis