Metabolic Pathways
Metabolism describes the sum total of all enzyme-catalysed reactions that occur within an organism in order to maintain life
-
Most chemical changes in a cell result from a series of reactions (pathways), with each step controlled by a specific enzyme
Metabolic pathways can be found both within the cytoplasm (intracellular) and outside of the cell (extracellular)
-
Intracellular reactions include glycolysis and the Krebs cycle (components of cellular respiration)
-
Examples of extracellular reactions include the breakdown of nutrients within the gut (chemical digestion)
The production of extracellular enzymes (exoenzymes) requires a well developed secretory pathway within the cell (rough ER, Golgi complex, vesicles, etc.)
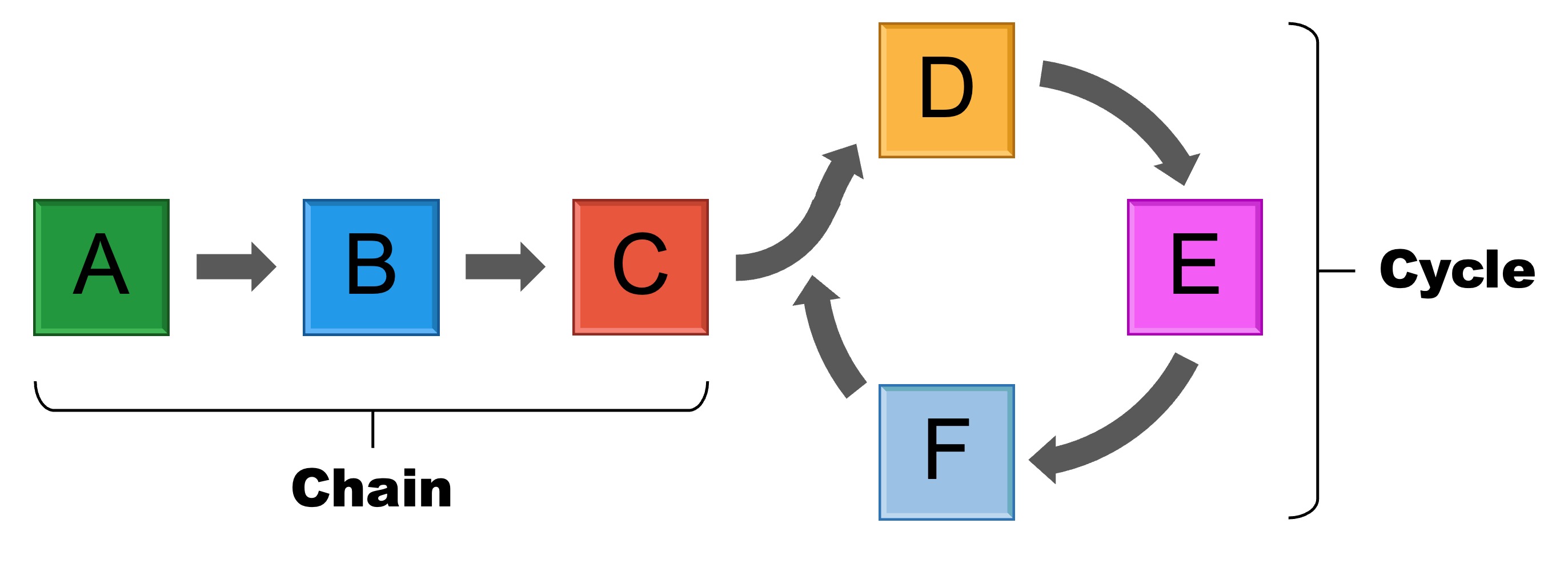
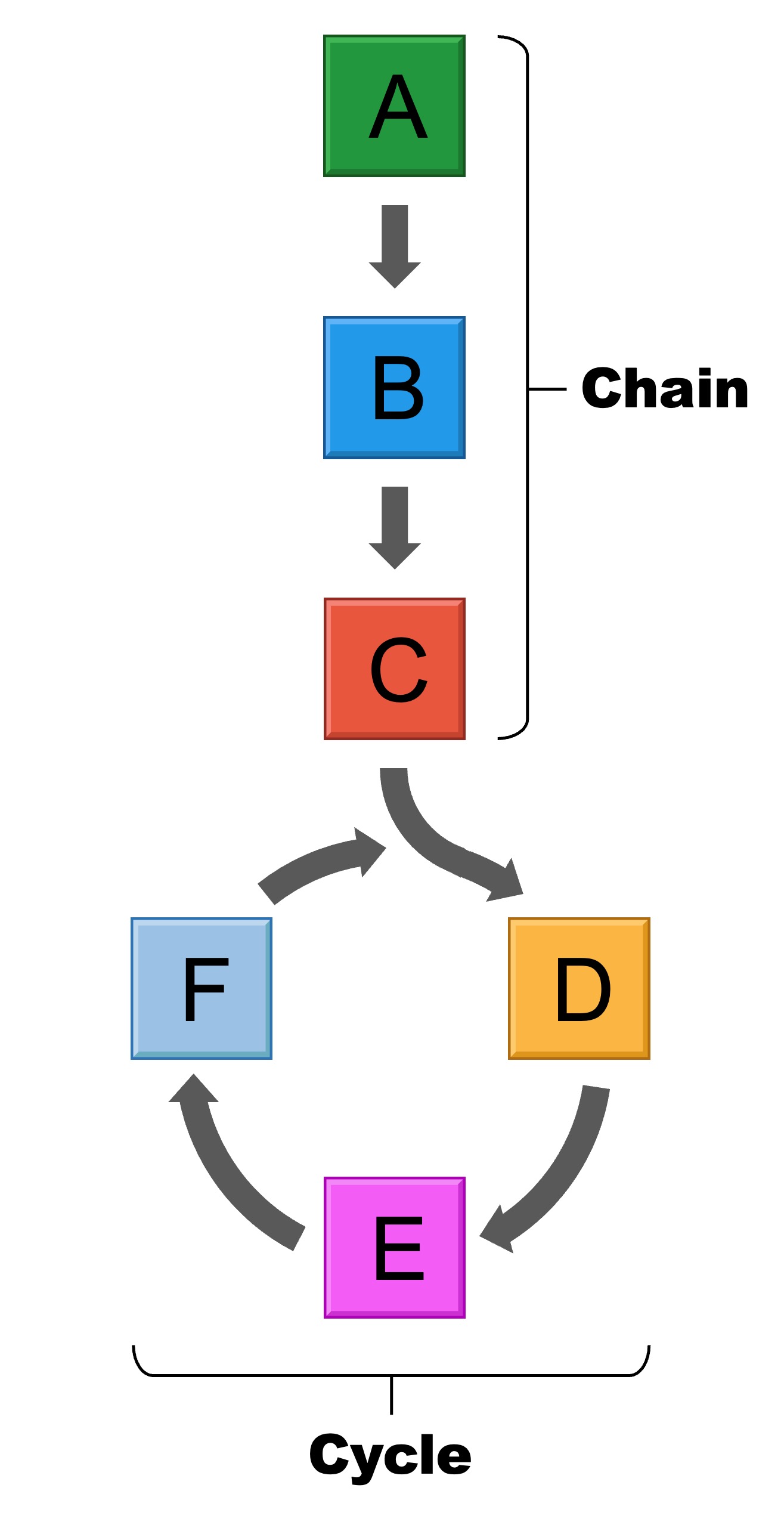
Metabolic pathways are typically organised into chains or cycles of enzyme-catalysed reactions
-
Linear pathways are present in processes such as glycolysis (intracellular) and blood clotting (extracellular)
-
Cyclical pathways are present in processes such as the Krebs cycle (cell respiration) and the Calvin cycle (photosynthesis)
Metabolic pathways allow for a greater level of regulation, as the chemical change is controlled by numerous intermediates