Membrane Structure
SL Content Statements
-
B2.1.1
Lipid bilayers as the basis of cell membranes
-
Phospholipids and other amphipathic lipids naturally form continuous sheet-like bilayers in water.
-
B2.1.2
Lipid bilayers as barriers
-
Students should understand that the hydrophobic hydrocarbon chains that form the core of a membrane have low permeability to large molecules and hydrophilic particles, including ions and polar molecules, so membranes function as effective barriers between aqueous solutions.
-
B2.1.4
Integral and peripheral proteins in membranes
-
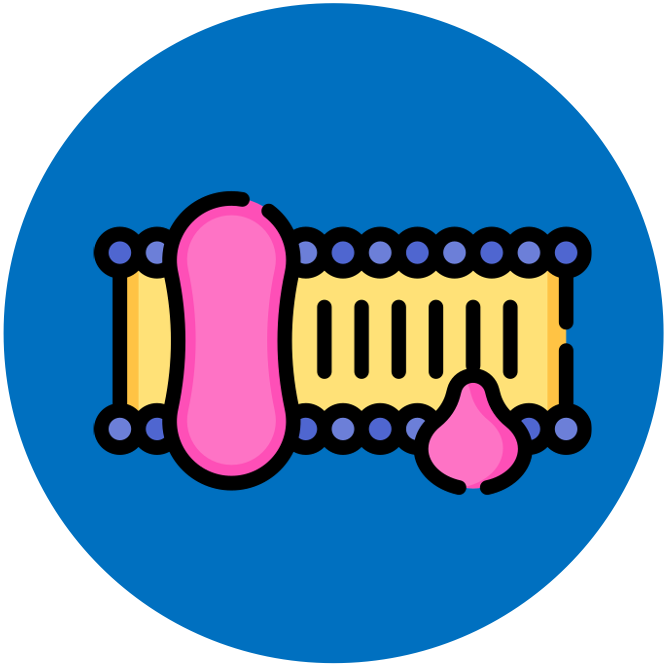
Emphasise that membrane proteins have diverse structures, locations and functions. Integral proteins are embedded in one or both of the lipid layers of a membrane. Peripheral proteins are attached to one or other surface of the bilayer.
-
B2.1.9
Structure and function of glycoproteins and glycolipids
-
Limit to carbohydrate structures linked to proteins or lipids in membranes, location of carbohydrates on the extracellular side of the membranes, and roles in cell adhesion and cell recognition.
-
B2.1.10
Fluid mosaic model of membrane structure
-
Students should be able to draw a two-dimensional representation of the model and include peripheral and integral proteins, glycoproteins, phospholipids and cholesterol. Indicate hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions.
-
B1.1.12
Formation of phospholipid bilayers as a consequence of the hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
-
Students should use and understand the term “amphipathic”.