Lung Capacity
Lung capacity refers to the volumes of air associated with the different phases of the respiratory cycle:
-
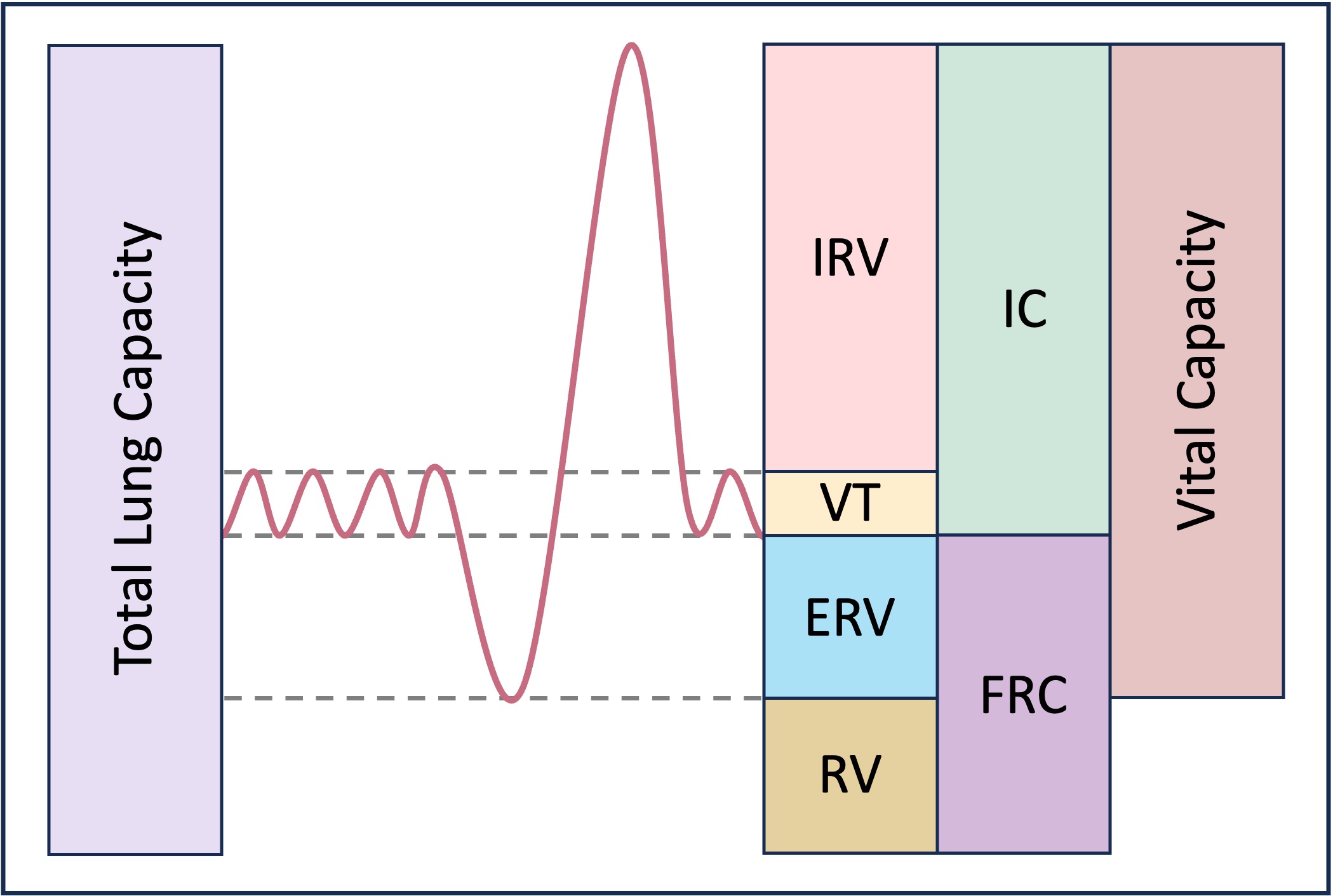
Total lung capacity – Volume of air in the lungs after a maximal inhalation (~ 6 litres in a normal adult male)
-
Vital capacity – Volume of air that can be exchanged by the lungs via a maximal inhalation and exhalation
-
Residual volume – Volume of air that is always present in the lungs (~ 20% of total lung capacity)
-
Tidal volume – Volume of air that is exchanged via normal breathing (~ 500 ml per breath)
-
Inspiratory Reserve Volume – Volume of air able to be inspired with maximum effort after a normal inhalation
-
Expiratory Reserve Volume – Volume of air able to be expired with maximum effort after a normal exhalation
-
Inspiratory Capacity – The sum of the inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) and tidal volume (VT)
-
Functional Residiual Capacity – Sum of the expiratory reserve volume (ERV) and residual volume (RV)
The ventilation rate (breathing frequency) for a typical adult at rest is roughly 12 – 16 breaths per minute
-
Ventilation rate can be substantially increased with physical activity (maximal increase is roughly 5 – 6 fold over normal)
A number of factors contribute to an individual’s total lung capacity and ventilation rate, including:
-
Height (taller people tend to have larger chests and hence larger total lung capacities)
-
Location (people living at high altitudes tend to have larger capacities to compensate for the lower atmospheric pressure)
-
Lifestyle (obese people and smokers tend to have lower capacities and higher rates of ventilation)
Measuring Ventilation
Ventilation in humans can be monitored in a number of ways:
-
Via simple observation (counting number of breaths per minute)
-
Chest belts and pressure meters (recording the rise and fall of the chest)
-
Spirometers (recording the volume of gas expelled per breath)
Spirometry involves measuring the amount (volume) and / or speed (flow) at which air can be inhaled or exhaled
-
A spirometer is a device that detects the changes in ventilation and presents the data on a digital display
-
A more simplistic method involves breathing into a balloon and measuring the volume of air in a single breath
-
The volume of air can be determined by submerging the balloon in water and measuring the volume displaced (1ml = 1cm3)
-
Overview of Lung Capacities