Lipid Properties
Lipids are a class of organic molecule composed primarily of hydrocarbon chains (fatty acids) or rings (steroids)
-
Hydrocarbons are non-polar (they lack charged regions) and will not dissolve in polar substances like water
-
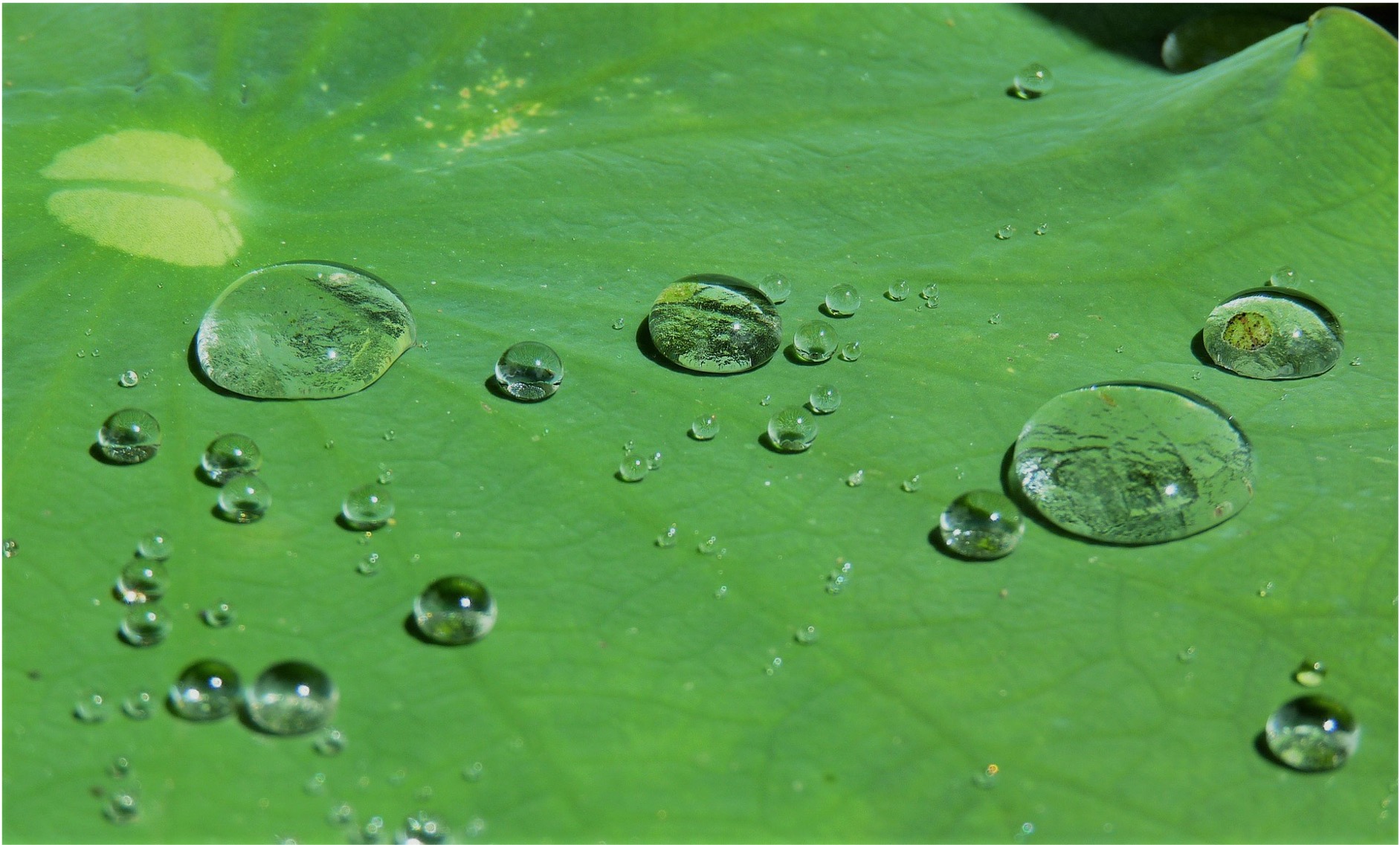
Hence lipids are considered to be hydrophobic molecules (they are water-repelling)
The hydrophobic properties of lipids have many important biological consequences
-
Waxes are used to prevent water loss from leaves while birds coat their feathers with oil to render them waterproof
-
Phospholipids provide a structural framework for cells by forming spontaneous membranes in aqueous solutions
-
Lipids in foods help the body to absorb certain fat-soluble micronutrients, including vitamins A and D
However, the hydrophobic properties of lipids make them difficult to transport around the body
-
Digested fats are packaged within a protein coat to become water soluble lipoproteins
-
Steroid hormones are bound to carrier proteins (such as albumin) to facilitate their movement through the bloodstream
Certain lipids have polar components, becoming amphipathic (having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions)
-
Phospholipids possess a polar phosphate head, cholesterol has a polar hydroxyl group and glycolipids can have polar carbohydrate chains
-
These amphipathic molecules all have a limited capacity to interact with water, helping them to function in maintaining membrane integrity
Water Repellant Surfaces
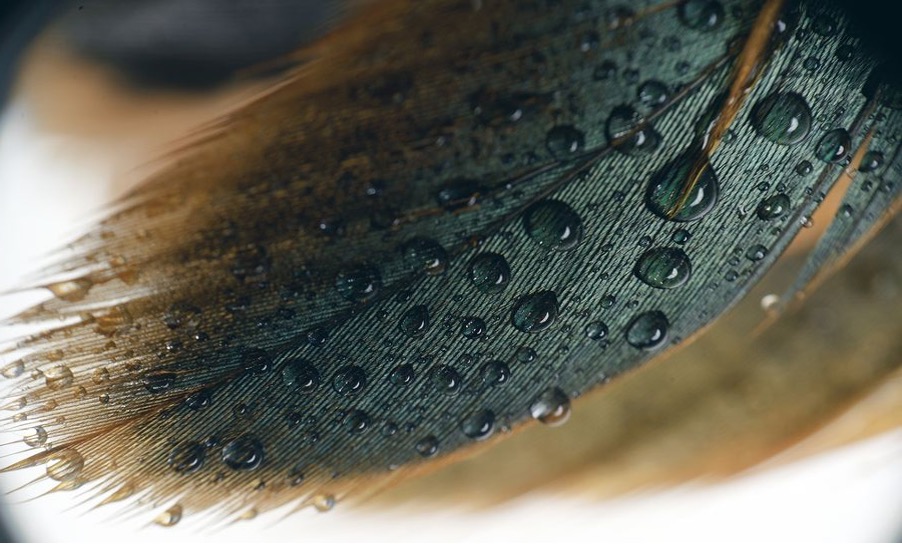

Bird Feathers (Oil)