Light Independent Reactions
Photosynthesis is a two step process:
-
The light dependent reactions convert light energy from the Sun into chemical energy (ATP)
-
The light independent reactions use the chemical energy to synthesise organic compounds (e.g. carbohydrates)
Light Independent Reactions
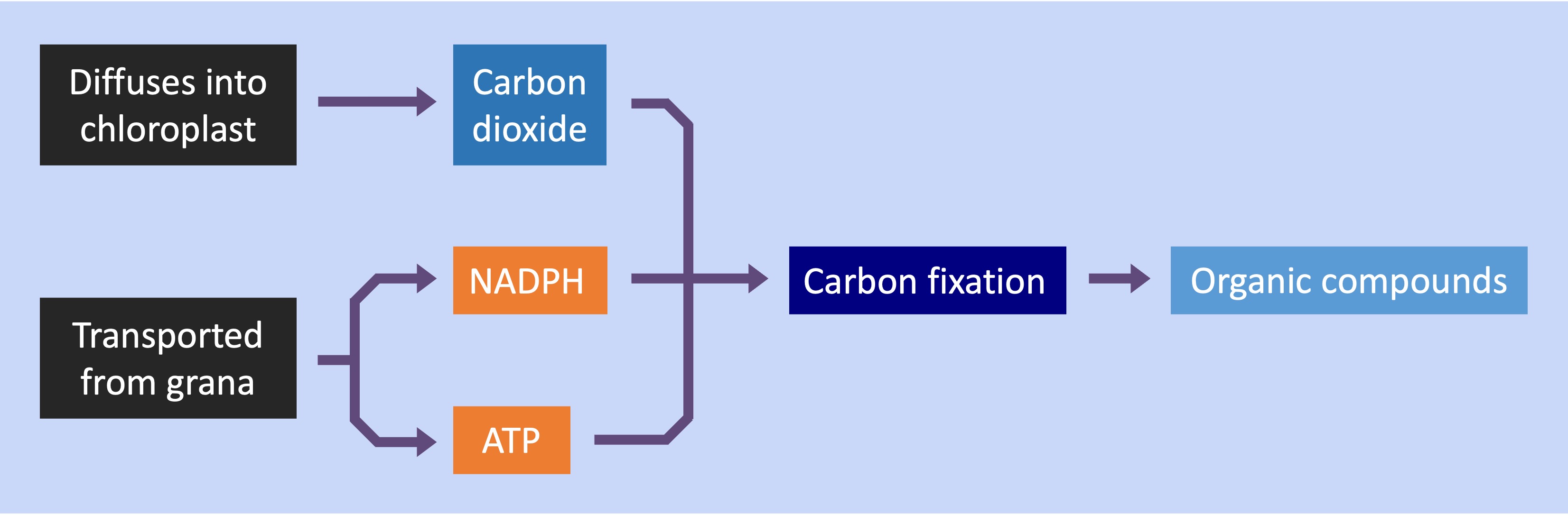
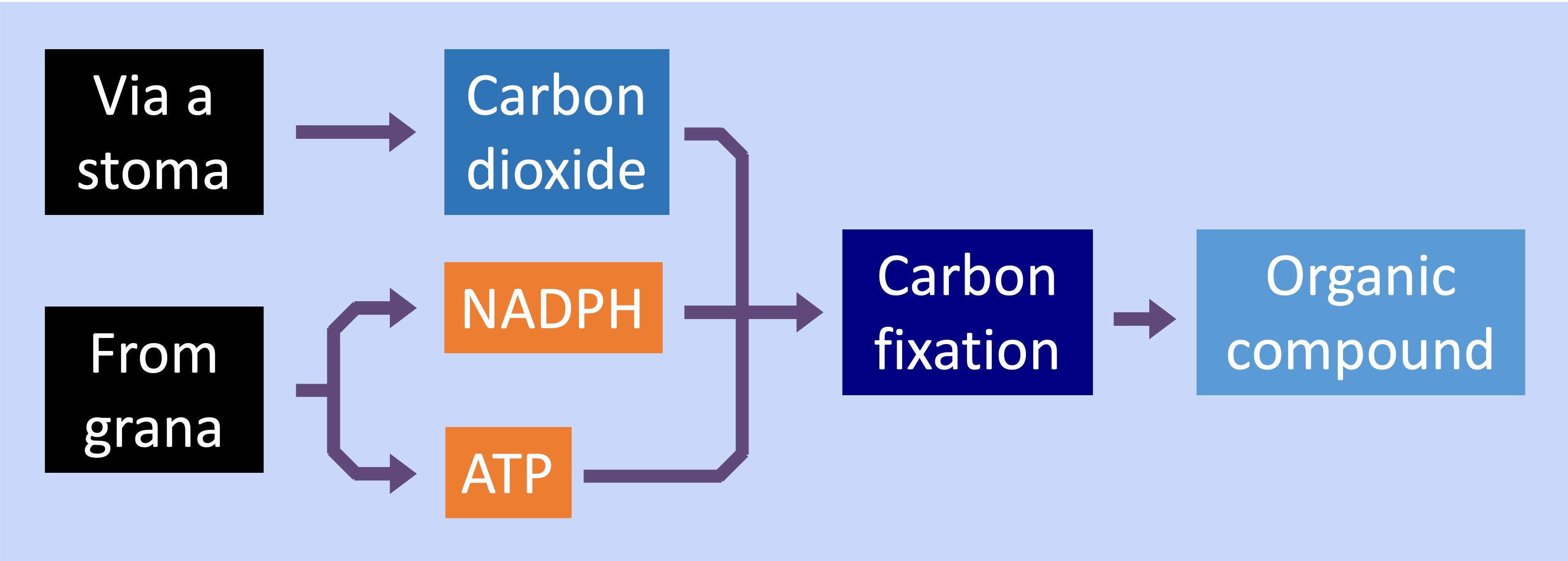
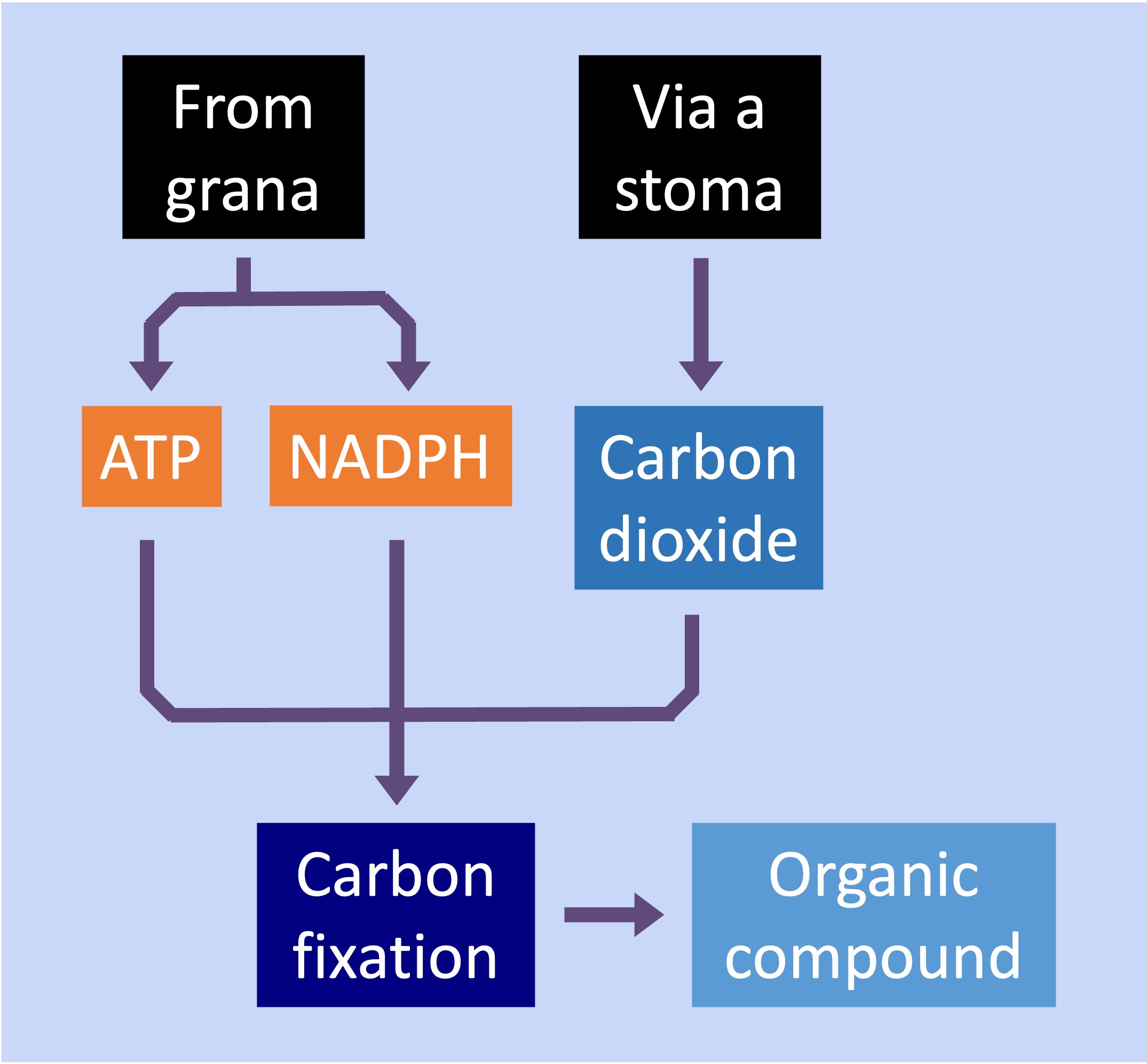
In plants, the light independent reactions occur within the fluid-filled interior of the chloroplast called the stroma
-
ATP and hydrogen (carried by NADPH) are transferred to the site of the light independent reactions
-
The hydrogen is combined with carbon dioxide to form complex organic compounds (e.g. carbohydrates, amino acids, etc.)
-
The carbon is fixed by the enzyme Rubisco, with ATP providing the chemical energy required to join the molecules together
-
This process is also commonly known as the Calvin cycle