Leaves
The leaves of a plant play a key role in photosynthesis and function as the site of both light absorption and gas exchange
-
Leaves are typically broad, flat and thin to maximise their surface area and optimise rates of photosynthesis
-
Most leaves are green due to the abundance of chlorophyll, however some leaves may have different colours (due to the presence of accessory pigments)
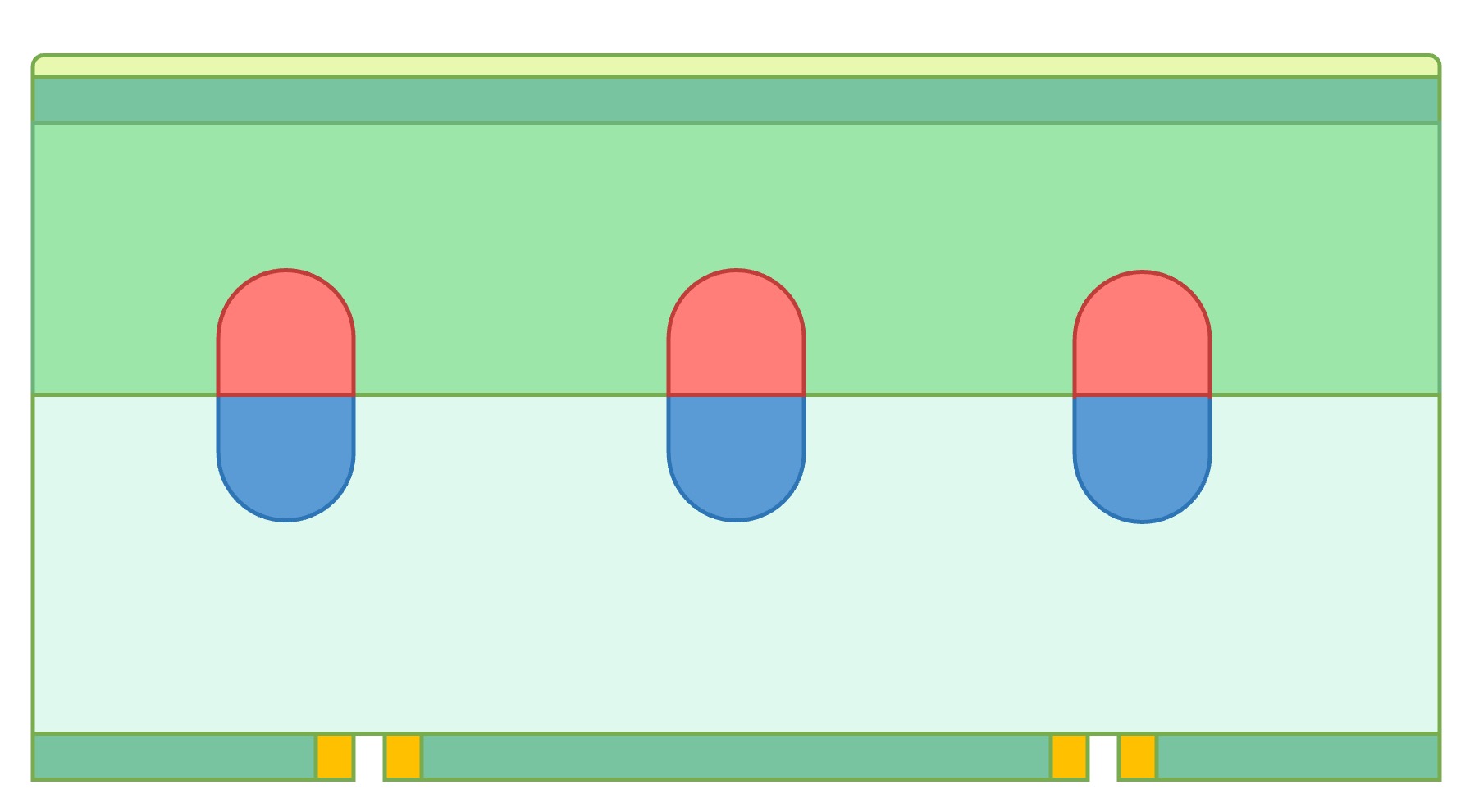
The outer surface of the leaf is composed of a thin layer of tissue called the epidermis
-
A waxy cuticle covers the epidermis to provide an impenetrable hydrophobic barrier (prevents water loss)
-
The lower epidermis is perforated with stomatal pores to facilitate the exchange of respiratory gases and water vapour
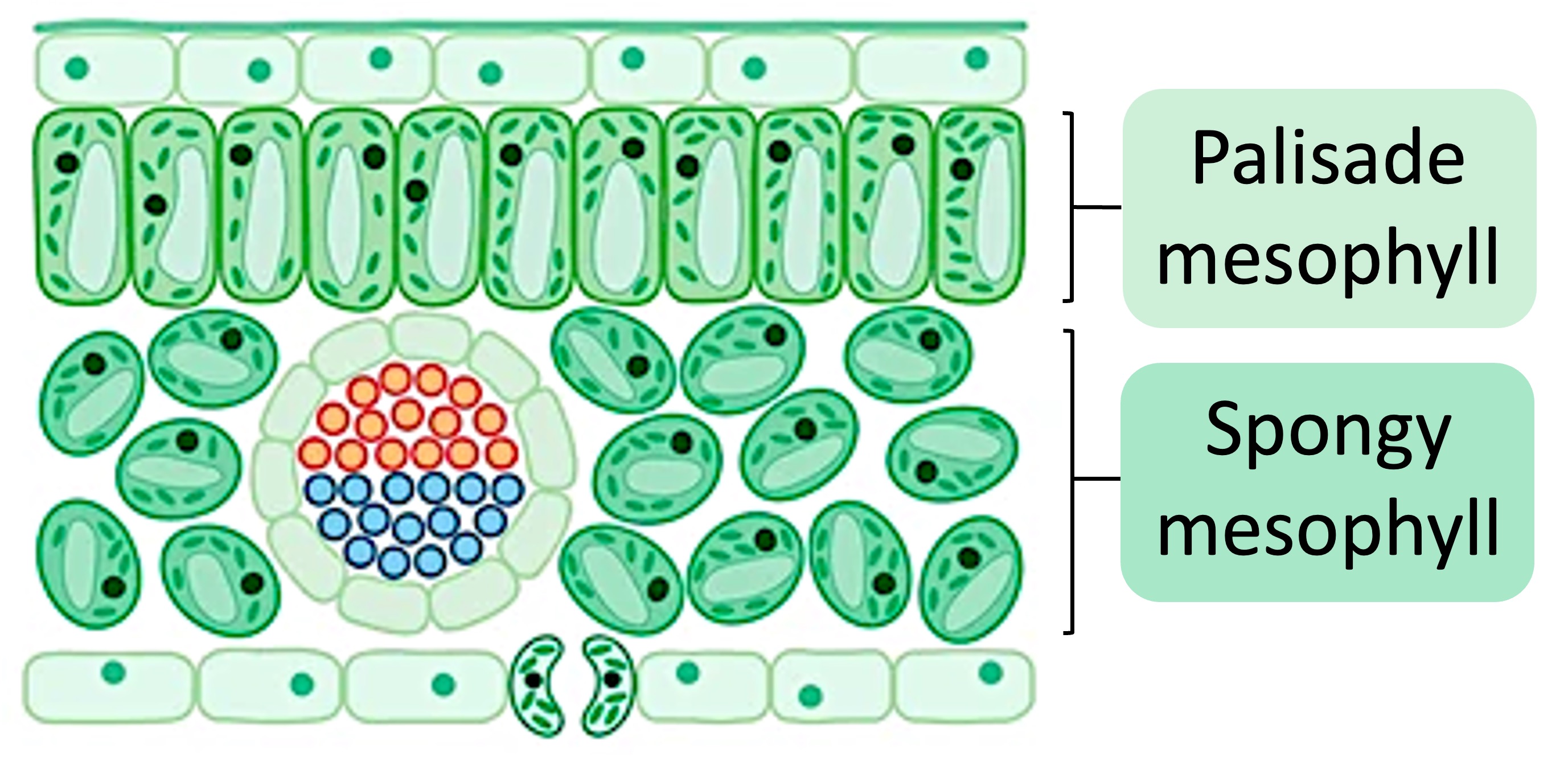
The interior of a leaf is composed of a layer of tissue called the mesophyll – which is organised into two sections:
-
The cells of the palisade mesophyll are tightly packed and rich in chloroplasts (optimised for photosynthesis)
-
The cells of the spongy mesophyll are loosely packed between intercellular air spaces (maximising gas exchange)
Leaves are extensively vascularised, with the veins made up of vascular bundles containing both xylem and phloem
-
The xylem functions to transport water and minerals from within the roots of the plant (via transpiration)
-
The phloem transports dissolved sugars produced by photosynthesis to other parts of the plant (as sap)
Leaf Cross-Section

Leaf Anatomy
The tissues in a leaf are specifically distributed to maximise the processes of photosynthesis and gas exchange
-
The waxy cuticle covers the exterior surface in order to prevent water loss from the leaf (except via stomata)
-
The palisade mesophyll is located on the upper half of the leaf (facing sunlight) to maximise light absorption
-
The spongy mesophyll is located on the lower half (near stomata) and contains air spaces for gas exchange
-
The stomata are on the underside of the leaf to prevent obstruction and maintain an open channel for gases
-
The vascular bundle is located centrally to allow for optimal access by all leaf tissue (palisade and spongy)
Leaf Tissue Distribution

Leaf Histology