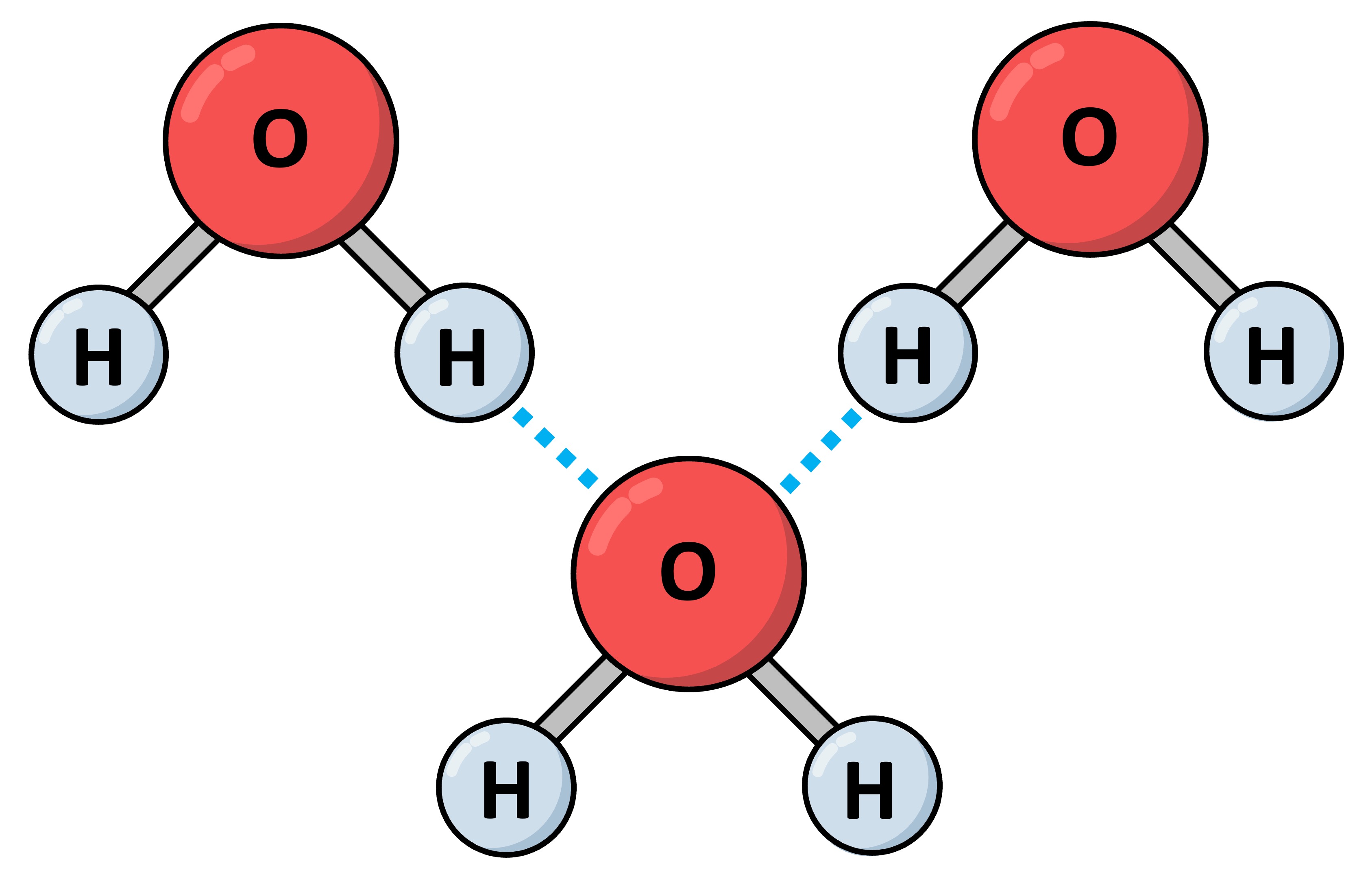
Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular associations formed as a consequence of the polar covalent bonds within water molecules
-
These bonds form when a δ+ hydrogen atom is attracted to a δ– fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen atom of another molecule
-
Hydrogen bonds are stronger than standard polar associations due to the particularly high electronegativity of F, O and N
Hydrogen bonding is responsible for several unique properties of water – including thermal, cohesive and solvent properties
Hydrogen Bonding