Hormone Signalling
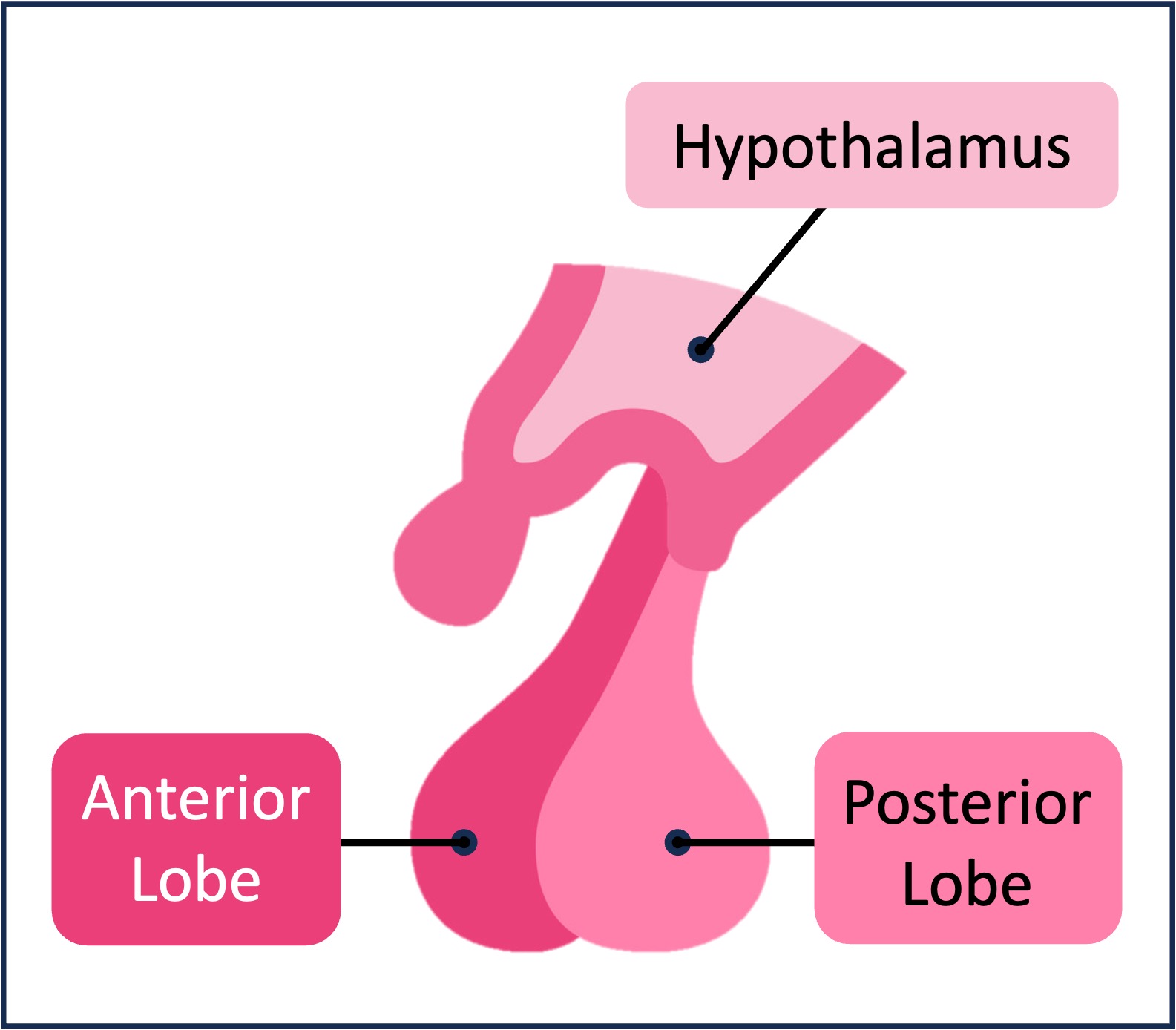
The nervous system and endocrine system are linked by a section of the brain called the hypothalamus
-
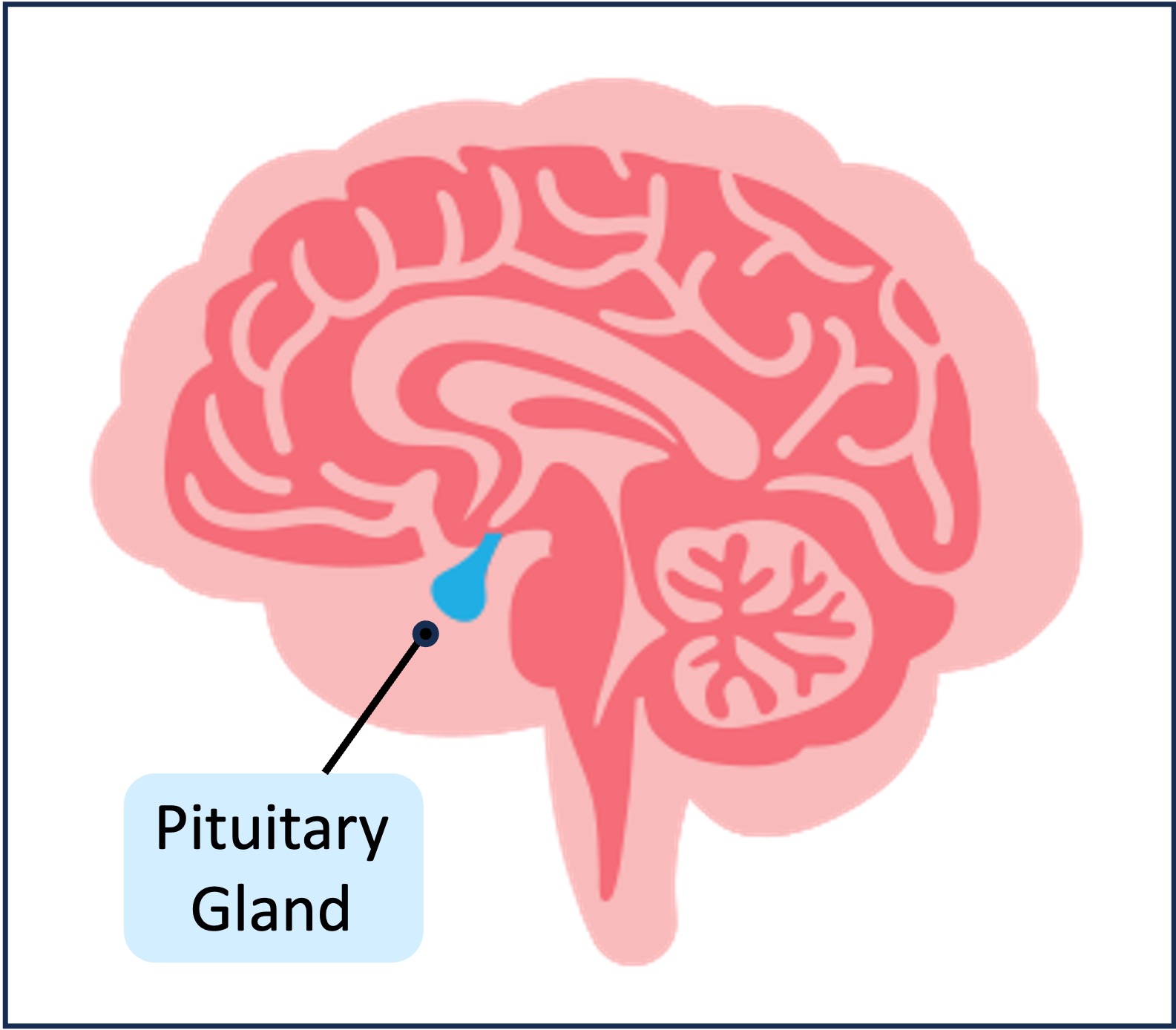
The hypothalamus acts as a homeostatic control centre and regulates hormonal secretion via the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland lies adjacent to the hypothalamus and consists of two lobes (anterior and posterior lobes)
-
The hypothalamus produces releasing factors which trigger the release of certain hormones synthesised in the anterior lobe
-
The hypothalamus also produces certain hormones which are directly released from the posterior lobe (via neurosecretory cells)
Pituitary Gland
Endocrine Signalling
The pituitary gland is often referred to as the ‘master gland’, as it controls the secretion of hormones from a number of other endocrine glands
-
Pituitary hormones will often target endocrine glands in other organs (e.g. gonads, pancreas, thyroid, mammary gland)
Examples of endocrine glands include:
-
Pancreas – Releases insulin and glucagon to regulate glucose concentrations within the bloodstream
-
Adrenal gland – Releases adrenaline (epinephrine) to stimulate 'fight or flight’ responses within the body
-
Thyroid gland – Releases thyroxin to increase metabolic activity and produce heat (for thermoregulation)
-
Gonads – Release sex hormones from either testes (testosterone) or ovaries (oestrogen and progesterone)
-
Pineal gland – Releases melatonin to regulate circadian rhythms (day-night cycles for sleeping and waking)
Endocrine Glands