Heterotrophs
Heterotrophs obtain their organic molecules from other organisms – this mode of nutrition can be holozoic or saprotrophic
-
In holozoic nutrition, organic matter is ingested and then digested internally, before being absorbed and assimilated
Holozoic Nutrition
All animals undertake holozoic nutrition but may be distinguished according to their feeding patterns:
-
Consumers feed on living or recently killed organisms (includes herbivores, carnivores and omnivores)
-
Scavengers feed on dead and decaying carcasses rather than hunting live prey (e.g. hyenas, carrion birds)
-
Detritivores feed on non-living organic matter – such as detritus and leaf litter (e.g. beetles, crabs, earthworms)
Types of Heterotrophs
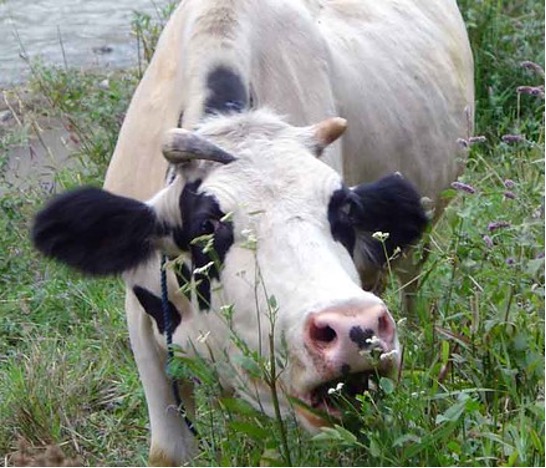

Consumer
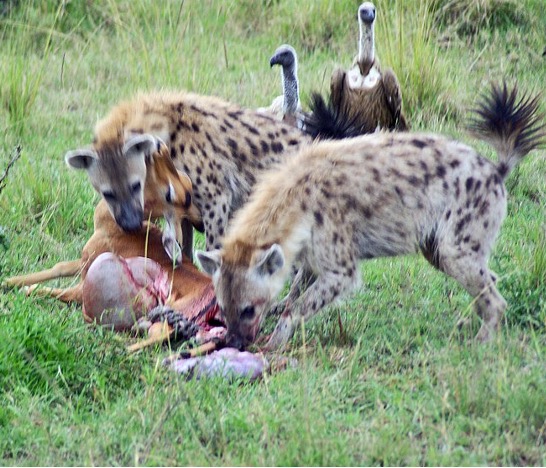

Scavenger
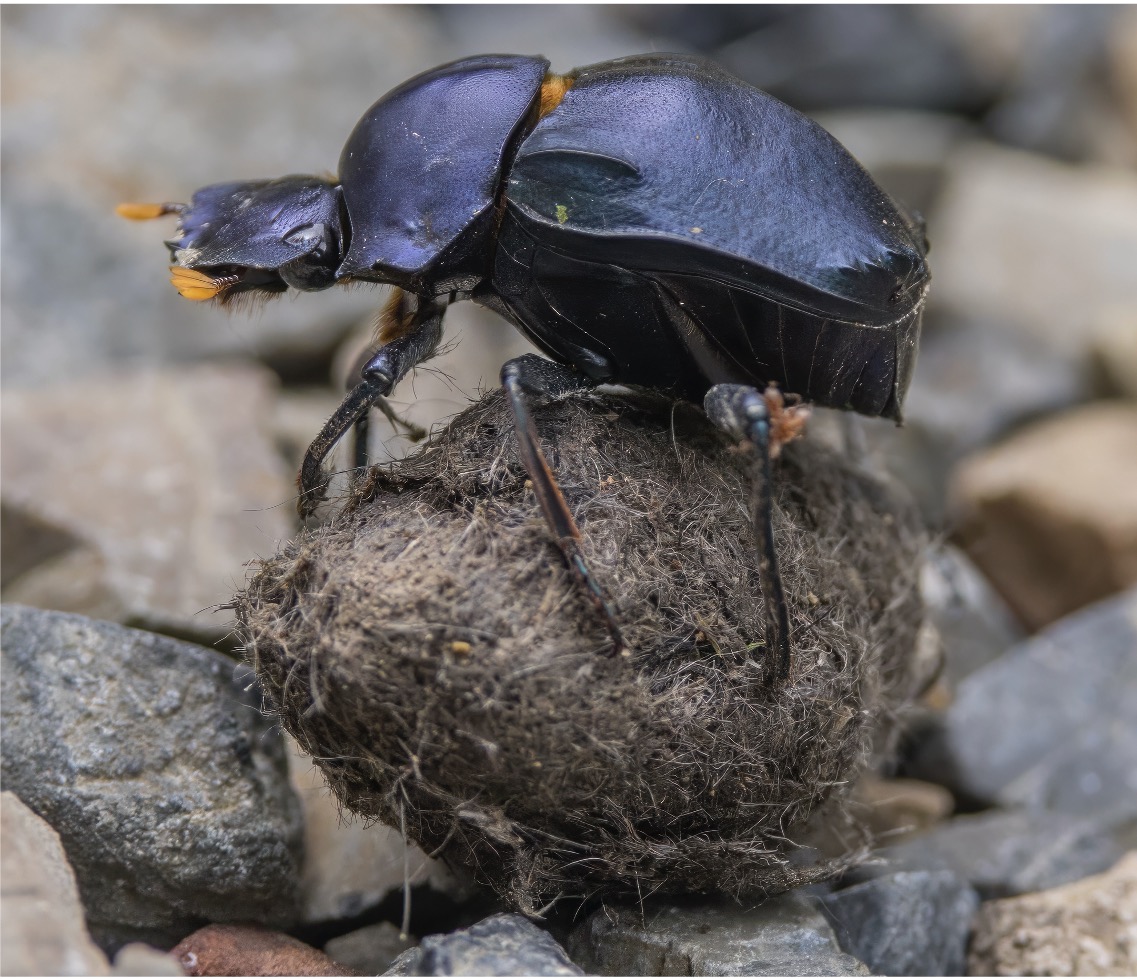

Detritivore
Saprotrophic Nutrition
In saprotrophic nutrition, organisms live on (or in) non-living organic matter and secrete digestive enzymes to break the material down externally
-
Saprotrophs are referred to as decomposers and include bacteria, fungi and molds
-
Saprotrophs play an important role in recycling nutrients and wastes within an ecosystem
Types of Saprotrophs
Bacteria
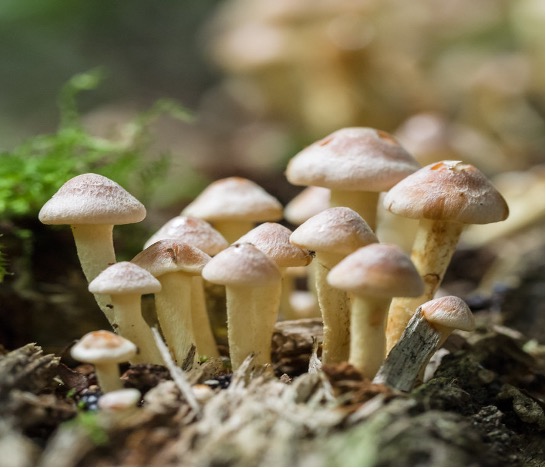

Fungi