Heart
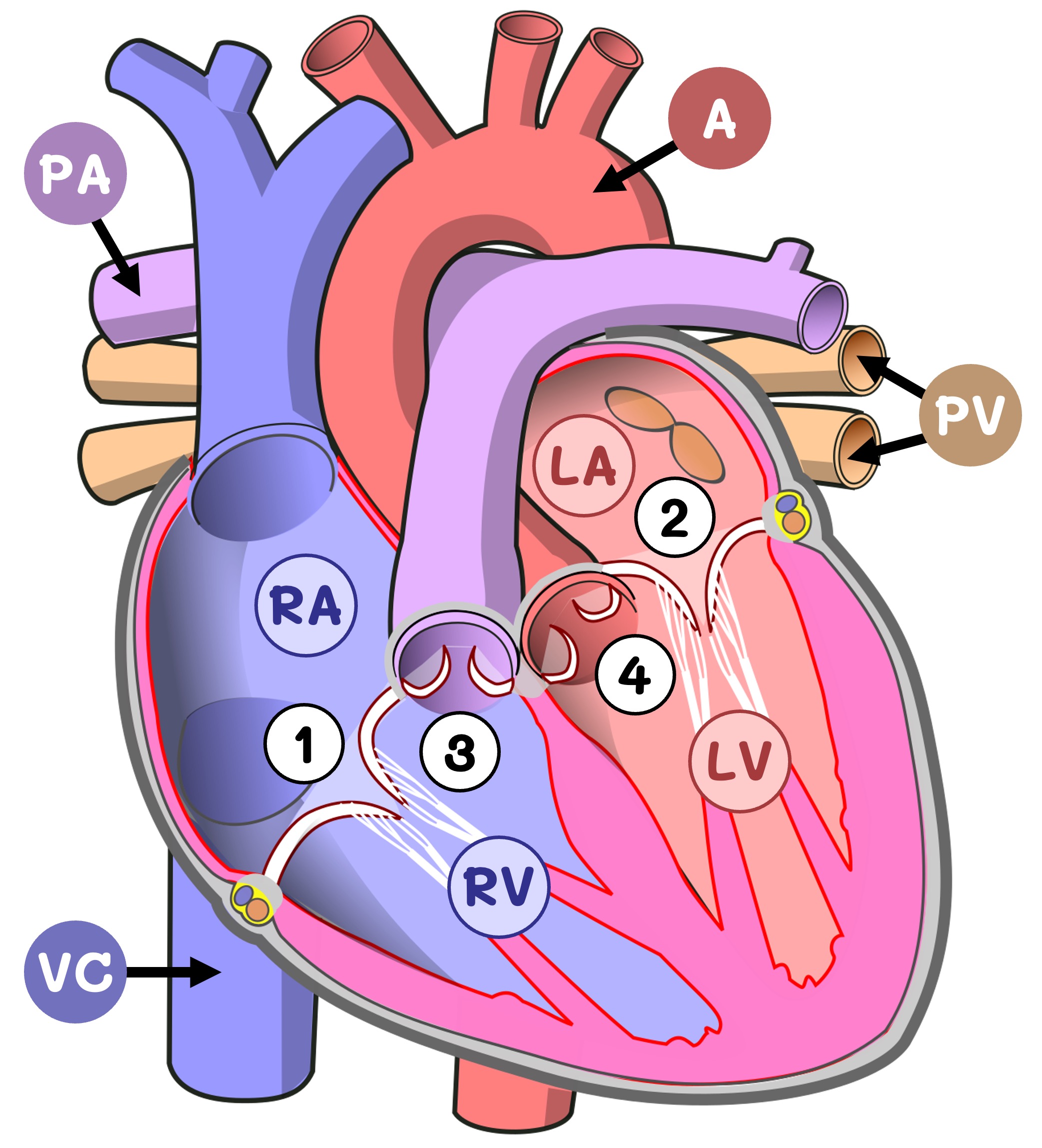
Mammalian hearts are muscular organs that have two distinct sides (left and right) separated by a central septum
-
The left side of the heart transports deoxygenated blood from the body to the lungs (pulmonary circulation)
-
The right side of the heart transports oxygenated blood from the lungs to the body tissues (systemic circulation)
The mammalian heart consists of a number of recognisable structures, including chambers, blood vessels and valves
-
The heart tissue consists of cardiac muscle fibres (for contraction) which are sustained by a surrounding network of coronary vessels (provides nutrition)
Chambers
-
Two smaller chambers called atria (singular = atrium) are positioned near the top of the heart and function to collect blood from the body and lungs
-
Two larger chambers called ventricles connect to the bottom of the atria and pump the collected blood to either the body or the lungs
Heart Valves
-
Atrioventricular valves are situated between the atria and ventricles (biscupid valve on the left; tricuspid valve on the right)
-
Semilunar valves are situated between the ventricles and arteries (aortic valve on the left; pulmonary valve on the right)
Blood Vessels
-
The vena cava (superior and inferior) feeds into the right atrium and returns deoxygenated blood from the body
-
The pulmonary artery connects to the right ventricle and sends the deoxygenated blood to the lungs
-
The pulmonary vein feeds into the left atrium and returns oxygenated blood from the lungs
-
The aorta extends from the left ventricle and sends oxygenated blood to the tissues around the body
A heart is labelled as it would appear in a chest, so the left side of an image represents the right side of the heart (and vice versa)
-
The left ventricle pumps blood around the entire body and so has a noticeably thicker muscle layer (myocardium) than the right ventricle
Structure of the Heart