Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (also known as Golgi complex or Golgi body) is responsible for sorting, storing, modifying and exporting cellular material
-
It is composed of a series of flattened sacs (called cisternae) that are located between the ER (cis facing) and the plasma membrane (trans facing)
-
Proteins (from rough ER) and lipids (from smooth ER) arrive in vesicles at the Golgi body and are modified into functional molecules
-
The different sacs are responsible for specific chemical modifications based on the enzymes involved (e.g. phosphorylation, glycosylation, etc.)
-
Secretory proteins, glycoproteins, cell membrane proteins, lysosomal proteins, and some glycolipids all pass through the Golgi apparatus
-
In plant cells, much of the cell wall material passes through the Golgi apparatus as well
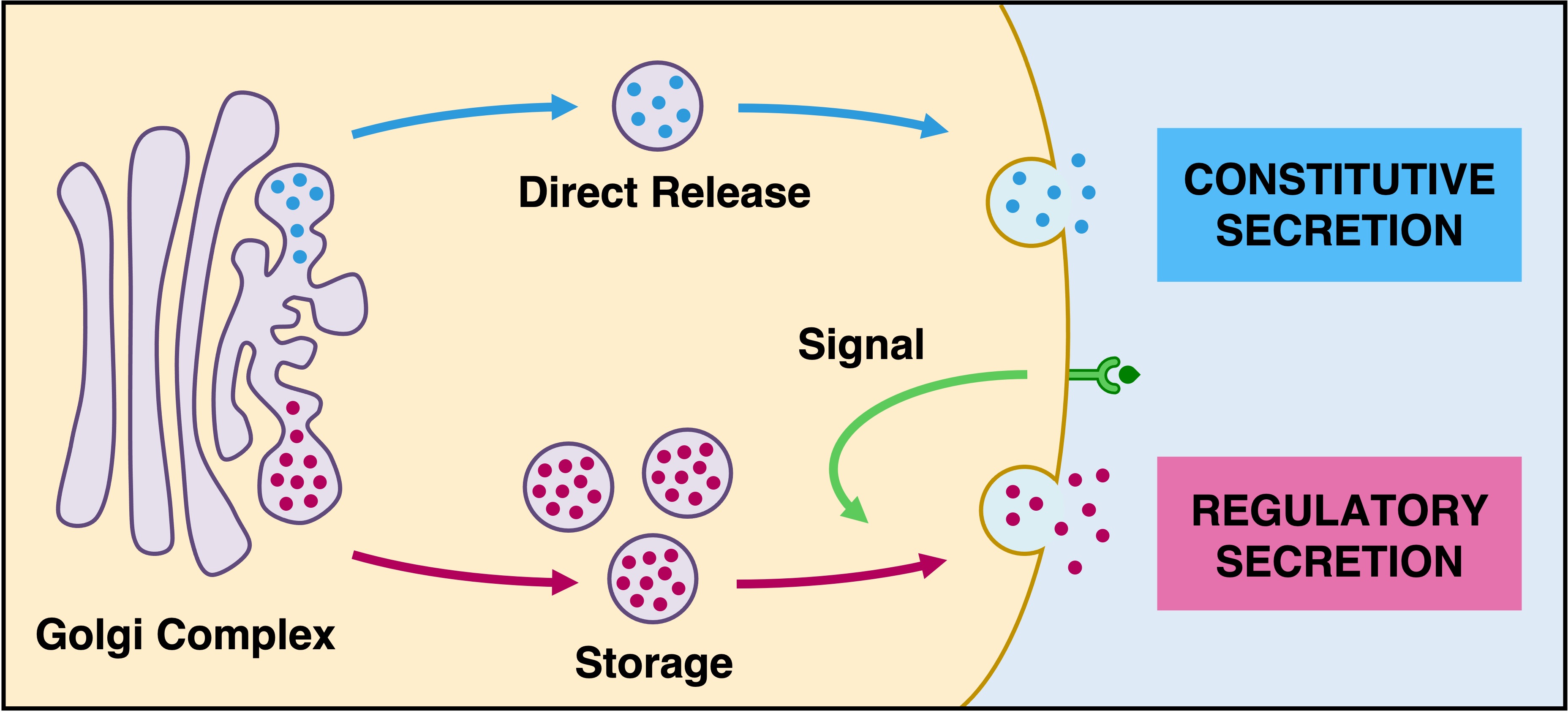
Materials destined for secretion are packaged into vesicles at the Golgi body for extracellular release (exocytosis)
-
These materials can be either released immediately (constitutive secretion) or stored in secretory vesicles for a sustained release (regulatory secretion)
-
Regulatory secretion is triggered by an external chemical signal (ligand) binding to a specific receptor
Golgi Secretion