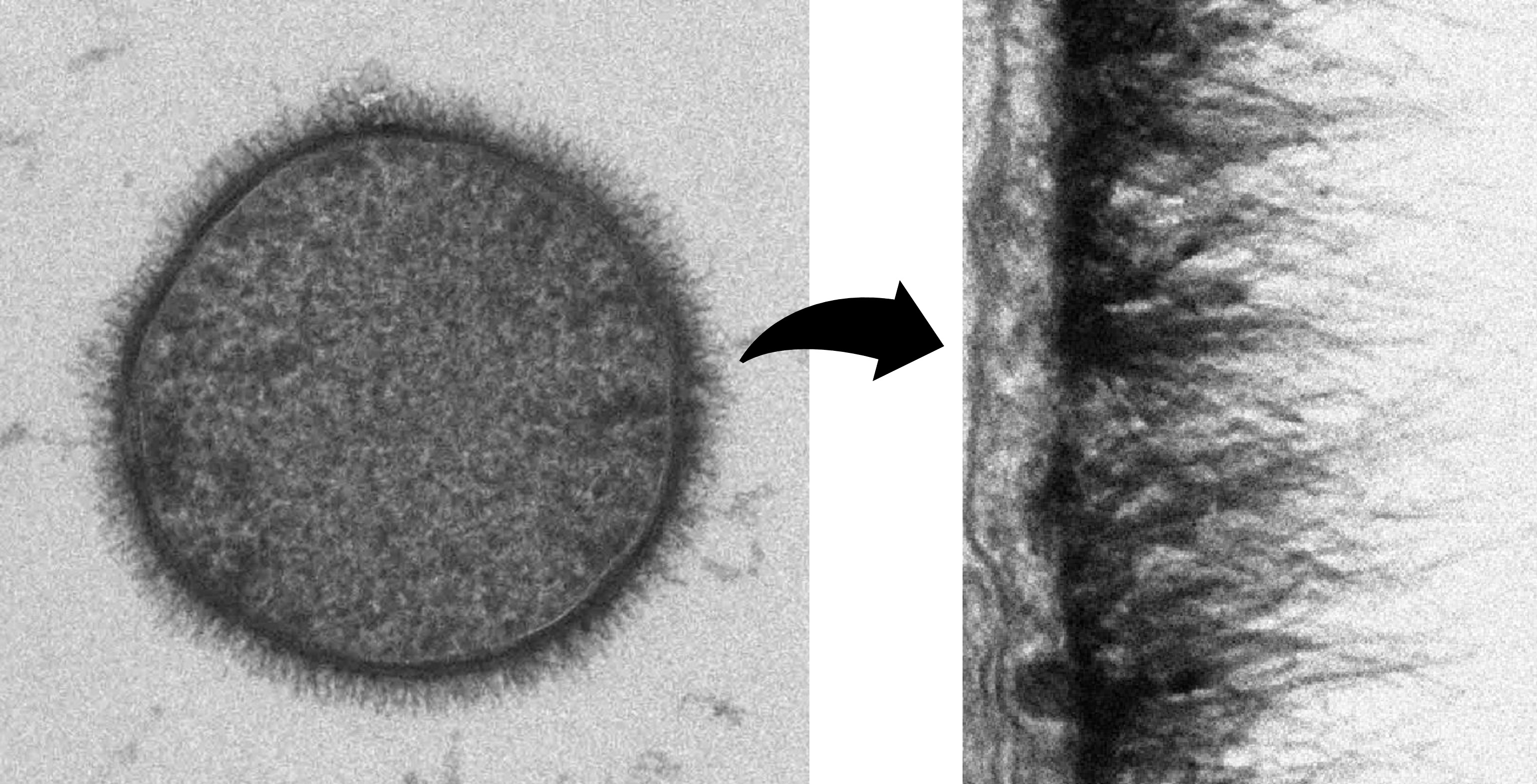
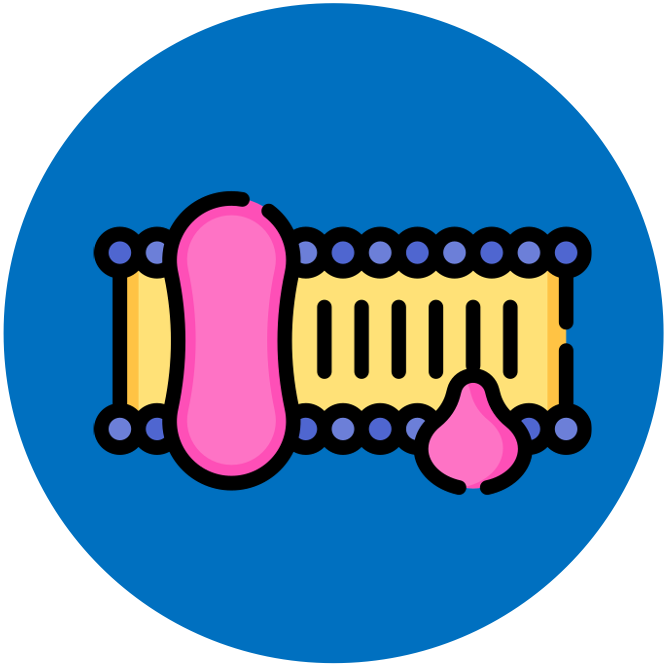
Glycosylation
Phospholipids and membrane proteins can have carbohydrate chains attached via the process of glycosylation ('glyco’ = sugar)
-
Glycosylation of a phospholipid results in a glycolipid while glycosylation of a membrane protein produces a glycoprotein
The carbohydrate chains are located on the extracellular side of the membrane and play important roles in cell adhesion and cell recognition
-
The surface carbohydrates can serve as an attachment point for other cells (e.g. sperm binding to an egg is mediated by glycoproteins)
-
The surface carbohydrates can also act as a point of recognition between cells (e.g. the ABO blood group antigens are glycolipids)
Glycoproteins and glycolipids also play an important role in maintaining the structural integrity of the extracellular matrix
-
The extracellular matrix is a network for external molecules that provide structure and biochemical support to surrounding cells
-
The carbohydrate chains can link these extracellular molecules together to help make the matrix a cohesive network
Ovum Glycocalyx (Sugar Coat)