Global Warming
The global warming resulting from anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions has a positive feedback effect on the climate condtions on Earth
-
A positive feedback loop is involves the output of a process reinforcing the stimulus, thereby amplifying the deviation from equilibrium
-
In this case, higher temperatures lead to more global warming – which is further destablising the ecosystem
There are several factors that contribute to the positive feedback cycle of global warming
-
These include the release of carbon dioxide by the oceans, a loss of reflective ice, accelerating rates of decomposition and higher frequencies of droughts and fires
Oceans as a Carbon Sink
-
The ocean acts as a carbon sink and absorbs more than a quarter of all anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions
-
The solubility of carbon dioxide in water is temperature dependent – it is more soluble when cooler, so less CO2 is absorbed when temperatures are higher
-
As global temperatures rise, dissolved carbon dioxide will be released from the deep ocean, further amplifying the enhanced greenhouse effect
Loss of Reflective Ice and Snow
-
The extent to which a surface reflects light is referred to as the albedo (the more light reflected, the higher the albedo
-
Light coloured surfaces (such as ice and snow) reflect more light and have a higher albedo than exposed rock or soil
-
Global warming is causing polar ice caps to melt, meaning more solar energy (i.e. heat) is being absorbed – this is further increasing global temperatures
Decomposition of Permafrost
-
Permafrost is any ground that remains permanently frozen for two or more years – as permafrost melts, it exposes previously undecomposed organic matter
-
Decomposition releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, so higher rates of decomposition will increase the greenhouse effect
-
Melting permafrost also releases methane, as methanogenic microorganisms within the permafrost are no longer inactive at higher temperatures
Increased Droughts and Fires
-
Global warming increases the frequency of droughts, which dries out vegetation resulting in more wildfires
-
The burning of plant material releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and reduces the available forest cover for photosynthesis
-
This means carbon dioxide levels build within the atmosphere, contributing further to an enhanced greenhouse effect
Global Warming Contributors

Deep Ocean

Loss of Ice

Permafrost

Bushfires
Boreal Forests
A carbon sink is a component of an ecosystem that absorbs more carbon from the atmosphere than it releases
-
If global warming alters this carbon sequestration process then it could trigger a tipping point whereby the climate changes irreversibly
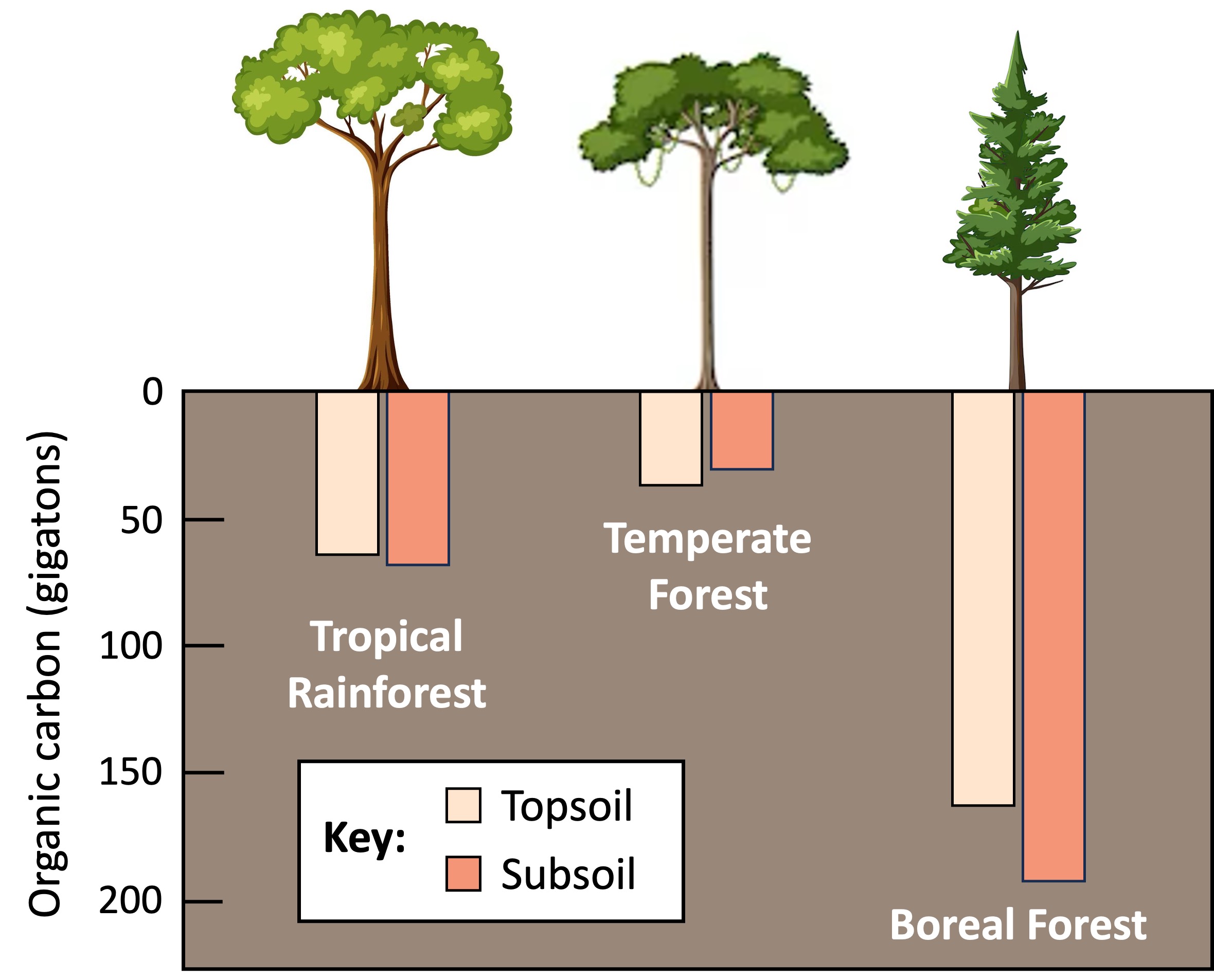
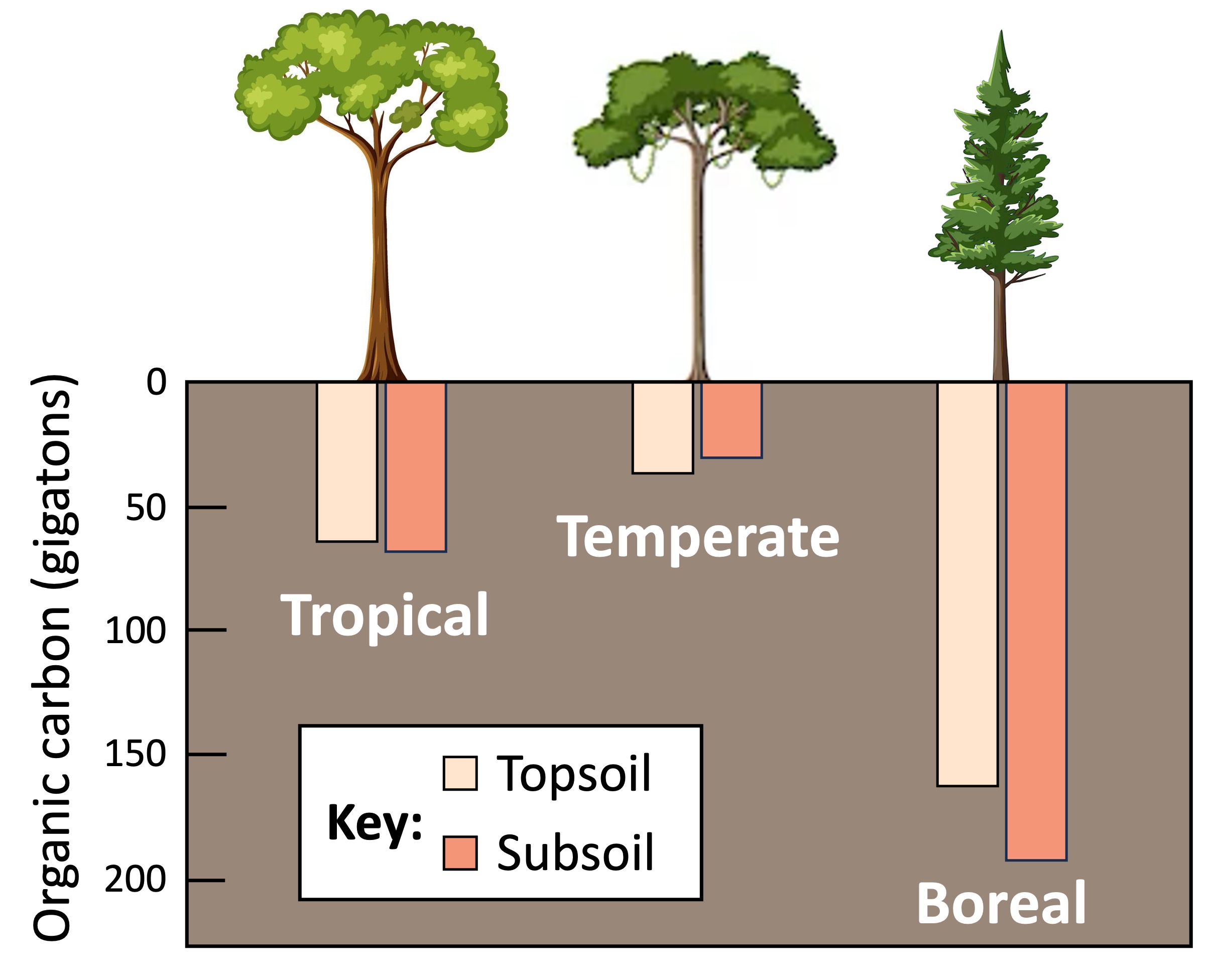
Boreal forests (taigas) normally act as a carbon sink and store carbon as organic matter within the soil
-
Because the climate is cold in a boreal forest, the rate of decomposition is decreased (saprotrophic organisms are inactive at low temperatures)
-
As the rate of decomposition is lower than the rate of photosynthesis, more carbon dioxide within the atmosphere is being absorbed than released
-
The carbon dioxide converted into organic material becomes trapped within the soil when the plant dies – it is estimated that over 80% of all carbon in a boreal forest is stored below ground
Global warming is changing boreal forests from being a carbon sink (net carbon accumulator) to a carbon source (net carbon releaser)
-
Warmer temperatures and decreased winter snowfall is leading to an increased incidence of drought
-
A reduced availability of water results in lower rates of photosynthesis, which decreases the primary productivity of the taiga
-
Prolonged drought conditions can also cause trees to wilt prematurely, with leaves and needles losing their photosynthetic pigments ('forest browning')
-
The drier conditions also increases the frequency and intensity of forest fires, releasing stored carbon back into the atmosphere ('legacy carbon combustion')
Carbon Storage