Gene Expression
The genome is the totality of genetic information of a cell, organism or organelle
-
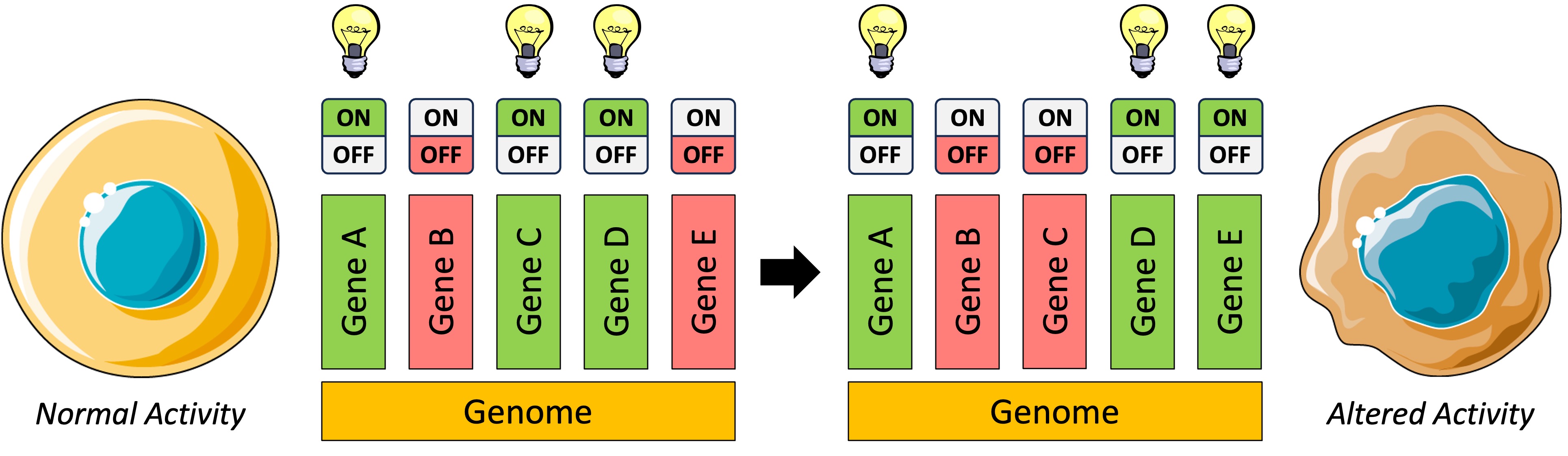
All cells of an organism share an identical genome – each cell contains the entire set of genetic instructions for that organism
Not all genes in a cell are expressed at any given time – genes can be switched on or off to give rise to different levels of protein synthesis
-
The expression of genes is determined by transcription – only genes that are transcribed will be active within the cell
-
Increasing transcription will lead to heightened expression of a gene, while decreasing transcription will reduce gene expression
By varying the levels of transcription, cellular activities can be controlled within a cell
-
Some genes may be permanently switched on or off within a cell (leading to cellular differentiation)
-
Other genes may be switched on or off in response to internal or external signals (regulating cellular activity)
Transcriptional Regulation