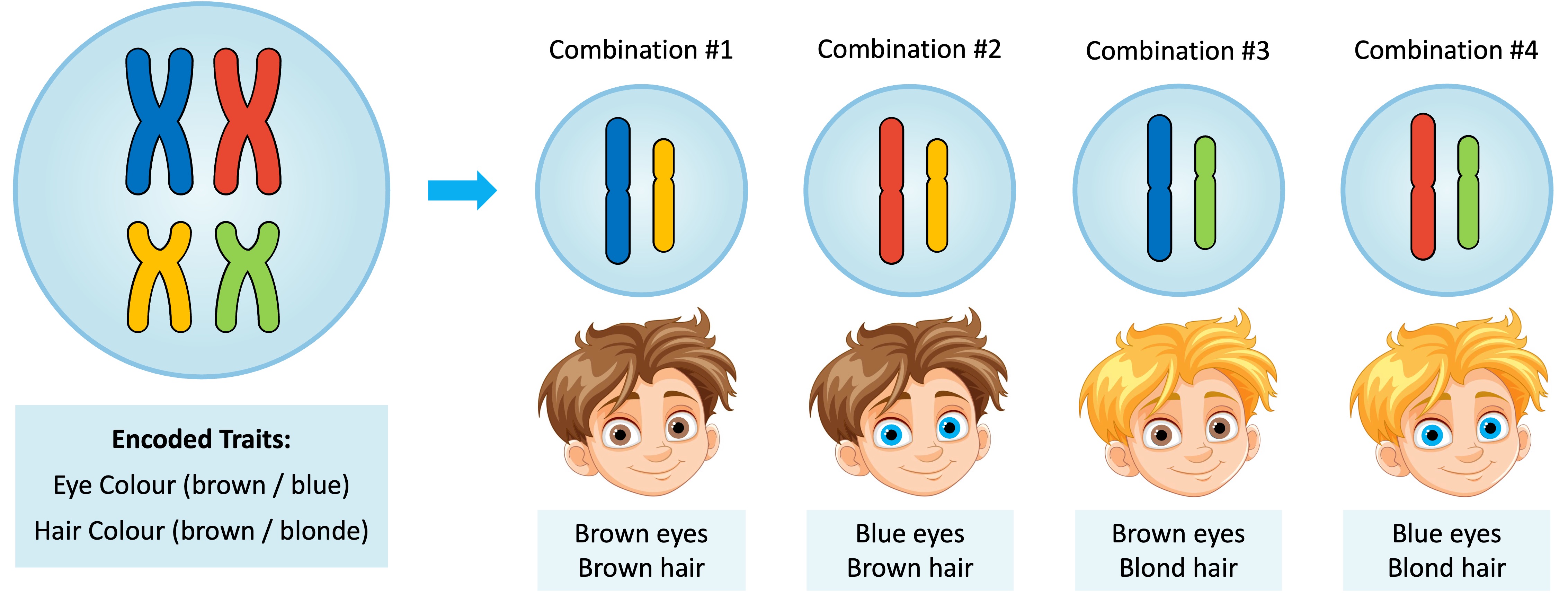
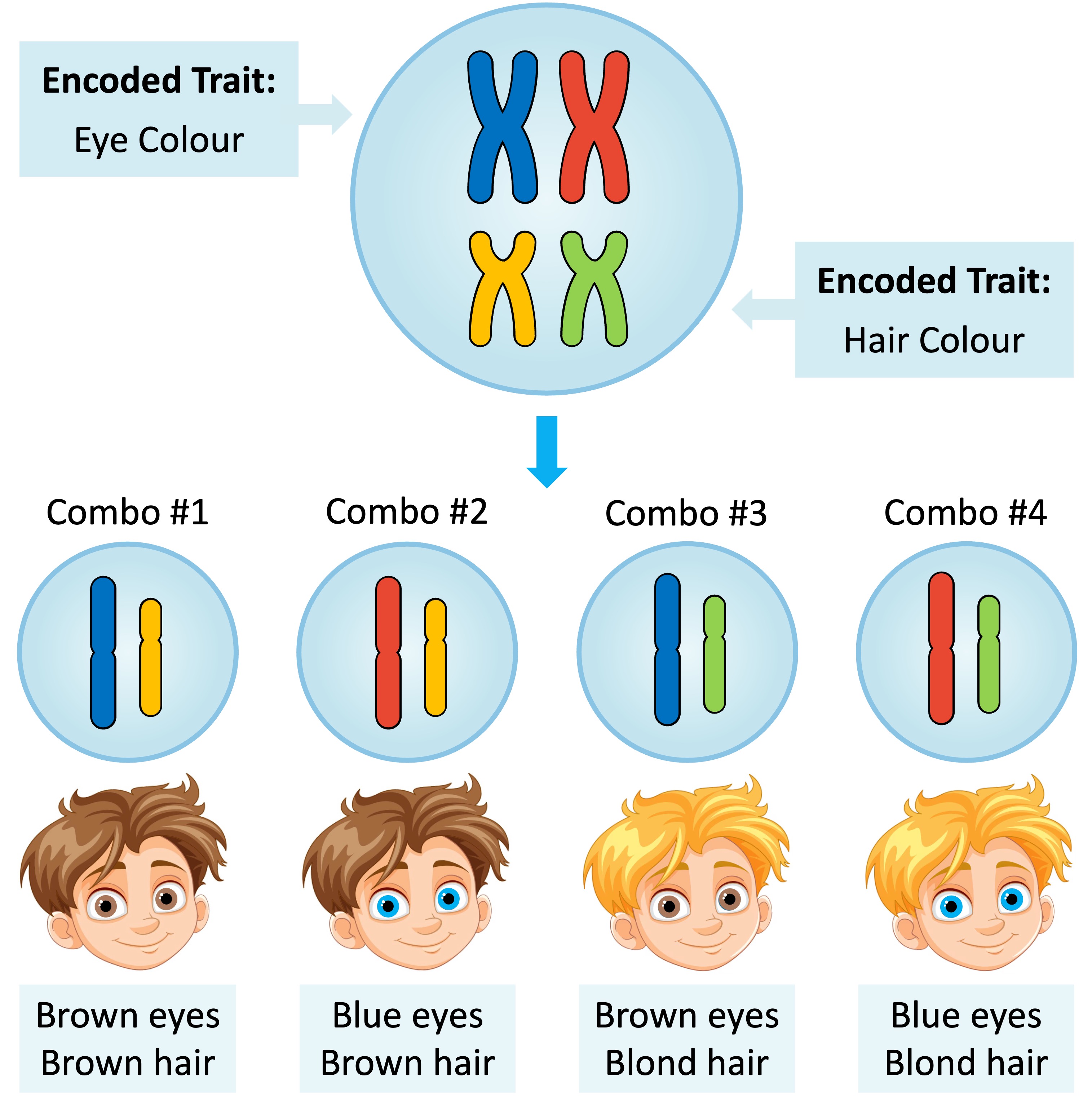
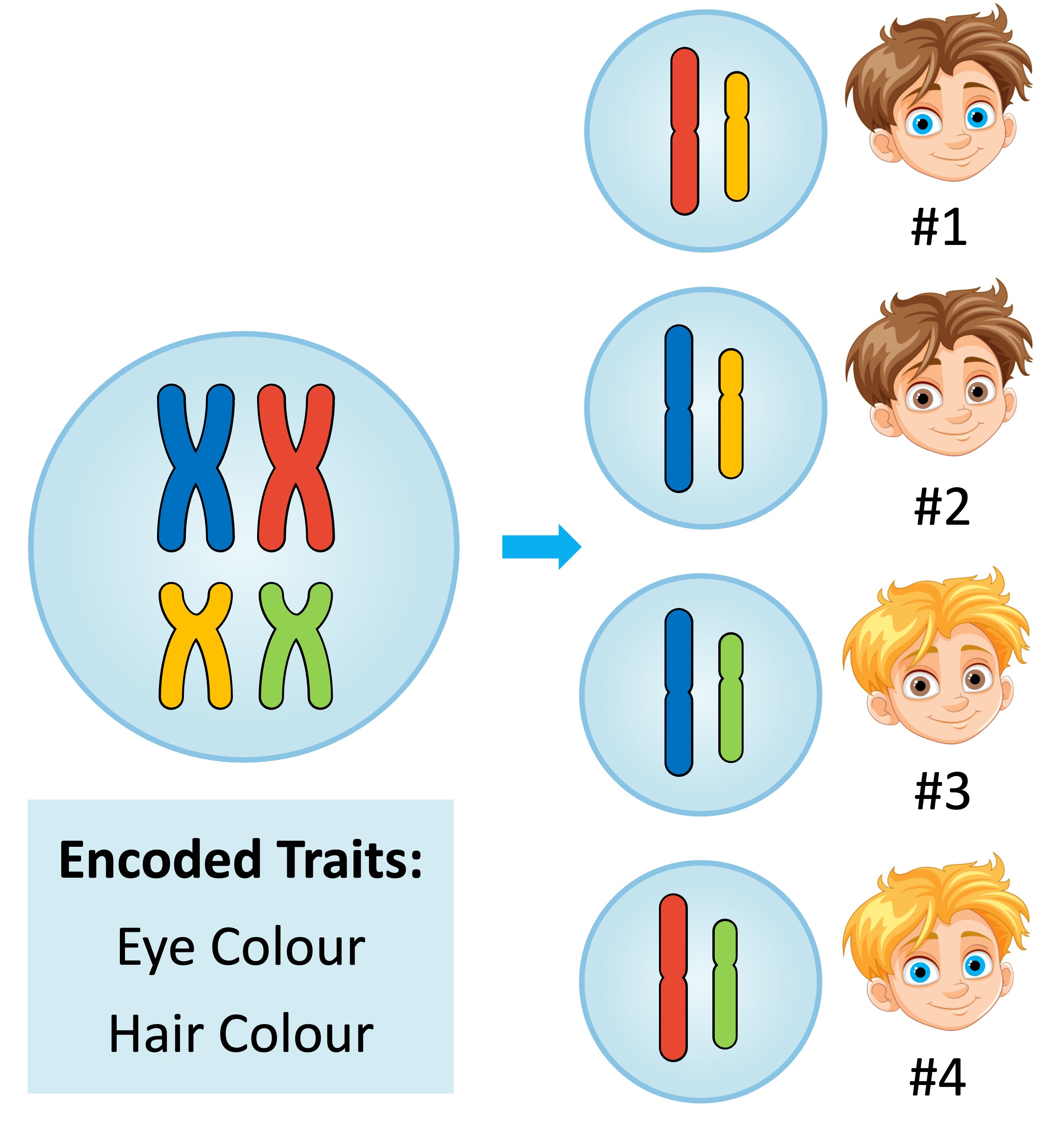
Gene Assortment
During meiosis, homologous chromosomes are separated to produce cells that are haploid (one copy of each chromosome)
-
The separation of homologous chromosomes (and their alleles) during anaphase of meiosis is called segregation
The segregation of each homologous pair in anaphase is random and is not affected by the segregation of any other homologous pair
-
This means an allele on one chromosome has an equal chance of being paired with, or separated from, any allele on another chromosome
-
The randomness of chromosome segregation creates variability in potential gametes (due to an increase in the number of potential allele combinations)
The random segregation of homologous chromosomes is known as the law of independent assortment
-
According to the law of independent assortment, the inheritance of one gene / trait will be independent to the inheritance of another gene / trait
-
This law only holds true for genes that are unlinked (on different chromosomes) – linked genes will not show independent assortment
Gene Assortment (n = 2)