Gametes
The sex cells involved in reproduction are called gametes and are produced in the gonads via gametogenesis
-
The male gametes are called spermatozoa (sperm) and are produced in the testes
-
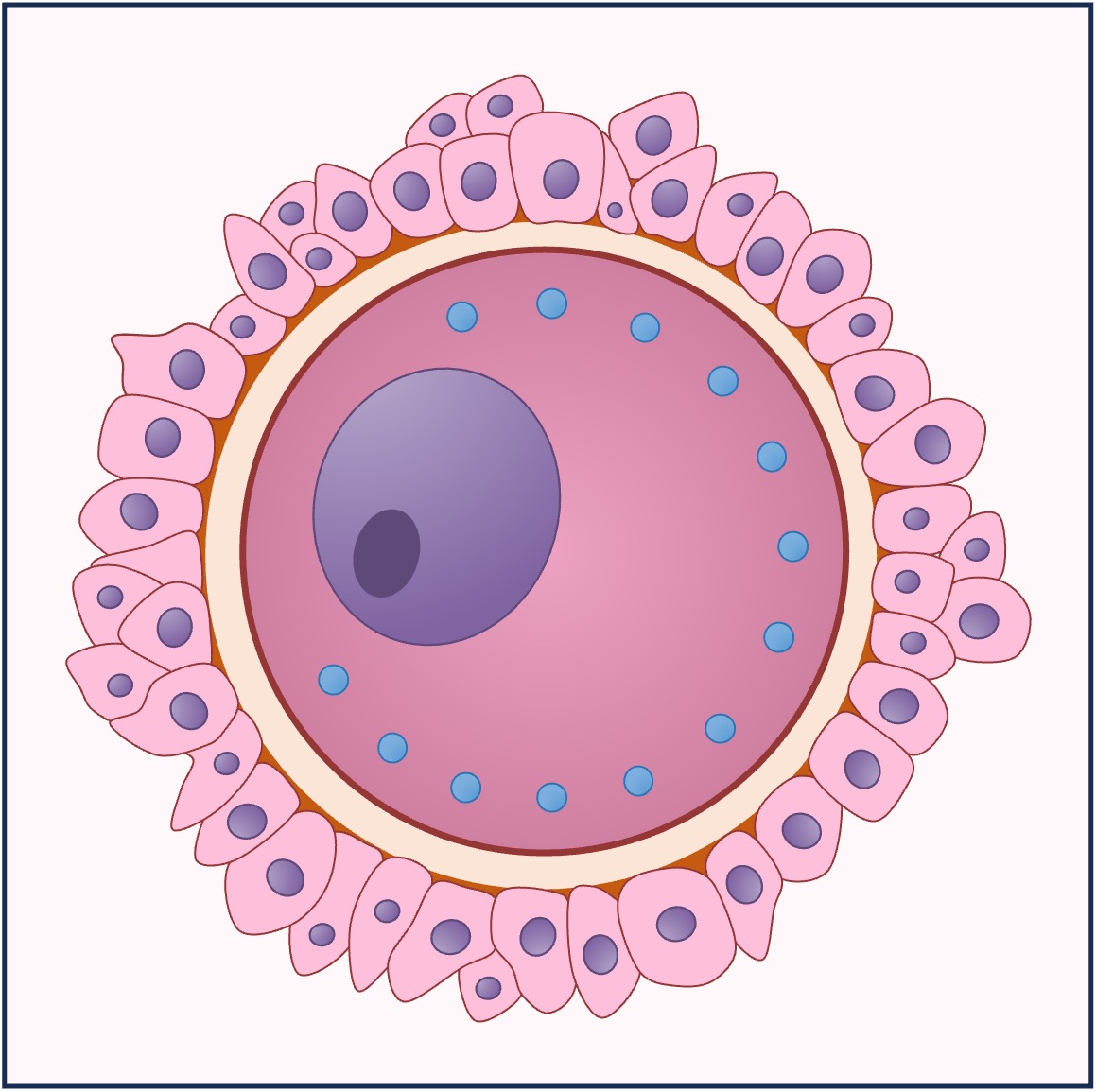
The female gametes are called ova (singular = ovum) and are produced in the ovaries
The male and female gametes have different roles, leading to morphological differences between them
-
The male gamete travels to the female gamete, so it is smaller and has less food reserves – it only contributes its DNA to the zygote
-
The female gamete is non-motile and much larger in size – it contributes all of the organelles within the cytoplasm of the zygote
Because of these functional differences, the process of gametogenesis is different in males and females
-
Males produce more gametes per germ cell than females (four sperm versus a solitary egg)
-
Sperm formation in males is life long (starting at puberty), while females only possess a fixed number of egg cells
Sperm and Egg
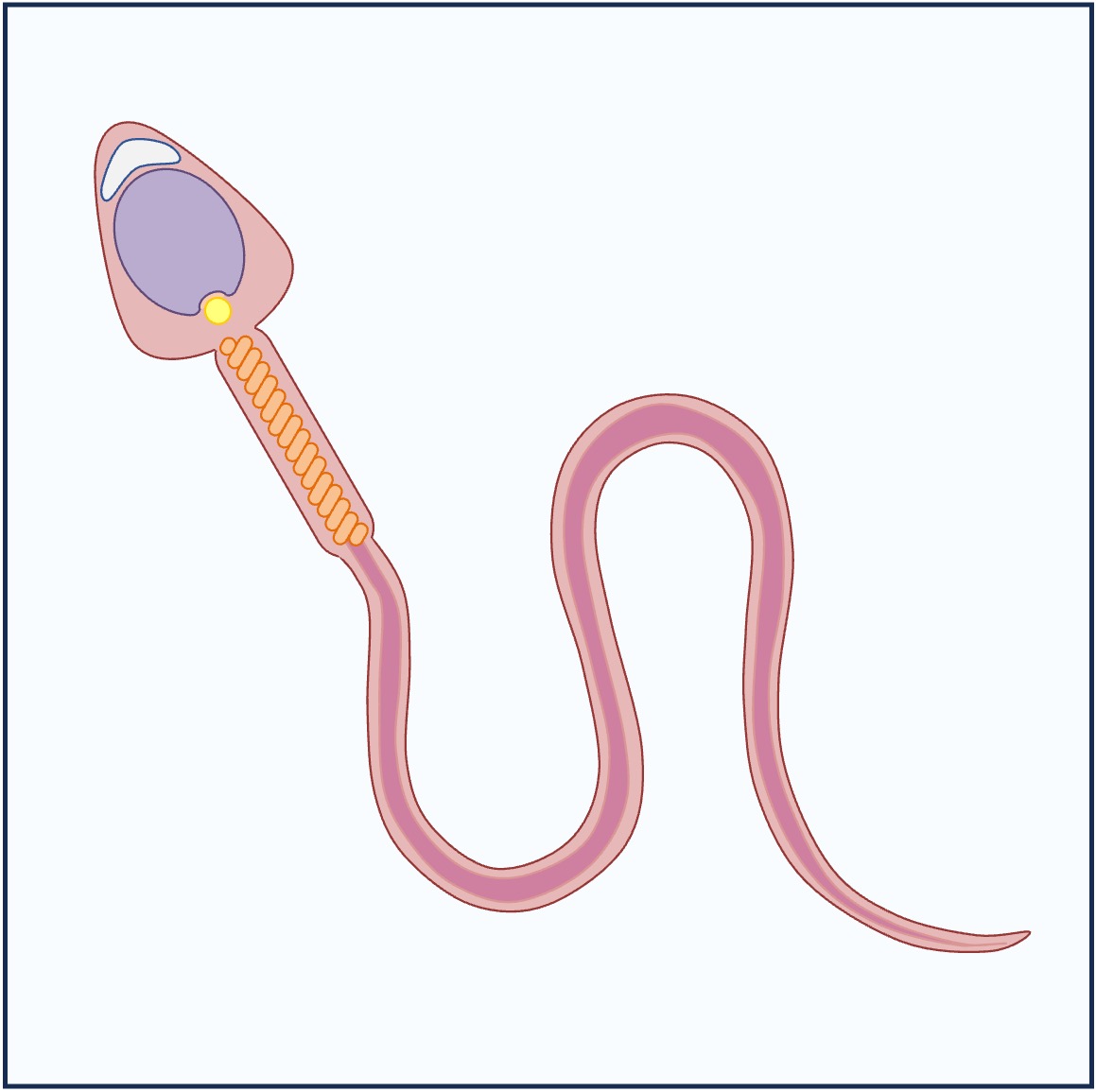
Spermatozoa