Eutrophication
Eutrophication describes the enrichment of an ecosystem with chemical nutrients (nitrates, phosphates, etc.)
-
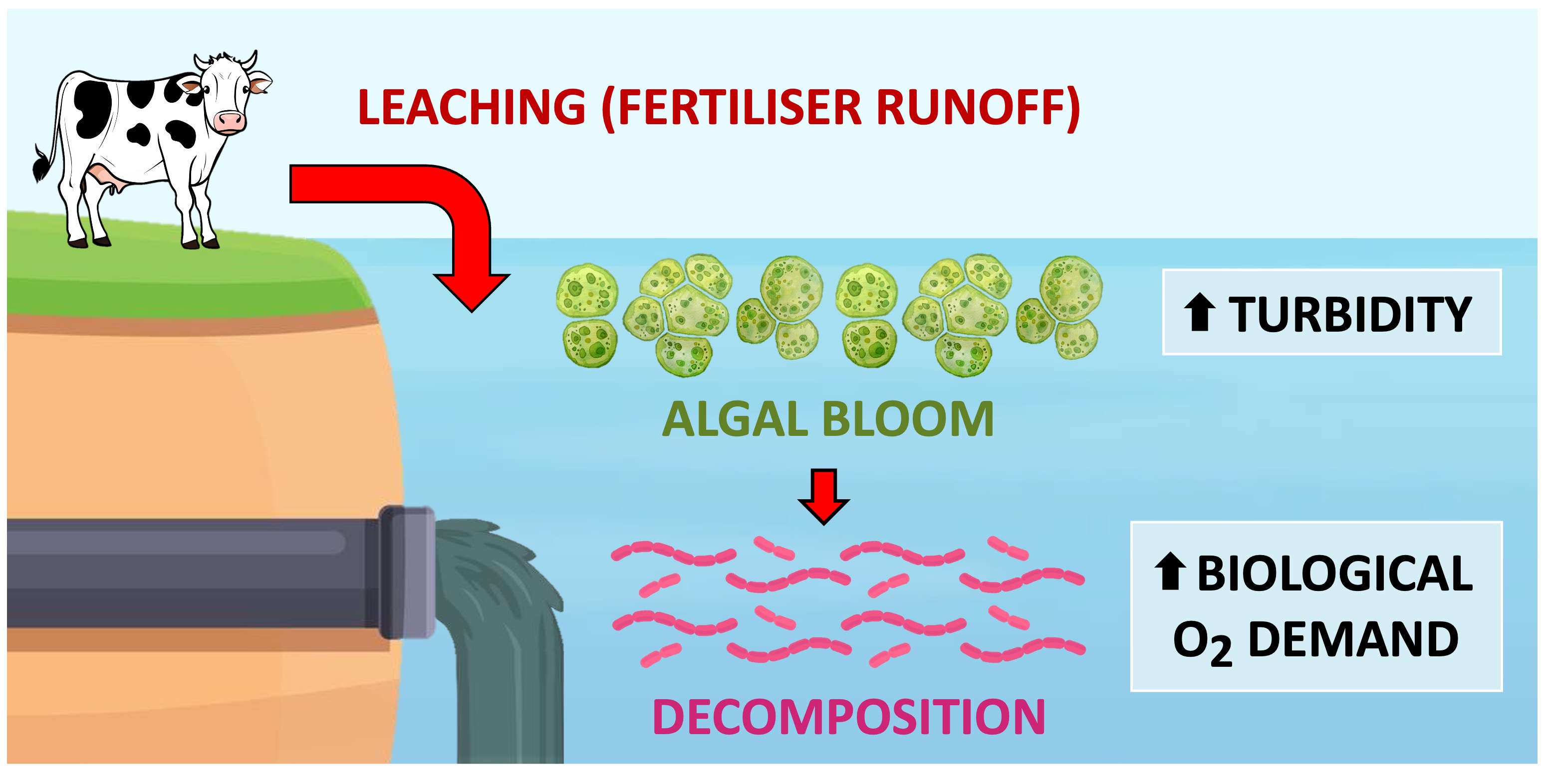
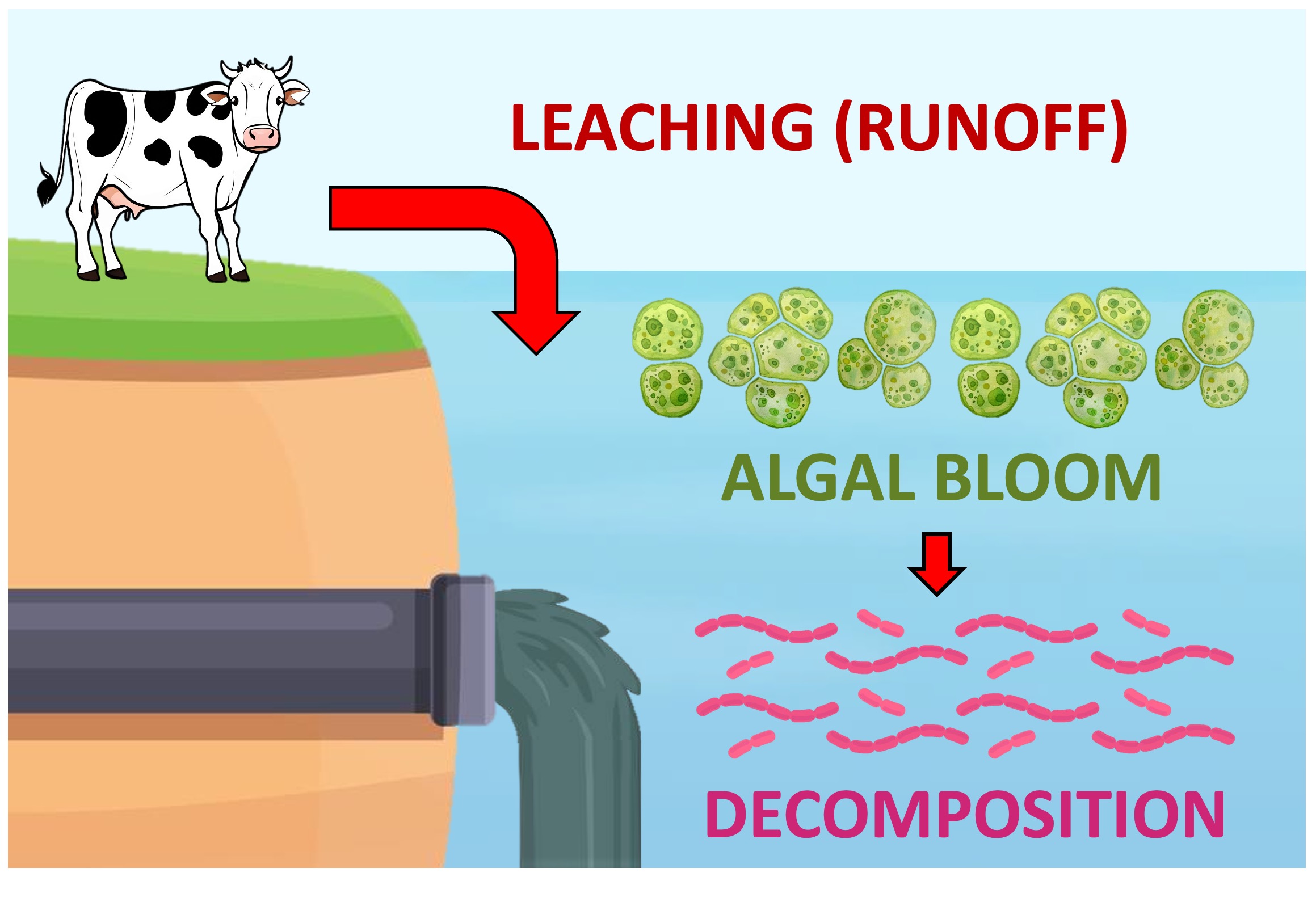
The nutrients can be introduced into waterways via leaching from soil by rainfall or released as part of sewage
-
Eutrophication is common around agricultural lands where the use of artificial fertilisers are prevalent
An increase in nutrient supply within aquatic and marine ecosystems will result in several ecological consequences:
-
A rapid growth in algal populations will occur (algal blooms) as a result of the increased availability of nutrients
-
As the algae die, there will be a subsequent spike in the numbers of saprotrophic microbes (decomposers)
-
The high rate of decomposition will result in an increased biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) by saprotrophic bacteria
-
The saprotrophs will consume available quantities of dissolved oxygen, leading to deoxygenation of the water supply
-
Eutrophication will also increase the turbidity of the water, which will reduce oxygen production by photosynthetic seaweeds
-
This will stress the survival of marine organisms, potentially leading to a reduction in biodiversity within the ecosystem
Eutrophication